Abstract
Purpose
Preclinical models showed TAC-101 (4-[3,5-bis(trimethylsilyl) benzamide] benzoic acid), an oral synthetic retinoid, has anti-tumor activity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A phase I/II study was performed in advanced HCC patients (pts).
Patients and methods
Thirty-three patients were enrolled. During Phase I, pts received 40 mg daily for 14 days q3 weeks; 2 of 5 patients developed DLT so dose was reduced to 20 mg/day. Twenty-eight patients received 20 mg/day.
Results
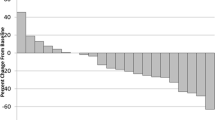
No pt had a CR or PR, but 12 of 21 (57%) had SD. Two pts (9.5%) had late PR after discontinuing TAC-101. Median survival (MS) for all 28 pts treated with 20 mg/day was 12.7 months (95% CI 8.8–22.7); MS for 21 evaluable pts was 19.2 months (95% CI 10.4–27.6).
Conclusions
20 mg of TAC- was well tolerated. Significant disease stabilization (12/21 pts, 57%), 2 late PRs, and prolonged MS (19.2 months) suggest that TAC-101 provides meaningful patient benefit.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S et al (2006) Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24(26):4293–4300
Abrams RA, Pajak TF, Haulk TL, Flam M, Asbell SO (1998) Survival results among patients with alpha-fetoprotein-positive, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of three sequential treatments of the RTOG and Johns Hopkins Oncology Center. Cancer J Sci Am 4(3):178–184
Barbare JC, Bouche O, Bonnetain F et al (2005) Randomized controlled trial of tamoxifen in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 23(19):4338–4346
Boige V, Taieb J, Hebbar M et al (2006) Irinotecan as first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter phase II study with dose adjustment according to baseline serum bilirubin level. Eur J Cancer 42(4):456–459
Bruserud O, Gjertsen BT (2000) New strategies for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia: differentiation induction-present use and future possibilities. Stem Cells 18:157–165
Dimery IW, Hong WK, Lee JJ et al (1997) Phase I trial of alpha-tocopherol effects on 13-cis-retinoic acid toxicity. Ann Oncol 8(1):85–89
Eferl R, Ricci R, Kenner L et al (2003) Liver tumor development. c-Jun antagonizes the proapoptotic activity of p53. Cell 112(2):181–192
El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ, McGlynn KA (2003) The continuing increase in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: an update. Ann Intern Med 139(10):817–823
El-Serag HB, Mason AC (1999) Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med 340(310):745–750
Fuchs CS, Clark JW, Ryan DP et al (2002) A phase II trial of gemcitabine in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 94(12):3186–3191
Fujimoto K, Hosotani R, Doi R et al (1999) Induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis by a novel retinobenzoic-acid derivative, TAC-101, in human pancreatic-cancer cells. Int J Cancer 81(4):637–644
Gish RG, Porta C, Lazar L et al (2007) Phase III randomized controlled trial comparing the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with nolatrexed or doxorubicin. J Clin Oncol 25(21):3069–3075
Guan Z, Wang Y, Maoleekoonpairoj S et al (2003) Prospective randomised phase II study of gemcitabine at standard or fixed dose rate schedule in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 89(10):1865–1869
Guo L, Guo Y, Xiao S, Shi X (2005) Protein kinase p-JNK is correlated with the activation of AP-1 and its associated Jun family proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci 77(15):1869–1878
Hashimoto Y, Kagechika H, Kawachi E et al (1996) Evaluation of differentiation-inducing activity of retinoids on human leukemia cell lines HL-60 and NB4. Biol Pharm Bull 19:1322–1328
Hasumi A, Matsui H, Sugioka A et al (2000) Precancerous conditions of biliary tract cancer in patients with pancreaticobiliary maljunction: reappraisal of nationwide survey in Japan. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 7(6):551–555
Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Ueno H, Takezako Y, Morizane C (2005) A phase II trial of continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil, mitoxantrone, and cisplatin for metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 103(4):756–762
Kato H, Nakamura M, Muramatsu M, Orito E, Ueda R, Mizokami M (2004) Spontaneous regression of hepatocellular carcinoma: two case reports and a literature review. Hepatol Res 29(3):180–190
