Abstract
Background
The development of brain metastases (BMs) was associated with poor prognosis in melanoma patients. Patients with BMs have a median survival of <6 months. Melanoma is the third most common tumor to metastasize to the brain with a reported incidence of 10–40 %. Our aim was to identify factors predicting development of BMs and survival.
Patients and methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of 470 melanoma patients between 2000 and 2012. The logistic regression analyses were used to identify the clinicopathological features of primary melanoma that are predictive of BMs development and survival after a diagnosis of brain metastases.
Results
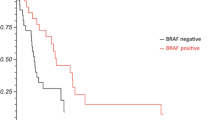
There were 52 patients (11.1 %) who developed melanoma BMs during the study period. The analysis of post-BMs with Kaplan–Meier curves has resulted in a median survival rate of 4.1 months (range 2.9–5.1 months). On logistic regression analysis site of the primary tumor on the head and neck (p = 0.002), primary tumor thickness (Breslow >4 mm) (p = 0.008), ulceration (p = 0.007), and pathologically N2 and N3 diseases (p = 0.001) were found to be significantly associated with the development of BMs. In univariate analysis, tumor thickness and performance status had a significant influence on post-BMs survival. In multivariate analysis, these clinicopathologic factors were not remained as significant predictive factors.
Conclusions
Our results revealed the importance of primary tumor characteristics associated with the development of BMs. Ulceration, primary tumor thickness, anatomic site, and pathologic ≥N2 disease were found to be significant predictors of BMs development.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal S, Kane JM 3rd, Guadagnolo BA et al (2009) The benefits of adjuvant radiation therapy after therapeutic lymphadenectomy for clinically advanced, high-risk, lymph node-metastatic melanoma. Cancer 115(24):5836–5844
Amer MH, Al-Sarraf M, Baker LH et al (1978) Malignant melanoma and central nervous system metastases: incidence, diagnosis, treatment and survival. Cancer 42:660–668
Balch CM, Murad TM, Soong SJ et al (1978) A multifactorial analysis of melanoma: prognostic histopathological features comparing Clark’s and Breslow’s staging methods. Annu Surg 188(6):732–742
Ballo MT, Ross MI, Cormier JN et al (2006) Combined modality therapy for patients with regional nodal metastases from melanoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64(1):106–113 Epub 2005 Sep 22
Bullard DE, Cox EB, Seigler HF (1981) Central nervous system metastases in malignant melanoma. Neurosurgery 8(1):26–30
Cassel WA, Weidenheim KM, Campbell WG Jr et al (1986) Malignant melanoma: inflammatory mononuclear cell infiltrates in cerebral metastases during concurrent therapy with viral oncolysate. Cancer 57:1302–1312
Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Santinami M et al (2008) Adjuvant therapy with pegylated interferon alfa-2b versus observation alone in resected stage III melanoma: final results of EORTC 18991, a randomised phase III trial. Lancet 372(9633):117–126
Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Testori A et al (2012) Ulceration and stage are predictive of interferon efficacy in melanoma: results of the phase III adjuvant trials EORTC 18952 and EORTC 18991. Eur J Cancer 48(2):218–225
Einhorn LH, Burgess MA, Vallejos C et al (1974) Prognostic correlations and response to treatment in advanced metastatic malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 34(8):1995–2004
Eton O, Legha SS, Bedikian AY et al (2002) Sequential biochemotherapy versus chemotherapy for metastatic melanoma: results from a phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 20(8):2045–2052
Fife KM, Colman MH, Stevens GN et al (2004) Determinants of outcome in melanoma patients with cerebral metastases. J Clin Oncol 22(7):1293–1300
Hofmann MA, Coll SH, Küchler I et al (2007) Prognostic factors and impact of treatment in melanoma brain metastases: better prognosis for women? Dermatology 215(1):10–16
Houghton AN, Balch CM (1992) Treatment for advanced melanoma. In: Balch CM, Houghton AN, Milton GW et al (eds) Cutaneous Melanoma. JB Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 468–497
Madajewicz S, Karakousis C, West CR et al (1984) Malignant melanoma brain metastases. Review of roswell park memorial institute experience. Cancer 53(11):2550–2552
Miller JG, Mac Neil S (1997) Gender and cutaneous melanoma. Br J Dermatol 136(5):657–665
Mitchell MS (1989) Relapse in the central nervous system in melanoma patients successfully treated with biomodulators. J Clin Oncol 7(11):1701–1709
Monsour PD, Sause WT, Avent JM, Noyes RD (1993) Local control following therapeutic nodal dissection for melanoma. J Surg Oncol 54(1):18–22
Morton DL, Wanek L, Nizze JA et al (1991) Improved long-term survival after lymphadenectomy of melanoma metastatic to regional nodes. Analysis of prognostic factors in 1134 patients from the John Wayne cancer clinic. Annu Surg 214(4):491–9; discussion 499–501
Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY et al (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14:48–54
Patel JK, Didolkar MS, Pickren JW et al (1978) Metastatic pattern of malignant melanoma: a study of 216 autopsy cases. Am J Surg 135(6):807–810
Raizer JJ, Hwu WJ, Panageas KS et al (2008) Brain and leptomeningeal metastases from cutaneous melanoma: survival outcomes based on clinical features. Neuro Oncol 10(2):199–207
Sampson JH, Carter JH Jr, Friedman AH et al (1998) Demographics, prognosis, and therapy in 702 patients with brain metastases from malignant melanoma. J Neurosurg 88:11–20
Stevens G, Firth I, Coates A (1992) Cerebral metastases from malignant melanoma. Radiother Oncol 23(3):185–191
Zakrzewski J, Geraghty LN, Rose AE et al (2011) Clinical variables and primary tumor characteristics predictive of the development of melanoma brain metastases and post-brain metastases survival. Cancer 117(8):1711–1720
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumusay, O., Coskun, U., Akman, T. et al. Predictive factors for the development of brain metastases in patients with malignant melanoma: a study by the Anatolian society of medical oncology. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 151–157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1553-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1553-7