Abstract
Purpose
We previously found that hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase-3 (PHD3) was frequently overexpressed in renal cell carcinomas (RCCs), unlike in normal tissues, and therefore, we studied the mechanism and role of PHD3 expression in RCC.
Methods
The von Hippel–Lindau (VHL)-gene-mutant RCC cell lines SMKT-R2 and SMKT-R3 and wild-type VHL cell lines Caki-1 and ACHN were used. Associations of the expression of PHD3 with HIF-α proteins and signal transduction pathways were evaluated under normoxic conditions. The effect of PHD3 on cell proliferation was also examined by small interference RNA and cDNA transfection. Moreover, the prognostic impact of PHD3 expression in clear cell RCC (CCRCC) was evaluated using primary cancer tissues.
Results
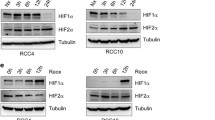
In SMKT-R2 and SMKT-R3, HIF-α proteins were expressed and PHD3 was highly expressed. On the other hand, ACHN had low expression of HIF-α proteins and PHD3. However, Caki-1 had high expression of PHD3 even though there was no distinct expression of HIF-α proteins. PHD3 expression was inhibited by blockade of Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), but not by HIF-1α and HIF-2α double knockdown. In addition, PHD3 knockdown resulted in the promotion of cell proliferation in SMKT-R2, SMKT-R3 and Caki-1. On the other hand, forced expression of PHD3 reduced cell proliferation in ACHN. In immunohistochemistry, PHD3 expression was a significant factor for better recurrence-free survival in patients with CCRCC.
Conclusions
PHD3 expression can be induced by the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway in RCC independently of HIF proteins. Furthermore, PHD3 has an antiproliferative function independent of HIF protein status in RCC, indicating a novel expression mechanism and function of PHD3.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelhoff RJ, Tian YM, Raval RR, Turley H, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Gleadle JM (2004) Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem 279:38458–38465
Aprelikova O, Chandramouli GV, Wood M, Vasselli JR, Riss J, Maranchie JK, Linehan WM, Barrett JC (2004) Regulation of HIF prolyl hydroxylases by hypoxia-inducible factors. J Cell Biochem 92:491–501
Atkins DJ, Gingert C, Justenhoven C, Schmahl GE, Bonato MS, Brauch H, Störkel S (2005) Concomitant deregulation of HIF1a and cell cycle proteins in VHL-mutated renal cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch 447:634–642
Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J (2003) HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1a in normoxia. EMBO J 22:4082–4090
Blancher C, Moore JW, Robertson N, Harris AL (2001) Effects of ras and von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene mutations on hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, HIF-2α, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression and their regulation by the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Cancer Res 61:7349–7355
Brugarolas JB, Vazquez F, Reddy A, Sellers WR, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) TSC2 regulates VEGF through mTOR-dependent and -independent pathways. Cancer Cell 4:147–158
Bruick RK, McKnight SL (2001) A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294:1337–1340
Cioffi CL, Liu XQ, Kosinski PA, Garay M, Bowen BR (2003) Differential regulation of HIF-1α prolyl-4-hydroxylase genes by hypoxia in human cardiovascular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:947–953
Cockman ME, Masson N, Mole DR, Jaakkola P, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Maher ER, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH (2000) Hypoxia inducible factor-a binding and ubiquitylation by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem 275:25733–25741
del Peso L, Castellanos MC, Temes E, Martin-Puig S, Cuevas Y, Olmos G, Landazuri MO (2003) The von Hippel Lindau/hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway regulates the transcription of the HIF-proline hydroxylase genes in response to low oxygen. J Biol Chem 278:48690–48695
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A (2010) American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging manual, 7th edn. Springer, Philadelphia
Fuhrman S, Lasky LC, Limas L (1982) Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 6:655
Gordan JD, Lal P, Dondeti VR, Letrero R, Parekh KN, Oquendo CE, Greenberg RA, Flaherty KT, Rathmell WK, Keith B, Simon MC, Nathanson KL (2008) HIF-α effects on c-Myc distinguish two subtypes of sporadic VHL-deficient clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Cell 14:435–446
Hirsila M, Koivunen P, Gunzler V, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J (2003) Characterization of the human prolyl 4-hydroxylases that modify the hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem 278:30772–30780
Huang J, Zhao Q, Mooney SM, Lee FS (2002) Sequence determinants in hypoxia-inducible factor-1a for hydroxylation by the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3. J Biol Chem 277:39792–39800
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F, Giaccia AJ, Abraham RT (2002) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1a expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol 22:7004–7014
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS, Kaelin WG Jr (2001) HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 292:464–468
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, von Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292:468–472
