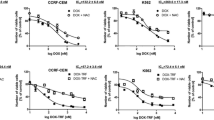
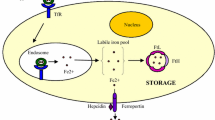
Abstract
Purpose
Due to the severe problems accompanied with multiple drug resistance (MDR), agents that can induce apoptosis independently of death-suppressing proteins are required. Here, we show that the ferrocene derivative HUNI 068 is active against cancer cells and overcomes different mechanisms of multiple drug resistance (MDR).
Methods
Proliferation inhibition was determined by using a CASY®CellCounter. DNA fragmentation assay and annexin-V/PI binding assays measured apoptosis, and necrosis was excluded by LDH-release assay. Drug-resistant cell lines were generated to test the ability to overcome MDR. By real-time PCR, alterations in gene expression of treated cells were analyzed. The apoptosis pathway was investigated by immunoblotting and measurement of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition.
Results
HUNI 068 leads to proliferation inhibition and apoptosis mediation, but only minimal necrosis induction. Healthy leukocytes seem to be less affected than cancer cells. The compound overcomes drug resistance to vincristine and daunorubicin. Independence of p-glycoprotein and Bcl-2 overexpression is probable, and upregulation of the anti-Bcl-2 protein harakiri was seen. Combined treatment with vincristine leads to synergistic effects. In different primary tumor cells, HUNI 068 achieved acceptable effects where tolerance to some conventional drugs was shown. Induction of apoptosis is FADD-independent, but associated with a reduced mitochondrial membrane potential and activation of caspase-9, indicating the intrinsic apoptosis pathway via mitochondria.
Conclusions
HUNI 068 is a promising new compound with activity even against MDR tumor cells. Further investigations into the class of ferrocene-derived agents might reveal compounds with improved activity for a more specific and safe anti-cancer therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allardyce CS, Dorcier A, Scolaro C, Dyson PJ (2005) Development of organometallic (organo-transition metal) pharmaceuticals. Appl Organomet Chem 19:1–10
Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A, van’t Veer MB (1995) Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the immunological characterization of leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia 9:1783–1786
Bene MC, Bernier M, Castoldi G, Faure GC, Knapp W, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A, van’t Veer M (1999) Impact of immunophenotyping on management of acute leukemias. Haematologica 84:1024–1034
Brozek J, Bryl E, Ploszynska A, Balcerska A, Witkowski JM (2009) P-glycoprotein activity predicts outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 31:493–499
Essmann F, Wieder T, Otto A, Muller EC, Dörken B, Daniel PT (2000) GDP dissociation inhibitor D4-GDI (Rho-GDI 2), but not the homologous rho-GDI 1, is cleaved by caspase-3 during drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem J 346(Pt 3):777–783
Fadok VA, Xue D, Henson P (2001a) If phosphatidylserine is the death knell, a new phosphatidylserine-specific receptor is the bellringer. Cell Death Differ 8:582–587
Fadok VA, de Cathelineau A, Daleke DL, Henson PM, Bratton DL (2001b) Loss of phospholipid asymmetry and surface exposure of phosphatidylserine is required for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages and fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276:1071–1077
Gaynon PS, Qu RP, Chappell RJ, Willoughby ML, Tubergen DG, Steinherz PG, Trigg ME (1998) Survival after relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: impact of site and time to first relapse—the children’s cancer group experience. Cancer 82:1387–1395
Hunold A, Neundorf I, James P, Neudörfl J, Schmalz HG (2009) Stereoselective synthesis of new ferrocene-derived amino acid building blocks. Eur J Org Chem 4429–4440
Inohara N, Ding L, Chen S, Nunez G (1997) Harakiri, a novel regulator of cell death, encodes a protein that activates apoptosis and interacts selectively with survival-promoting proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L). EMBO J 16:1686–1694
James P, Neudorfl J, Eissmann M, Jesse P, Prokop A, Schmalz HG (2006) Enantioselective synthesis of ferrocenyl nucleoside analogues with apoptosis-inducing activity. Org Lett 8:2763–2766
Jaouen G (2005) Bioorganometallics: biomolecules, labeling, medicine. Viley-VCH, New York
Jenkins CE, Swiatoniowski A, Power MR, Lin TJ (2006) Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced human mast cell apoptosis is associated with up-regulation of endogenous Bcl-xS and down-regulation of Bcl-xL. J Immunol 177:8000–8007
Kealy T, Pauson P (1951) A new type of organo-iron compound. Nature 168:1039–1040
Kopf-Maier P, Erkenswick P (1984) Teratogenicity and embryotoxicity of titanocene dichloride in mice. Toxicology 33:171–181
Krishna R, Mayer LD (2000) Multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer. Mechanisms, reversal using modulators of MDR and the role of MDR modulators in influencing the pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs. Eur J Pharm Sci 11:265–283
