Abstract
Purpose
Rat thyroid follicular cell carcinomas invading into the thyroid capsule are highly produced by promotion with sulfadimethoxine (SDM) in a rat two-stage thyroid carcinogenesis model. In this study, we investigated the participation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway that is associated with malignant phenotypes of many cancers on the development of SDM-induced capsular invasive carcinomas.
Methods
Thyroid proliferative lesions developed 10 or 15 weeks after promotion with SDM in male F344 rats initiated with N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)nitrosamine were immunohistochemically analyzed with regard to cellular distribution of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and Akt isoforms, as well as their downstream molecules.
Results
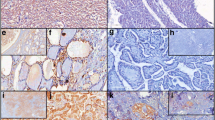
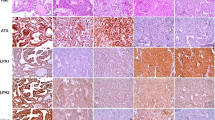
Increased expression of PI3K signaling molecules was evident in association with the development of lesion stages from the early focal hyperplasia to the late carcinomas. Capsular carcinomas, and the less frequent parenchymal carcinomas, exclusively expressed phosphorylated, inactive PTEN, and active Akt isoforms, as did their downstream molecules. Among the Akt isoforms, enhanced expression of Akt1 was more prominent than that of Akt2 in both capsular and parenchymal carcinomas.
Conclusions
Activation of the PI3K pathway through phosphorylation of PTEN promotes the high production of capsular carcinomas as well as the development of less frequent parenchymal carcinomas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ago K, Saegusa Y, Nishimura J, Dewa Y, Kemmochi S, Kawai M, Harada T, Mitsumori K, Shibutani M (2010) Involvement of glycogen synthase kinase-3β signaling and aberrant nucleocytoplasmic localization of retinoblastoma protein in tumor promotion in a rat two-stage thyroid carcinogenesis model. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:269–280
Arboleda MJ, Lyons JF, Kabbinavar FF, Bray MR, Snow BE, Ayala R, Danino M, Karlan BY, Slamon DJ (2003) Overexpression of AKT2/protein kinase Bβ leads to up-regulation of β1 integrins, increased invasion, and metastasis of human breast and ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 63:196–206
Asnaghi L, Bruno P, Priulla M, Nicolin A (2004) mTOR: a protein kinase switching between life and death. Pharmacol Res 50:545–549
Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A (2007) PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis 28:1379–1386
Blaustein M, Pelisch F, Coso OA, Bissell MJ, Kornblihtt AR, Srebrow A (2004) Mammary epithelial-mesenchymal interaction regulates fibronectin alternative splicing via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 279:21029–21037
Cantley LC, Neel BG (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4240–4245
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378:785–789
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ (1998) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization. Genes Dev 12:3499–3511
Dillon RL, Marcotte R, Hennessy BT, Woodgett JR, Mills GB, Muller WJ (2009) Akt1 and akt2 play distinct roles in the initiation and metastatic phases of mammary tumor progression. Cancer Res 69:5057–5064
Furuya F, Lu C, Willingham MC, Cheng SY (2007) Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delays tumor progression and blocks metastatic spread in a mouse model of thyroid cancer. Carcinogenesis 28:2451–2458
Guigon CJ, Zhao L, Willingham MC, Cheng SY (2009) PTEN deficiency accelerates tumour progression in a mouse model of thyroid cancer. Oncogene 28:509–517
Horowitz JC, Lee DY, Waghray M, Keshamouni VG, Thomas PE, Zhang H, Cui Z, Thannickal VJ (2004) Activation of the pro-survival phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway by transforming growth factor-β1 in mesenchymal cells is mediated by p38 MAPK-dependent induction of an autocrine growth factor. J Biol Chem 279:1359–1367
Imai T, Onose J, Hasumura M, Ueda M, Takizawa T, Hirose M (2004) Sequential analysis of development of invasive thyroid follicular cell carcinomas in inflamed capsular regions of rats treated with sulfadimethoxine after N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)nitrosamine-initiation. Toxicol Pathol 32:229–236