Klatte T, Seligson DB, Riggs SB, Leppert JT, Berkman MK, Kleid MD, Yu H, Kabbinavar FF, Pantuck AJ, Belldegrun AS (2007) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:7388–7393
Kroeze SG, Vermaat JS, van Brussel A, van Melick HH, Voest EE, Jonges TG, van Diest PJ, Hinrichs J, Bosch JL, Jans JJ (2010) Expression of nuclear FIH independently predicts overall survival of clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Eur J Cancer 46:3375–3382
Ku JH, Park YH, Myung JK, Moon KC, Kwak C, Kim HH (2011) Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α and 2α in conventional renal cell carcinoma with or without sarcomatoid differentiation. Urol Oncol 29:731–737
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC, Semenza GL (2001) HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol Cell Biol 21:3995–4004
Lee S, Nakamura E, Yang H, Wei W, Linggi MS, Sajan MP, Farese RV, Freeman RS, Carter BD, Kaelin WG Jr, Schlisio S (2005) Neuronal apoptosis linked to EglN3 prolyl hydroxylase and familial pheochromocytoma genes: developmental culling and cancer. Cancer Cell 8:155–167
Lieb ME, Menzies K, Moschella MC, Ni R, Taubman MB (2002) Mammalian EGLN genes have distinct patterns of mRNA expression and regulation. Biochem Cell Biol 80:421–426
Lipscomb E, Sarmiere P, Crowder R, Freeman RS (1999) Expression of the SM-20 gene promotes death in nerve growth factor-dependent sympathetic neurons. J Neurochem 73:429–432
Lipscomb E, Sarmiere P, Freeman RS (2001) SM-20 is a novel mitochondrial protein that causes caspase-dependent cell death in nerve growth factor-dependent neurons. J Biol Chem 276:11775–11782
Marxsen JH, Stengel P, Doege K, Heikkinen P, Jokilehto T, Wagner T, Jelkmann W, Jaakkola P, Metzen E (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) promotes its degradation by induction of HIF-α-prolyl-4-hydroxylases. Biochem J 381:761–767
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399:271–275
Maynard MA, Ohh M (2007) The role of hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2170–2180
Pescador N, Cuevas Y, Naranjo S, Alcaide M, Villar D (2005) Landázuri MO, del Peso L: identification of a functional hypoxia-responsive element that regulates the expression of the egl nine homologue 3 (egln3/phd3) gene. Biochem J 390:189–197
Pore N, Jiang Z, Shu HK, Bernhard E, Kao GD, Maity A (2006) Akt1 activation can augment hypoxia-inducible factor-1a expression by increasing protein translation through a mammalian target of rapamycin-independent pathway. Mol Cancer Res 4:471–479
Sato E, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y, Kitamura H, Tanaka T, Honma I, Asanuma H, Harada K, Takasu H, Masumori N, Ito N, Hasegawa T, Tsukamoto T, Sato N (2008) Identification of an immunogenic CTL epitope of HIFPH3 for immunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14:6916–6923
Semenza GL, Wang GL (1992) A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 12:5447–5454
Shinojima T, Oya M, Takayanagi A, Mizuno R, Shimizu N, Murai M (2007) Renal cancer cells lacking hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α expression maintain vascular endothelial growth factor expression through HIF-2α. Carcinogenesis 28:529–536
Straub JA, Lipscomb EA, Yoshida ES, Freeman RS (2003) Induction of SM-20 in PC12 cells leads to increased cytochrome c levels, accumulation of cytochrome c in the cytosol, and caspase-dependent cell death. J Neurochem 85:318–328
Su Y, Loos M, Giese N, Hines OJ, Diebold I, Görlach A, Metzen E, Pastorekova S, Friess H, Büchler P (2010) PHD3 regulates differentiation, tumour growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 103:1571–1579
Tanaka T, Kitamura H, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y, Sato E, Masumori N, Sato N, Tsukamoto T (2011) Autoantibody against hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase-3 is a potential serological marker for renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137:789–794
Volpe A, Jewett MAS (2005) The natural history of small renal masses. Nat Clin Pract Urol 2:384–390
Wang GL, Semenza GL (1995) Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 270:1230–1237
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5510–5514
Yamamoto M, Torigoe T, Kamiguchi K, Hirohashi Y, Nakanishi K, Nabeta C, Asanuma H, Tsuruma T, Sato T, Hata F, Ohmura T, Yamaguchi K, Kurotaki T, Hirata K, Sato N (2005) A novel isoform of TUCAN is overexpressed in human cancer tissues and suppresses both caspase-8- and caspase-9-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res 65:8709–8714
Yu F, White SB, Zhao Q, Lee FS (2001) HIF-1α binding to VHL is regulated by stimulus-sensitive proline hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9630–9635
Zhong H, Agani F, Baccala AA, Laughner E, Rioseco-Camacho N, Isaacs WB, Simons JW, Semenza GL (1998) Increased expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1a in rat and human prostate cancer. Cancer Res 58:5280–5284
Acknowledgments
We thank Emiri Nakazawa, Akari Takahashi and Eri Saka for their skillful technical assistance, and Mr. Kim Barrymore for English correction of this manuscript. This study was supported in part by a grant-aid from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Conflict of interest
All authors of this paper reported no financial interests or potential conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, T., Torigoe, T., Hirohashi, Y. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-independent expression mechanism and novel function of HIF prolyl hydroxylase-3 in renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 503–513 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1593-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1593-7