Abstract
Purpose
Although polychemotherapy regiments have improved clinical outcome for Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) patients, salvage treatment of patients with refractory disease remains very poor. Combined therapies protocols have been emerging to improve treatment strategies to circumvent responseless BL patients. We evaluate the cell death effect of histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) combined with etoposide (VP-16) and cisplatin (CDDP) on BL cell lines.
Methods
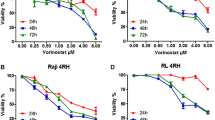
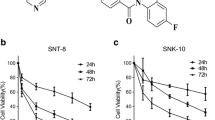
3-(4,5-Dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assay was performed to assess drug toxicity. To establish the concentrations and time of incubation for the combined treatment, a kinetic analysis was performed for each drug on BL41 and Raji BL cell lines for 24, 48 and 72 h. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry using Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) and cleaved caspase 3 labeling assays. Caspase 9 activation and levels of Bcl-2 family proteins were analyzed by Western blot.
Results
The doses of NaB (1.0 mM), CDDP (1.0 and 2.5 μM), and VP-16 (0.1 and 0.3 μM) after 24 h of incubation were chosen for the evaluation of combined therapy. The apoptotic effects on BL cell lines of NaB/VP-16 and NaB/CDDP were followed by upregulation of Bim protein (P < 0.05), activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9, followed by Mcl-1 downregulation (P < 0.05). However, Bim overexpression was not correlated with Bcl-2 inhibition (P > 0.05) and was accompanied by increase in Bax expression (P < 0.05). The combination effects of NaB/VP-16 and NaB/CDDP were found to be synergistic and additive, respectively, in both the cell lines.
Conclusions
The study provides strong evidence for the synergistic effects of the association with HDCI and chemotherapy in BL cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldoss IT, Weisenburger DD, Fu K, Chan WC, Vose JM, Bierman PJ, Bociek RG, Armitage JO (2008) Adult Burkitt lymphoma: advances in diagnosis and treatment. Oncology 22:1508–1517
Atra A, Gerrard M, Hobson R, Imeson JD, Hann IM, Pinkerton CR (2001) Outcome of relapsed or refractory childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma treated with the UKCCSG 9003/9002 protocols. Br J Haematol 112:965–968. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02647.x
Belloc F, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Lavignolle V, Bascans E, Braz-Pereira E, Durrieu F, Lacombe F (2000) Flow cytometry detection of caspase 3 activation in preapoptotic leukemic cells. Cytometry 40:150–151. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0320(20000601)40:2<151:AID-CYTO9>3.0.CO;2-9
Bornkamm GW (2009) Epstein-Barr virus and its role in the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma: an unresolved issue. Semin Cancer Biol 19:351–365. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2009.07.002
Burkitt D (1958) A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg 46:218–223
Cairo MS, Sposto R, Perkins SL, Meadows AT, Hoover-Regan ML, Anderson JR, Siegel SE, Lones MA, Tedeschi-Blok N, Kadin ME, Kjeldsberg CR, Wilson JF, Sanger W, Morris E, Krailo MD, Finlay JL (2003) Burkitt’s and Burkitt-like lymphoma in children and adolescents: a review of the children’s cancer group experience. Br J Haematol 120:660–670
Calender A, Billaud M, Aubry JP, Banchereau J, Vuillaume M, Lenoir GM (1987) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8060–8064
Cang S, Ma Y, Liu D (2009) New clinical developments in histone deacetylase inhibitors for epigenetic therapy of cancer. J Hematol Oncol 2:22–32. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-2-22
Carew JS, Giles FJ, Nawrocki ST (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: mechanisms of cell death and promise in combination cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 269:7–17. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.03.037
Chen X, Wong P, Radany E, Wong JY (2009) HDAC Inhibitor, Valproic acid, induces p53-dependent radiosensitization of colon cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 24:689–699. doi:10.1089/cbr.2009.0629
Cherney BW, Bhatia KG, Sgadari C, Gutierrez MI, Mostowski H, Pike SE, Gupta G, Magrath IT, Tosato G (1997) Role of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in the tumorigenicity of Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Cancer Res 57:2508–2515
Chou T, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effects relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibtors. Adv Enzyme Regul 22:27–55
Craig RW (2002) MCL1 provides a window on the role of the BCL2 family in cell proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 16:444–454. doi:10.1038/sj/leu/2402416
