Abstract
Background
In addition to sprouting angiogenesis, other mechanisms, such as mosaic tumor vessel formation, have been recognized to contribute to tumor vascularization. We sought to examine vascular alteration as well as tumor growth inhibition after treatment with antiangiogenic therapy, chemotherapy alone or in combination.
Methods
Hepatocellular carcinoma cells (Hep3B) expressed green fluorescent protein were utilized to establish orthotopic xenograft model in nude mice. The formation and distribution of mosaic vessels was analyzed quantitatively by immunolabeling. Next, changes in tumor microcirculation and therapeutic effects on tumor growth were evaluated in several different treatment groups: control, conventional doxorubicin, metronomic doxorubicin, bevacizumab, bevacizumab plus conventional doxorubicin, and bevacizumab plus metronomic doxorubicin. In addition, we examined the effects of combined regimens on lung metastasis using a highly metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCCLM3) mouse model.
Results
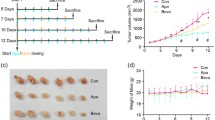
Approximately 62 % of the vessels were present in the central part or near the midsection of the tumor and were mosaic. Only the combined antiangiogenic treatment and chemotherapy (metronomic schedule, P = 0.00; conventional schedule, P = 0.02) had a significant effect on the degree of mosaic vasculature. Metronomic doxorubicin in combination with bevacizumab had an even more profound effect than bevacizumab plus conventional doxorubicin (P < 0.05) on tumor growth inhibition and survival. However, bevacizumab plus metronomic doxorubicin failed to inhibit lung metastasis compared with antiangiogenic monotherapy.
Conclusions
Metronomic chemotherapy in combination with antiangiogenic treatment results in the reduction of mosaic tumor vasculature, inhibition of tumor growth, and enhanced survival of mice. Further investigation of drug scheduling is required to optimize antitumor activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, Douillard JY, Lathia C, Schwartz B, Taylor I, Moscovici M, Saltz LB (2006) Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24(26):4293–4300
Auguste P, Lemiere S, Larrieu-Lahargue F, Bikfalvi A (2005) Molecular mechanisms of tumor vascularization. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 54(1):53–61
Bocci G, Nicolaou KC, Kerbel RS (2002) Protracted low-dose effects on human endothelial cell proliferation and survival in vitro reveal a selective antiangiogenic window for various chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Res 62(23):6938–6943
Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J (2000) Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res 60(7):1878–1886
Bruix J, Hessheimer AJ, Forner A, Boix L, Vilana R, Llovet JM (2006) New aspects of diagnosis and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 25(27):3848–3856
Burroughs A, Hochhauser D, Meyer T (2004) Systemic treatment and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: two ends of the therapeutic spectrum. Lancet Oncol 5(7):409–418
Chang YS, di Tomaso E, McDonald DM, Jones R, Jain RK, Munn LL (2000) Mosaic blood vessels in tumors: frequency of cancer cells in contact with flowing blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(26):14608–14613
Chaudhuri TR, Cao Z, Rodriguez-Burford C, LoBuglio AF, Zinn KR (2002) A non-invasive approach for monitoring breast tumor cells during therapeutic intervention. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 17(2):205–212
di Tomaso E, Capen D, Haskell A, Hart J, Logie JJ, Jain RK, McDonald DM, Jones R, Munn LL (2005) Mosaic tumor vessels: cellular basis and ultrastructure of focal regions lacking endothelial cell markers. Cancer Res 65(13):5740–5749
Dickson PV, Hamner JB, Sims TL, Fraga CH, Ng CY, Rajasekeran S, Hagedorn NL, McCarville MB, Stewart CF, Davidoff AM (2007) Bevacizumab-induced transient remodeling of the vasculature in neuroblastoma xenografts results in improved delivery and efficacy of systemically administered chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 13(13):3942–3950
Dome B, Hendrix MJ, Paku S, Tovari J, Timar J (2007) Alternative vascularization mechanisms in cancer: pathology and therapeutic implications. Am J Pathol 170(1):1–15
Duff SE, Li C, Garland JM, Kumar S (2003) CD105 is important for angiogenesis: evidence and potential applications. FASEB J 17(9):984–992
