Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the association between two Xeroderma pigmentosum group C polymorphism (XPC Lys939Gln and insertion/deletion PAT −/+ in intron 9) and bladder cancer (BC) susceptibility.
Materials and methods
Genotyping was performed in 208 BC patients and 245 controls by PCR–RFLP method.
Results
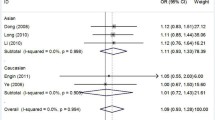
XPC PAT +/+ genotype was associated with elevated risk of BC (p = 0.021, OR = 2.49). XPC Lys939Gln AC + CC genotype was significantly associated with risk in invasive stage of BC (p = 0.041, OR = 2.52). Haplotype analysis revealed that variant genotypes C of XPC Lys939Gln and + of PAT, C+ were significantly associated with risk of BC (p = 0.004, OR = 1.70). The CC genotype of Lys939Gln was associated with high risk for recurrence in BCG-treated patients (HR = 3.21, p = 0.036) thus, showing reduced recurrence-free survival (AC + CC/AA = 36/60 months; log rank p = 0.045).
Conclusion
Polymorphisms and haplotypes in XPC appear to influence susceptibility to BC risk. The variant C allele at Lys939Gln may be responsible for early recurrence in BCG-treated patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- XPC :
-
Xeroderma pigmentosum group C
- BCG:
-
Bacillus Calmette–Guerin
- BC:
-
Bladder cancer
- MMC:
-
Mitomycin-C
References
Berwick M, Vineis P (2000) Markers of DNA repair and susceptibility to cancer in humans: an epidemiologic review. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:874–897
Blankenburg S, Konig IR, Moessner R et al (2005) Assessment of 3 xeroderma pigmentosum groupC gene polymorphisms and risk of cutaneous melanoma: a case–control study. Carcinogenesis 26:1085–1090
Casson AG, Zheng Z, Evans SC et al (2005) Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes in the molecular pathogenesis of esophageal (Barrett) adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 26:1536–1541
Chopin DK, Gattegno B (2002) Superficial bladder tumors. Eur Urol 42:533–541
Excoffier L, Slatkin M (1995) Maximum-likelihood estimation of molecular haplotype frequencies in a diploid population. Mol Biol Evol 12:921–927
Fontana L, Bosviel R, Delort L et al (2008) DNA repair gene ERCC2, XPC, XRCC1, XRCC3 polymorphisms and associations with bladder cancer risk in a French cohort. Anticancer Res 28:1853–1856
Garcia-Closas M, Malats N, Real FX et al (2006) Genetic variation in the nucleotide excision repair pathway and bladder cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:536–542
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Hoeijmakers JH (2001) Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature 411:366–374
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T et al (2004) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 54:8–29
Larsson P, Wijkstrom H, Thorstenson A et al (2003) A population-based study of 538 patients with newly detected urinary bladder neoplasms followed during 5 years. Scand J Urol Nephrol 37:195–201
Legerski R, Peterson C (1992) Expression cloning of a human DNA repair gene involved in xeroderma pigmentosum group C. Nature 359:70–73
Li L, Peterson C, Legerski R (1996) Sequence of the mouse XPC cDNA and genomic structure of the human XPC gene. Nucleic Acids Res 24:1026–1028
López-Cima MF, González-Arriaga P, García-Castro L et al (2007) Polymorphisms in XPC, XPD, XRCC1, and XRCC3 DNA repair genes and lung cancer risk in a population of Northern Spain. BMC Cancer 7:162–173
Lynch CF, Lohen MB (1995) Urinary system. Cancer 75:316–329
Merz VW, Marth D, Kraft R et al (1995) Analysis of early failures after intravesical instillation therapy with Bacille Calmette–Guerin for carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Br J Urol 75:180–184
Messing EM, Young TB, Hunt VB et al (1995) Comparison of bladder cancer outcome in men undergoing hematuria home screening versus those with standard clinical presentations. Urology 45:396–397
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Pashos CL, Botteman MF, Laskin BL et al (2002) Bladder cancer: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Cancer Pract 10:311–322
Qiao Y, Spitz MR, Guo Z et al (2002) Rapid assessment of repair of ultraviolet DNA damage with a modified host-cell reactivation assay using a luciferase reporter gene and correlation with polymorphisms of DNA repair genes in normal human lymphocytes. Mutat Res 509:165–174
Sak SC, Barrett JH, Paul AB et al (2005) The polyAT, intronic IVS11-6 and Lys939Gln XPC polymorphisms are not associated with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Cancer 92:2262–2265
Sands AT, Abuin A, Sanchez A et al (1995) High susceptibility to ultraviolet-induced carcinogenesis in mice lacking XPC. Nature 377:162–165
Schenk-Braat EA, Bangma CH (2005) Immunotherapy for superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54:414–423
Shen H, Sturgis EM, Khan SG et al (2001) An intronic poly (AT) polymorphism of the DNA repair gene XPC and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a case–control study. Cancer Res 61:3321–3325
Sobin LH, Wittekind Ch (2002) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 6th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 199–202
Sugasawa K, Ng JM, Masutani C et al (1998) Xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein complex is the initiator of global genome nucleotide excision repair. Mol Cell 2:223–232
van Hoffen A, Balajee AS, van Zeeland AA et al (2003) Nucleotide excision repair and its interplay with transcription. Toxicology 193:79–90
Wood RD, Mitchell M, Sgouros J et al (2001) Human DNA repair genes. Science 291:1284–1289
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Yan W (2005) Single nucleotide polymorphisms for DNA repair genes in breast cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta 359:150–155
Zhang D, Chen C, Fu X et al (2008) A meta-analysis of DNA repair gene XPC polymorphisms and cancer risk. J Hum Genet 53:18–33
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the grant of Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi Govt. of India. RG is thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi for JRF.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gangwar, R., Mandhani, A. & Mittal, R.D. XPC gene variants: a risk factor for recurrence of urothelial bladder carcinoma in patients on BCG immunotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 779–786 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0717-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0717-y