Abstract
Objective
Brain metastasis as the first symptom of lung cancer is a unique clinical entity. We conducted a retrospective study to investigate the clinical characteristics and survival of patients with lung cancer whose first symptom was brain metastases in an Asian population.
Methods
A retrospective study of 186 such patients who had been admitted to one institution in China between January 1, 2003 and December 30, 2008 was performed. The following data were collected and analyzed: manifesting signs and symptoms, imaging studies, extracerebral metastases, initial diagnosis, treatment, and patient survival.
Results
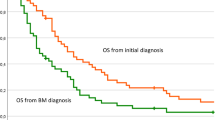
This sample population exhibited high rates of misdiagnosis upon initial presentation (46.8 %). Fifty-seven (30.6 %) patients presented with silent extracerebral metastases. Pathologies among this cohort varied, and adenocarcinomas were most commonly observed. Most patients received surgical resection, and some patients had additional whole-brain radiotherapy or stereotactic radiosurgery. The median survival time for the entire cohort was 15 months (95 % confidence interval, 12.9–17.1 months). Survival rates for 1, 2, and 5 years were 58.2, 34.2, and 6.5 %, respectively. The median survival time was 15, 14, 19, and 7 months for the gross total resection, incomplete resection, surgery + whole-brain radiotherapy, and surgery + stereotactic radiosurgery groups, respectively.
Conclusions
Brain metastasis as the first symptom of lung cancer is a distinct clinical entity. Although overall survival was poor, combined treatments based on surgery for selected patients were reasonable with the exception of a minority who experienced long-term survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Barker FG 2nd (2004) Craniotomy for the resection of metastatic brain tumors in the U.S., 1988–2000: decreasing mortality and the effect of provider caseload. Cancer 100(5):999–1007
Campos S, Davey P, Hird A et al (2009) Brain metastasis from an unknown primary, or primary brain tumour? A diagnostic dilemma. Curr Oncol 16:62–66
Chen WQ (2009) Estimation of cancer incidence and mortality in China in 2004–2005. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 31:664–668
Eichler AF, Loeffler JS (2007) Multidisciplinary management of brain metastases. Oncologist 12(7):884–898
Giordana MT, Cordera S, Boghi A (2000) Cerebral metastases as first symptom of cancer: a clinico-pathologic study. J Neurooncol 50:265–273
Gu HW, Sohn MJ, Lee DJ et al (2009) Clinical analysis of novalis stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 46:245–251
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141
Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC, Nowak PJ et al (1999) Identification of prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases: a review of 1292 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43(4):795–803
Lu-Emerson C, Eichler AF (2012) Brain metastases. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 18(2):295–311
Merchut MP (1989) Brain metastases from undiagnosed systemic neoplasms. Arch Intern Med 149:1076–1080
Narita Y, Shibui S (2009) Strategy of surgery and radiation therapy for brain metastases. Int J Clin Oncol 14:275–280
Nathoo N, Toms SA, Barnett GH (2004) Metastases to the brain: current management perspectives. Expert Rev Neurother 4(4):633–640
Nguyen LN, Maor MH, Oswald MJ (1998) Brain metastases as the only manifestation of an undetected primary tumor. Cancer 83:2181–2184
Nieder C, Mehta MP (2009) Prognostic indices for brain metastases—usefulness and challenges. Radiat Oncol 4:10
Paek SH, Audu PB, Sperling MR et al (2005) Reevaluation of surgery for the treatment of brain metastases: review of 208 patients with single or multiple brain metastases treated at one institution with modern neurosurgical techniques. Neurosurgery 56(5):1021–1034 Discussion 1021-1034
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280(17):1485–1489
Regine WF, Huhn JL, Patchell RA et al (2002) Risk of symptomatic brain tumor recurrence and neurologic deficit after radiosurgery alone in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: results and implications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52:333–338
Richards GM, Khuntia D, Mehta MP (2007) Therapeutic management of metastatic brain tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 61(1):70–78
Rudà R, Borgognone M, Benech F et al (2001) Brain metastases from unknown primary tumor: a prospective study. J Neurol 248:394–398
Salvati M, Cervoni L, Raco A (1995) Single brain metastases from unknown primary malignancies in CT-era. J Neurooncol 23:75–80
Sánchez de Cos J, Sojo González MA, Montero MV et al (2009) Non-small cell lung cancer and silent brain metastasis. Survival and prognostic factors. Lung Cancer 63:140–145
Soffietti R, Costanza A, Laguzzi E et al (2005) Radiotherapy and chemotherapy of brain metastases. J Neurooncol 75:31–42
van de Pol M, van Aalst VC, Wilmink JT et al (1996) Brain metastases from an unknown primary tumor: which diagnostic procedures are indicated? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61:321–323
Walbert T, Gilbert MR (2009) The role of chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with brain metastases from solid tumors. Int J Clin Oncol 14:299–306
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This retrospective study has been approved by the Institutional Review Board of Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. The decision number is 2010-081.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Zhou, X., Liang, X. et al. Brain metastases as the first symptom of lung cancer: a clinical study from an Asian medical center. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 403–408 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1344-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1344-6