Czabotar PE, Colman PM, Huang DC (2009) Bax activation by Bim? Cell Death Differ 16:1187–1191. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.83
Ellis L, Pili R (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: advancing therapeutic strategies in hematological and solid malignancies. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 3:2411–2469. doi:10.3390/ph3082441
Ellis L, Bots M, Lindemann RK, Bolden JE, Newbold A, Cluse LA, Scott CL, Strasser A, Atadja P, Lowe SW, Johnstone RW (2009) The histone deacetylase inhibitors LAQ824 and LBH589 do not require death receptor signaling or a functional apoptosome to mediate tumor cell death or therapeutic efficacy. Blood 114:380–393. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-10-182758
Emanuele S, Lauricella M, Tesoriere G (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: apoptotic effects and clinical implications Int J Oncol 33:637–646. doi:10.3892/ijo_00000049
Fischel J-L, Formento P, Milano G (2005) Epidermal growth factorreceptor double targeting by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Iressa) and a monoclonal antibody (Cetuximab). Impact on cell growth and molecular factors Br J Cancer 92:1063–1068. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602428
Gerrard M, Cairo MS, Weston C, Auperin A, Pinkerton R, Lambilliote A, Sposto R, McCarthy K, Lacombe MJ, Perkins SL, Patte C (2008) FAB LMB96 International Study Committee. Excellent survival following two courses of COPAD chemotherapy in children and adolescents with resected localized B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: results of the FAB/LMB 96 international study. Br J Haematol 141:840–847. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07144.x
Griffin TC, Weitzman S, Weinstein H, Chang M, Cairo M, Hutchison R, Shiramizu B, Wiley J, Woods D, Barnich M, Gross TG, Group Children’sOncology (2009) A study of rituximab and ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide chemotherapy in children with recurrent/refractory B-cell (CD20+) non-Hodgkin lymphoma and mature B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 52:177–181. doi:10.1002/pbc.21753
Guo F, Sigua C, Tao J, Bali P, George P, Li Y, Wittmann S, Moscinski L, Atadja P, Bhalla K (2004) Cotreatment with histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 enhances Apo-2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced death inducing signaling complex activity and apoptosis of human acute leukemia cells. Cancer Res 64:2580–2589. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
Jazirehi AR (2010) Regulation of apoptosis-associated genes by histone deacetylase inhibitors: implications in cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 21:805–813. doi:10.1097/CAD.0b013e32833dad91
Kelly GL, Rickinson AB (2007) Burkitt lymphoma: revisiting the pathogenesis of a virus-associated malignancy. Hematology 20:277–284, http://asheducationbook. hematologylibrary.org
Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Chipuk JE, Bonzon C, Sullivan BA, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (2005) BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly. Molecular Cell 17:525–535. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.003
Lemoine M, Younes A (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of lymphoma. Discov Med 10:462–470
Magrath I, Jain V, Bhatia K (1982) Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt’s lymphoma. Semin Cancer Biol 3:285–295
Martínez-Iglesias O, Ruiz-Llorente L, Sánchez-Martínez R, García L, Zambrano A, Aranda A (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: mechanism of action and therapeutic use in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 10:395–398
Mellert HS, Stanek TJ, Sykes SM, Rauscher FJ, Schultz DC, McMahon SB (2011) Deacetylation of the DNA-binding domain regulates p53-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 286:4264–4270. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.184663
Mercurio C, Minucci S, Pelicci PG (2010) Histone deacetylases and epigenetic therapies of hematological malignancies. Pharmacol Res 62:18–34. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2010.02.010
Mérino D, Giam M, Hughes PD, Siggs OM, Heger K, O’Reilly LA, Adams JM, Strasser A, Lee EF, Fairlie WD, Bouillet P (2009) The role of BH3-only protein Bim extends beyond inhibiting Bcl-2-like prosurvival proteins. J Cell Biol 186:355–362. doi:10.1083/jcb.200905153
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and citotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E, Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F, Wang X (2003) Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes Dev 17:1475–1486. doi:10.1101/gad.1093903