Imai T, Hasumura M, Onose J, Ueda M, Takizawa T, Cho YM, Hirose M (2005) Development of invasive follicular cell carcinomas in a rat thyroid carcinogenesis model: biological impact of capsular inflammation and reduced cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Cancer Sci 96:31–37
Imai T, Hasumura M, Cho YM, Onose J, Hirose M (2007) Depression of T cell-mediated immunity reduces sulfadimethoxine-induced capsular inflammation and inhibits associated development of invasive thyroid follicular cell carcinomas in rats. Cancer Sci 98:294–298
Kallergi G, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Stournaras C (2007) Phosphorylation of FAK, PI-3K, and impaired actin organization in CK-positive micrometastatic breast cancer cells. Mol Med 13:79–88
Kovács KA, Lengyel F, Vértes Z, Környei JL, Gocze PM, Sumegi B, Szabó I, Vértes M (2007) Phosphorylation of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten) protein is enhanced in human fibromyomatous uteri. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 103:196–199
Krasilnikov MA (2000) Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase dependent pathways: the role in control of cell growth, survival, and malignant transformation. Biochemistry (Mosc) 65:59–67
Larson SD, Jackson LN, Riall TS, Uchida T, Thomas RP, Qiu S, Evers BM (2007) Increased incidence of well-differentiated thyroid cancer associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis and the role of the PI3k/Akt pathway. J Am Coll Surg 204:764–775
Lee K-Y, Shibutani M, Inoue K, Kuroiwa K, Mami U, Woo G-H, Hirose M (2006) Methacarn fixation—effects of tissue processing and storage conditions on detection of mRNAs and proteins in paraffin-embedded tissues. Anal Biochem 351:36–43
Lipscomb EA, Mercurio AM (2005) Mobilization and activation of a signaling competent α6β4integrin underlies its contribution to carcinoma progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:413–423
Liu H, Radisky DC, Wang F, Bissell MJ (2004) Polarity and proliferation are controlled by distinct signaling pathways downstream of PI3-kinase in breast epithelial tumor cells. J Cell Biol 164:603–612
LoPiccolo J, Granville CA, Gills JJ, Dennis PA (2007) Targeting Akt in cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 18:861–874
Maroulakou IG, Oemler W, Naber SP, Tsichlis PN (2007) Akt1 ablation inhibits, whereas Akt2 ablation accelerates, the development of mammary adenocarcinomas in mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV)-ErbB2/neu and MMTV-polyoma middle T transgenic mice. Cancer Res 67:167–177
Ringel MD, Hayre N, Saito J, Saunier B, Schuppert F, Burch H, Bernet V, Burman KD, Kohn LD, Saji M (2001) Overexpression and overactivation of Akt in thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res 61:6105–6111
Srivastava AK, Pandey SK (1998) Potential mechanism(s) involved in the regulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin. Mol Cell Biochem 182:135–141
Toker A, Yoeli-Lerner M (2006) Akt signaling and cancer: surviving but not moving on. Cancer Res 66:3963–3966
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Wang F, Weaver VM, Petersen OW, Larabell CA, Dedhar S, Briand P, Lupu R, Bissell MJ (1998) Reciprocal interactions between β1-integrin and epidermal growth factor receptor in three-dimensional basement membrane breast cultures: a different perspective in epithelial biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14821–14826
Wyszomierski SL, Yu D (2005) A knotty turnabout?: Akt1 as a metastasis suppressor. Cancer Cell 8:437–439
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs. Shigeko Suzuki for her technical assistance in preparing histological specimens.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors disclose that there are no conflicts of interest that could inappropriately influence the outcome of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kemmochi, S., Fujimoto, H., Woo, GH. et al. Involvement of PTEN/Akt signaling in capsular invasive carcinomas developed in a rat two-stage thyroid carcinogenesis model after promotion with sulfadimethoxine. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137, 723–732 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0931-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0931-7