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lambert IH, Hoffmann EK, Jorgensen F (1989) Membrane potential, anion and cation conductances in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Membr Biol 111:113–131
Nagata S (1997) Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88:355–365
Nguyen A, Vessières A, Hillard E, Top S, Pigeon P, Jaouen G (2007) Ferrocifens and ferrocifenols as new potential weapons against breast cancer. Chimia 61:716–724
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 139:271–279
Prokop A, Wieder T, Sturm I, Essmann F, Seeger K, Wuchter C, Ludwig WD, Henze G, Dörken B, Daniel PT (2000) Relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with a decrease of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and loss of spontaneous caspase-3 processing in vivo. Leukemia 14:1606–1613
Prokop A, Wrasidlo W, Lode H, Herold R, Lang F, Henze G, Dorken B, Wieder T, Daniel PT (2003) Induction of apoptosis by enediyne antibiotic calicheamicin thetaII proceeds through a caspase-mediated mitochondrial amplification loop in an entirely Bax-dependent manner. Oncogene 22:9107–9120
Reers M, Smiley ST, Mottola-Hartshorn C, Chen A, Lin M, Chen LB (1995) Mitochondrial membrane potential monitored by JC-1 dye. Methods Enzymol 260:406–417
Schatzschneider U, Metzler-Nolte N (2006) New principles in medicinal organometallic chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 45:1504–1507
Schlawe D, Majdalani A, Velcicky J, Hessler E, Wieder T, Prokop A, Schmalz HG (2004) Iron-containing nucleoside analogues with pronounced apoptosis-inducing activity. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 43:1731–1734
Schlegel RA, Williamson P (2001) Phosphatidylserine, a death knell. Cell Death Differ 8:551–563
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Srinivas G, Kusumakumary P, Nair MK, Panicker KR, Pillai MR (2000) Mutant p53 protein, Bcl-2/Bax ratios and apoptosis in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:62–67
Tillner J, Winckler T, Dingermann T (1994) A simple cytotoxicity assay using the eucaryotic microorganism Dictyostelium discoideum. Pharmazie 49:759–761
Top S, Vessieres A, Leclercq G, Quivy J, Tang J, Vaissermann J, Huche M, Jaouen G (2003) Synthesis, biochemical properties and molecular modelling studies of organometallic specific estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), the ferrocifens and hydroxyferrocifens: evidence for an antiproliferative effect of hydroxyferrocifens on both hormone-dependent and hormone-independent breast cancer cell lines. Chem Eur J 9:5223–5236
Uderzo C, Conter V, Dini G, Locatelli F, Miniero R, Tamaro P (2001) Treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia after the first relapse: curative strategies. Haematologica 86:1–7
Van Cruchten S, Van Den Broeck W (2002) Morphological and biochemical aspects of apoptosis, oncosis and necrosis. Anat Histol Embryol 31:214–223
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Viotte M, Gautheron B, Kubicki MM, Nifant’ev IE, Fricker SP (1995) Synthesis, structure of nitrogen-containing phosphinogold(I) ferrocenes. In vitro Activity against bladder and colon carcinoma cell lines. Met Based Drugs 2:311–326
Voisard R, Dartsch PC, Seitzer U, Roth D, Kochs M, Hombach V (1991) Cell culture as a prescreening system for drug prevention of restenosis? Vasa Suppl 33:140–141
von Haefen C, Wieder T, Essmann F, Schulze-Osthoff K, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2003) Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in BJAB cells proceeds via a death receptor-independent, caspases-3–8-driven mitochondrial amplification loop. Oncogene 22:2236–2247
Wieder T, Geilen CC, Wieprecht M, Becker A, Orfanos CE (1994) Identification of a putative membrane-interacting domain of CTP: phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase from rat liver. FEBS Lett 345:207–210
Wieder T, Orfanos CE, Geilen CC (1998) Induction of ceramide-mediated apoptosis by the anticancer phospholipid analog, hexadecylphosphocholine. J Biol Chem 273:11025–11031
Wieder T, Essmann F, Prokop A, Schmelz K, Schulze-Osthoff K, Beyaert R, Dörken B, Daniel PT (2001) Activation of caspase-8 in drug-induced apoptosis of B-lymphoid cells is independent of CD95/Fas receptor-ligand interaction and occurs downstream of caspase-3. Blood 97:1378–1387
Wilkinson G (1975) The iron sandwich. A recollection of the first four months. J Organometal Chem 100:273–278
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, Germany; FOR 630), Kinderleben e.V. (Berlin, Germany) and Dr. Kleist-Stiftung (Berlin, Germany). The excellent technical assistance of Corazon Frias, Soo-Young Lee, Liliane Abodo and Ulrike Schmitt is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kater, B., Hunold, A., Schmalz, HG. et al. Iron containing anti-tumoral agents: unexpected apoptosis-inducing activity of a ferrocene amino acid derivative. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137, 639–649 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0924-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0924-6