O’Connor OA, Heaney ML, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Willim R, MacGregor-Cortelli B, Curly T, Moskowitz C, Portlock C, Horwitz S, Zelenetz AD, Frankel S, Richon V, Marks P, Kelly WK (2006) Clinical experience with intravenous and oral formulations of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 24:166–173. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.9679
Oriol A, Ribera JM, Bergua J, Giménez MesaE, Grande C, Esteve J, Brunet S, Moreno MJ, Escoda L, Hernandez-Rivas JM, Hoelzer D (2008) High-dose chemotherapy and immunotherapy in adult Burkitt lymphoma: comparison of results in human immunodeficiency virus-infected and noninfected patients. Cancer 113:117–125. doi:10.1002/cncr.23522
Patte C, Auperin A, Gerrard M, Michon J, Pinkerton R, Sposto R, Weston C, Raphael M, Perkins SL, McCarthy K, Cairo MS (2007) FAB/LMB96 International Study Committee. Results of the randomized international FAB/LMB96 trial for intermediate risk B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and adolescents: it is possible to reduce treatment for the early responding patients. Blood 109:2773–2780. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-036673
Richter-Larrea JA, Robles EF, Fresquet V, Beltran E, Rullan AJ, Agirre X, Calasanz MJ, Panizo C, Richter JA, Hernandez JM, Roman-Gomez J, Prosper F, Martinez-Climent JA (2010) Reversion of epigenetically mediated Bim silencing overcomes chemoresistance in Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 116:2531–2542. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-02-268003
Rosato R, Maggio SC, Almenara JA, Payne SG, Atadja P, Spiegel S, Dent P, Grant S (2006) The histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 induces human leukemia cell death through a process involving XIAP down-regulation, oxidative injury, and the acid sphingomyelinase-dependent generation of ceramide. Mol Pharmacol 69:216–225. doi:10.1124/mol.105.017145
Sakajiri S, Kumagai T, Kawamata N, Saitoh T, Said JW, Koeffler HP (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibitors profoundly decrease proliferation of human lymphoid cancer cell lines. Exp Hematol 33:53–61. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2004.09.008
Siegel D, Hussein M, Belani C, Robert F, Galanis E, Richon VM, Garcia-Vargas J, Sanz-Rodriguez C, Rizvi S (2009) Vorinostat in solid and hematologic malignancies. J Hematol Oncol 2:31–41. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-2-31
Silva KL, Vasconcellos DV, Castro EDP, Coelho AM, Linden R, Maia RC (2006) Apoptotic effect of fludarabine is independent of expression of IAPs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Apoptosis 11:277–285. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-3560-5
Tan J, Cang S, Ma Y, Petrillo RL, Liu D (2010) Novel histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical trials as anti-cancer agents. J Hematol Oncol 4:3–5. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-3-5
Thorley-Lawson DA, Allday MJ (2008) The curious case of the tumour virus: 50 years of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:913–924. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2015
Vayssade M, Haddada H, Faridoni-Laurens L, Tourpin S, Valent A, Bénard J, Ahomadegbe JC (2005) P73 functionally replaces p53 in Adriamycin-treated, p53-deficient breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 116:860–869. doi:10.1002/ijc.21033
Walkinshaw DR, Yang XJ (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as novel anticancer therapeutics. Curr Oncol 15:237–243
Wang S, Yan-Neale Y, Cai R, Alimov I, Cohen D (2006) Activation of mitochondrial pathway is crucial for tumor selective induction of apoptosis by LAQ824. Cell Cycle 5:1662–1668. doi:10.4161/cc.5.15.3099
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292:727–730. doi:10.1126/science.1059108
Xu WS, Parmigiani R, Marks PA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene 26:5541–5552. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210620
Youle J, Strasser A (2008) The Bcl-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:47–59. doi:10.1038/nrm2308
Acknowledgments
We thank Flavia da Cunha Vasconcelos for helping on flow cytometry analysis. This work was supported by a grant from INCT para Controle do Câncer, CNPq 573806/2008-0 e FAPERJ E26/170.026/2008.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any financial interest related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos Ferreira, A.C., Fernandes, R.A., Kwee, J.K. et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis through Bim upregulation in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 317–325 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-1093-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-1093-y