Abstract
Purpose
To examine the expression profile and promoter methylation status of WIF-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and identify the possible relationship between the WIF-1 expression pattern and promoter methylation status.
Methods
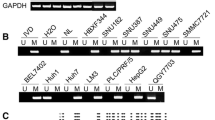
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to detect mRNA level of WIF-1 in 4 HCC cell lines, 15 paired HCC clinical samples and 3 normal liver tissues. Methylation-specific PCR and bisulfite DNA sequencing were used in methylation analysis. In vitro assays for HCC cells, colony formation and cell proliferation assay were carried out to observe the effect of WIF-1 on cell growth; TOP-flash luciferase analysis was employed to determine its role in the Wnt pathway.
Results
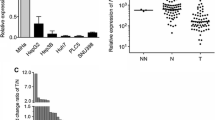
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showed the extensive low expression of WIF-1 mRNA in HCC, and this down-regulation was generally dependent on the degree of methylation at its promoter region. In vitro assays indicated WIF-1 can inhibit cell growth by blocking Wnt signaling in HCC cells.
Conclusions
WIF-1 silencing as a result of its promoter hypermethylation may be a frequent event in HCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batra S, Shi Y, Kuchenbecker KM et al (2006) Wnt inhibitory factor-1, a Wnt antagonist, is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:1228–1232
Bengochea A, de Souza MM, Lefrançois L et al (2008) Common dysregulation of Wnt/frizzled receptor elements in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 99:143–150
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M et al (2004) Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 5:215–219
Cebrat M, Strzadala L, Kisielow P (2004) Wnt inhibitory factor-1: a candidate for a new player in tumorigenesis of intestinal epithelial cells. Cancer Lett 206:107–113
Civenni G, Holbro T, Hynes NE (2003) Wnt1 and Wnt5a induce cyclin D1 expression through ErbB1 transactivation in HC11 mammary epithelial cells. EMBO Rep 4:166–171
Clevers H (2004) Wnt breakers in colon cancer. Cancer Cell 5:5–6
Farazi PA, DePinho RA (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer 6:674–687
He B, Reguart N, You L et al (2005a) Blockade of Wnt-1 signaling induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells containing downstream mutations. Oncogene 24:3054–3058
He B, Lee AY, Dadfarmay S et al (2005b) Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 is silenced by hypermethylation and induces apoptosis in beta-catenin-deficient human mesothelioma cells. Cancer Res 65:743–748
Hsieh JC, Kodjabachian L, Rebbert ML et al (1999) A new secreted protein that binds to Wnt proteins and inhibits their activities. Nature 398:431–436
Huang H, He X (2008) Wnt/β-catenin signaling: new (and old) players and new insights. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:119–125
Kensler TW, Qian GS, Chen JG et al (2003) Translational strategies for cancer prevention in liver. Nat Rev Cancer 3:321–329
Kim M, Lee HC, Tsedensodnom O et al (2008) Functional interaction between Wnt3 and Frizzled-7 leads to activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Hepatol 48:780–791
Kirikoshi H, Sekihara H, Katoh M (2001) Expression of WNT14 and WNT14B mRNAs in human cancer, up-regulation of WNT14 by IFN gamma and up-regulation of WNT14B by β-estradiol. Int J Oncol 19:1221–1225
Klaus A, Birchmeier W (2008) Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:387–398
Lee HC, Kim M, Wands JR (2006) Wnt/frizzled signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Biosci 11:1901–1915
Lin YC, You L, Xu Z et al (2007) Wnt inhibitory factor-1 gene transfer inhibits melanoma cell growth. Hum Gene Ther 18:379–386
Mazieres J, He B, You L et al (2004) Wnt inhibitory factor-1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in human lung cancer. Cancer Res 64:4717–4720
Saitoh T, Mine T, Katoh M (2002) Frequent up-regulation of WNT5A mRNA in primary gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med 9:515–519
Smith K, Bui TD, Poulsom R et al (1999) Up-regulation of macrophage wnt gene expression in adenoma-carcinoma progression of human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 81:496–502
Staal FJ, Luis TC, Tiemessen MM (2008) WNT signalling in the immune system: WNT is spreading its wings. Nat Rev Immunol 8:581–593
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H et al (2006) Epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 plays an important role in bladder cancer through aberrant canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res 12:383–391
Wissmann C, Wild PJ, Kaiser S et al (2003) WIF1, a component of the Wnt pathway, is down-regulated in prostate, breast, lung, and bladder cancer. J Pathol 201:204–212
Xie L, Qin WX, Li JJ et al (2007) BNIPL-2 promotes the invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 17:605–610
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shanghai Municipal Program of International Cooperation in Science and Technology (08410700900), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2009CB521803), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30973492), and the Projects of State Key Laboratory for Oncogenes and Related Genes (80-08-02, 91-09-01), and the National Key Sci-Tech Special Project of China (2008ZX10002-019).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Deng, B. Yu and Q. Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Yu, B., Cheng, Q. et al. Epigenetic silencing of WIF-1 in hepatocellular carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1161–1167 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0763-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0763-5