Abstract
Purpose
Purpose of this study is to analyze outcomes and pre-treatment prognostic factors in high-risk prostate cancer patients with initial PSA ≥20 ng/mL, treated with high-dose external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in a single institution.
Methods
Between March 2003 and December 2011, 155 consecutive high-risk prostate cancer patients (a) presenting with pre-treatment PSA level ≥20 ng/mL, (b) treated with definitive EBRT, and (c) with a minimum follow-up of 24 months were included in this retrospective analysis. Phoenix definition was used to define biochemical control. Primary endpoints were as follows: biochemical disease-free survival (bDFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS). Multivariate analysis was performed to determine the independent prognostic impact of pre-treatment clinical factors [T stage, PSA, and Gleason score (GS)].
Results
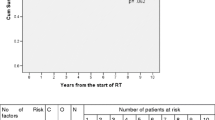
At a median follow-up time of 62 months, actuarial bDFS, DMFS, CSS, and OS at 5 years were 64.8, 85.2, 95.8, and 94.4 %, respectively. On multivariate analysis, only GS was significantly associated with three clinical endpoints (bDFS: HR 1.6; p = 0.022, CSS: HR 4.27, p = 0.044, OS: HR 2.6; p = 0.038). Pre-treatment zenith PSA was associated only with bDFS (HR 1.87; p = 0.027).
Conclusions
Patients with “high” PSA levels (≥20 ng/mL) showed favorable clinical outcomes, supporting the role of local radiotherapy as primary therapy in combination with long-term ADT in patients with high PSA levels at diagnosis. A GS of 8–10 is the strongest predictor of outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastian PJ, Boorjian SA, Bossi A, Briganti A, Heidenreich A, Freedland SJ et al (2012) High-risk prostate cancer: from definition to contemporary management. Eur Urol 61:1096–1106. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.02.031
Bolla M, de Reijke TM, Van Tienhoven G, Van den Bergh AC, Oddens J, Poortmans PM et al (2009) Duration of androgen suppression in the treatment of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 360:2516–2527. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810095
Cooperberg MR, Broering JM, Carroll PR (2010a) Time trends and local variation in primary treatment of localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1117–1123. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.0133
Cooperberg MR, Vickers AJ, Broering JM, Carroll PR (2010b) Comparative risk-adjusted mortality outcomes after primary surgery, radiotherapy, or androgen-deprivation therapy for localized prostate cancer. Cancer 116:5226–5234. doi:10.1002/cncr.25456
Donohue JF, Bianco FJ Jr, Kuroiwa K, Vickers AJ, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT et al (2006) Poorly differentiated prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy: long-term outcome and incidence of pathological downgrading. J Urol 176:991–995
Eastham JA, Evans CP, Zietman A (2010) What is the optimal management of high risk, clinically localized prostate cancer? Urol Oncol 28:557–567. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.038
Gontero P, Spahn M, Tombal B, Bader P, Hsu CY, Marchioro G et al (2011) Is there a prostate-specific antigen upper limit for radical prostatectomy? BJU Int 108:1093–1100. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10076.x
Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V et al (2011) EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol 59:61–71. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2010.10.039
Horwitz EM, Bae K, Hanks GE, Porter A, Grignon DJ, Brereton HD et al (2008) Ten-year follow-up of radiation therapy oncology group protocol 92–02: a phase III trial of the duration of elective androgen deprivation in locally advanced prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:2497–2504. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.9021
Kibel AS, Ciezki JP, Klein EA, Reddy CA, Lubahn JD, Haslag-Minoff J et al (2012) Survival among men with clinically localized prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy in the prostate specific antigen era. J Urol 187:1259–1265. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2011.11.084
Ladjevardi S, Berglund A, Varenhorst E, Bratt O, Widmark A, Sandblom G (2012) Treatment with curative intent and survival in men with high-risk prostate cancer. A population-based study of 11380 men with serum PSA level 20–100 ng/mL. BJU Int. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11320.x. (Epub ahead of print)
Lawton CA, DeSilvio M, Roach M 3rd, Uhl V, Kirsch R, Seider M et al (2007) An update of the phase III trial comparing whole pelvic to prostate only radiotherapy and neoadjuvant to adjuvant total androgen suppression: updated analysis of RTOG 94–13, with emphasis on unexpected hormone/radiation interactions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:646–655
Oderda M, Joniau S, Spahn M, Gontero P (2012) Debulking surgery in the setting of very high-risk prostate cancer scenarios. BJU Int 110:E192–E198. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.10942.x
Pollack A, Zagars GK, Starkschall G, Antolak JA, Lee JJ, Huang E et al (2002) Prostate cancer radiation dose response: results of the M. D. Anderson phase III randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:1097–1105
Roach M 3rd, Hanks G, Thames H Jr, Schellhammer P, Shipley WU, Sokol GH et al (2006) Defining biochemical failure following radiotherapy with or without hormonal therapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer: recommendations of the RTOG-ASTRO Phoenix Consensus Conference. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:965–974
Rodrigues G, Bae K, Roach M, Lawton C, Donnelly B, Grignon D et al (2011) Impact of ultrahigh baseline PSA levels on biochemical and clinical outcomes in two Radiation Therapy Oncology Group prostate clinical trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80:445–452. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.02.034
Tai P, Tonita J, Woitas C, Zhu T, Joseph K, Skarsgard D (2012) Treatment outcomes in non-metastatic prostate cancer patients with ultra-high prostate-specific antigen. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e525–e530. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.01.041
Tendulkar RD, Reddy CA, Stephans KL, Ciezki JP, Klein EA, Mahadevan A et al (2012) Redefining high-risk prostate cancer based on distant metastases and mortality after high-dose radiotherapy with androgen deprivation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1397–1404. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.04.042
Zapatero A, García-Vicente F, Martín de Vidales C, Cruz Conde A, Ibáñez Y, Fernández I et al (2011) Long-term results after high-dose radiotherapy and adjuvant hormones in prostate cancer: how curable is high-risk disease? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:1279–1285. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.07.1975
Zelefsky MJ, Levin EJ, Hunt M, Yamada Y, Shippy AM, Jackson A et al (2008) Incidence of late rectal and urinary toxicities after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:1124–1129. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.11.044
Zietman AL, Bae K, Slater JD, Shipley WU, Efstathiou JA, Coen JJ et al (2010) Randomized trial comparing conventional-dose with high-dose conformal radiation therapy in early-stage adenocarcinoma of the prostate: long-term results from proton radiation oncology group/american college of radiology 95–09. JCO 28:1106–1111. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.8475
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guarneri, A., Botticella, A., Filippi, A.R. et al. Radical radiotherapy in high-risk prostate cancer patients with high or ultra-high initial PSA levels: a single institution analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 1141–1147 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1426-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1426-0