Emmenegger U, Kerbel RS (2007) Five years of clinical experience with metronomic chemotherapy: achievements and perspectives. Onkologie 30(12):606–608
Emmenegger U, Man S, Shaked Y, Francia G, Wong JW, Hicklin DJ, Kerbel RS (2004) A comparative analysis of low-dose metronomic cyclophosphamide reveals absent or low-grade toxicity on tissues highly sensitive to the toxic effects of maximum tolerated dose regimens. Cancer Res 64(11):3994–4000
Feng D, Nagy JA, Pyne K, Dvorak HF, Dvorak AM (2004) Ultrastructural localization of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1, CD31) in vascular endothelium. J Histochem Cytochem 52(1):87–101
Folkman J (2001) Can mosaic tumor vessels facilitate molecular diagnosis of cancer? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(2):398–400
Fujimoto A, Onodera H, Mori A, Nagayama S, Yonenaga Y, Tachibana T (2006) Tumour plasticity and extravascular circulation in ECV304 human bladder carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 26(1A):59–69
Fukumura D, Jain RK (2007) Tumor microvasculature and microenvironment: targets for anti-angiogenesis and normalization. Microvasc Res 74(2–3):72–84
Gerber HP, Ferrara N (2005) Pharmacology and pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies. Cancer Res 65(3):671–680
Huang GW, Tao YM, Ding X (2009) Endocan expression correlated with poor survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 54(2):389–394
Hurwitz H, Kabbinavar F (2005) Bevacizumab combined with standard fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy regimens to treat colorectal cancer. Oncology 69(Suppl 3):17–24
Huynh H, Chow PK, Palanisamy N, Salto-Tellez M, Goh BC, Lee CK, Somani A, Lee HS, Kalpana R, Yu K, Tan PH, Wu J, Soong R, Lee MH, Hor H, Soo KC, Toh HC, Tan P (2008) Bevacizumab and rapamycin induce growth suppression in mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 49(1):52–60
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7(9):987–989
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307(5706):58–62
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS (2006) Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3(1):24–40
Jang SH, Wientjes MG, Lu D, Au JL (2003) Drug delivery and transport to solid tumors. Pharm Res 20(9):1337–1350
Joyce JA (2005) Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 7(6):513–520
Kerbel RS, Kamen BA (2004) The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4(6):423–436
Kurz H, Burri PH, Djonov VG (2003) Angiogenesis and vascular remodeling by intussusception: from form to function. News Physiol Sci 18:65–70
Langenkamp E, Molema G (2009) Microvascular endothelial cell heterogeneity: general concepts and pharmacological consequences for anti-angiogenic therapy of cancer. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):205–222
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 362(9399):1907–1917
Lowery A, Onishko H, Hallahan DE, Han Z (2011) Tumor-targeted delivery of liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin by use of a peptide that selectively binds to irradiated tumors. J Controlled Release 150(1):117–124
Ma J, Waxman DJ (2008) Combination of antiangiogenesis with chemotherapy for more effective cancer treatment. Mol Cancer Ther 7(12):3670–3684
Mabuchi S, Terai Y, Morishige K, Tanabe-Kimura A, Sasaki H, Kanemura M, Tsunetoh S, Tanaka Y, Sakata M, Burger RA, Kimura T, Ohmichi M (2008) Maintenance treatment with bevacizumab prolongs survival in an in vivo ovarian cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 14(23):7781–7789
McDonald DM, Munn L, Jain RK (2000) Vasculogenic mimicry: how convincing, how novel, and how significant? Am J Pathol 156(2):383–388
Minchinton AI, Tannock IF (2006) Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer 6(8):583–592
Palmer GM, Boruta RJ, Viglianti BL, Lan L, Spasojevic I, Dewhirst MW (2010) Non-invasive monitoring of intra-tumor drug concentration and therapeutic response using optical spectroscopy. J Control Release 142(3):457–464
Pang R, Poon RT (2006) Angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 242(2):151–167
Pastorino F, Di Paolo D, Piccardi F, Nico B, Ribatti D, Daga A, Baio G, Neumaier CE, Brignole C, Loi M, Marimpietri D, Pagnan G, Cilli M, Lepekhin EA, Garde SV, Longhi R, Corti A, Allen TM, Wu JJ, Ponzoni M (2008) Enhanced antitumor efficacy of clinical-grade vasculature-targeted liposomal doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res 14(22):7320–7329
Semela D, Dufour JF (2004) Angiogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 41(5):864–880
Sosman JA, Carrillo C, Urba WJ, Flaherty L, Atkins MB, Clark JI, Dutcher J, Margolin KA, Mier J, Gollob J, Kirkwood JM, Panka DJ, Crosby NA, O’Boyle K, LaFleur B, Ernstoff MS (2008) Three phase II cytokine working group trials of gp100 (210M) peptide plus high-dose interleukin-2 in patients with HLA-A2-positive advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol 26(14):2292–2298
Sun B, Zhang S, Zhang D, Du J, Guo H, Zhao X, Zhang W, Hao X (2006) Vasculogenic mimicry is associated with high tumor grade, invasion and metastasis, and short survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 16(4):693–698
Tailor TD, Hanna G, Yarmolenko PS, Dreher MR, Betof AS, Nixon AB, Spasojevic I, Dewhirst MW (2010) Effect of pazopanib on tumor microenvironment and liposome delivery. Mol Cancer Ther 9(6):1798–1808
Tang TC, Man S, Lee CR, Xu P, Kerbel RS (2010) Impact of metronomic UFT/cyclophosphamide chemotherapy and antiangiogenic drug assessed in a new preclinical model of locally advanced orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia 12(3):264–274
Tannock IF, Lee CM, Tunggal JK, Cowan DS, Egorin MJ (2002) Limited penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue: a potential cause of resistance of solid tumors to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 8(3):878–884
Urva SR, Shin BS, Yang VC, Balthasar JP (2009) Sensitive high performance liquid chromatographic assay for assessment of doxorubicin pharmacokinetics in mouse plasma and tissues. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 877(8–9):837–841
Vajkoczy P, Menger MD, Goldbrunner R, Ge S, Fong TA, Vollmar B, Schilling L, Ullrich A, Hirth KP, Tonn JC, Schmiedek P, Rempel SA (2000) Targeting angiogenesis inhibits tumor infiltration and expression of the pro-invasive protein SPARC. Int J Cancer 87(2):261–268
Yang AD, Bauer TW, Camp ER, Somcio R, Liu W, Fan F, Ellis LM (2005) Improving delivery of antineoplastic agents with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Cancer 103(8):1561–1570
Ye QH, Qin LX, Forgues M, He P, Kim JW, Peng AC, Simon R, Li Y, Robles AI, Chen Y, Ma ZC, Wu ZQ, Ye SL, Liu YK, Tang ZY, Wang XW (2003) Predicting hepatitis B virus-positive metastatic hepatocellular carcinomas using gene expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med 9(4):416–423
Zhang L, Yu D, Hicklin DJ, Hannay JA, Ellis LM, Pollock RE (2002) Combined anti-fetal liver kinase 1 monoclonal antibody and continuous low-dose doxorubicin inhibits angiogenesis and growth of human soft tissue sarcoma xenografts by induction of endothelial cell apoptosis. Cancer Res 62(7):2034–2042
Zhang S, Guo H, Zhang D, Zhang W, Zhao X, Ren Z, Sun B (2006) Microcirculation patterns in different stages of melanoma growth. Oncol Rep 15(1):15–20
Zhang D, Li B, Shi J, Zhao L, Zhang X, Wang C, Hou S, Qian W, Kou G, Wang H, Guo Y (2010) Suppression of tumor growth and metastasis by simultaneously blocking vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A and VEGF-C with a receptor-immunoglobulin fusion protein. Cancer Res 70(6):2495–2503
Zhu AX, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Muzikansky A, Horgan K, Sheehan S, Hale KE, Enzinger PC, Bhargava P, Stuart K (2006) Phase II study of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in combination with bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24(12):1898–1903
Zhu AX, Holalkere NS, Muzikansky A, Horgan K, Sahani DV (2008) Early antiangiogenic activity of bevacizumab evaluated by computed tomography perfusion scan in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist 13(2):120–125
Acknowledgments
A special thanks to Dr. Wei Yang for her expert technical assistance. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30960373), Youth Science Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (Grant No. GJJ10066), and Youth Science Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial Science and Technology Department (Grant No. 20114BAB215009).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fan Zhou and Juan Hu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, F., Hu, J., Shao, JH. et al. Metronomic chemotherapy in combination with antiangiogenic treatment induces mosaic vascular reduction and tumor growth inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 1879–1890 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1270-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1270-7