Kim WR, Brown RS Jr, Terrault NA, El-Serag H (2002) Burden of liver disease in the United States: summary of a workshop. Hepatology 36(1):227–242
Lee J, Park JO, Kim WS et al (2004) Phase II study of doxorubicin and cisplatin in patients with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 54(5):385–390
Lee SJ, Ohashi Y, Sakurai H, Saiki I (2003) TAC-101 inhibits intrahepatic metastasis of orthotopically implanted murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 198(2):169–177
Leung CS, Tang CN, Fung KH, Li MK (2002a) A retrospective review of transcatheter hepatic arterial embolisation for ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma. J R Coll Surg Edinb 47(5):685–688
Leung TW, Tang AM, Zee B et al (2002b) Factors predicting response and survival in 149 patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated by combination cisplatin, interferon-alpha, doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy. Cancer 94(2):421–427
Lin F, Xiao D, Kolluri SK, Zhang X (2000) Unique anti-activator protein-1 activity of retinoic acid receptor beta. Cancer Res 60(12):3271–3280
Lippman SM (1997) Head and neck chemoprevention: recent advances. Cancer Control 4(2):128–135
Lippman SM, Benner SE, Hong WK (1993a) Chemoprevention strategies in lung carcinogenesis. Chest 103(1 Suppl):15S–19S
Lippman SM, Benner SE, Hong WK (1993b) Retinoids in chemoprevention of head and neck carcinogenesis. Prev Med 22(5):693–700
Lippman SM, Garewal H, Meyskens FL Jr (1989) Retinoids as potential chemopreventive agents in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Prev Med 18:740–48
Llovet JM, Bruix J (2000) Prospective validation of the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) score: a new prognostic system for patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 32(3):679–680
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2007) Sorafenib improves survival in advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): results of a Phase III randomized placebo-controlled trials (SHARP trial). American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, Chicago
Lotan R (1997) Retinoids and chemoprevention of aerodigestive tract cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev 16(3–4):349–356
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Okuno M, Takano Y, Kojima S, Friedman SL, Moriwaki H (2003) Molecular mechanism for growth suppression of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by acyclic retinoid. Carcinogenesis 24(8):1353–1359
Matthews CP, Colburn NH, Young MR (2007) AP-1 a target for cancer prevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 7(4):317–324
Mechta-Grigoriou F, Gerald D, Yaniv M (2001) The mammalian Jun proteins: redundancy and specificity. Oncogene 20(19):2378–2389
Meyskens FL Jr, Jacobson J, Nguyen B, Weiss GR, Gandara DR, MacDonald JS (1998) Phase II trial of oral beta-all trans-retinoic acid in hepatocellular carcinoma (SWOG 9157). Invest New Drugs 16(2):171–173
Minagawa N, Nakayama Y, Inoue Y et al (2004) 4-[3, 5-Bis(trimethylsilyl) benzamido] benzoic acid inhibits angiogenesis in colon cancer through reduced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Oncol Res 14(9):407–414
Miyagawa N, Homma T, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Nagai H (2003) Effect of synthetic retinoid, TAC-101, on experimental autoimmune disease. Pharmacology 67(1):21–31
Miyaguchi T, Nomata K, Noguchi M et al (2001) TAC-101, a novel retinobenzoic-acid derivative, enhances gap junctional intercellular communication among renal epithelial cells treated with renal carcinogens. Anticancer Res 21:4025–4030
Mok TS, Leung TW, Lee SD et al (1999) A multi-centre randomized phase II study of nolatrexed versus doxorubicin in treatment of Chinese patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44(4):307–311
Murakami K, Wierzba K, Sani M et al (1998a) TAC-101, a benzoic acid derivative, inhibits liver metastasis of human gastrointestinal cancer and prolongs the life-span. Clin Exp Metastasis 16:323–331
Murakami K, Matsuura T, Sano M et al (1998b) 4-[3, 5-Bis(trimethylsilyl) benzamido] benzoic acid (TAC-101) inhibits the intrahepatic spread of hepatocellular carcinoma and prolongs the life-span of tumor-bearing animals. Clin Exp Metastasis 16(7):633–643
Murakami K, Yamaura T, Suda K et al (1999) TAC-101 (4-[3, 5-bis(trimethylsilyl) benzamido]benzoic acid) inhibits spontaneous mediastinal lymph node metastasis produced by orthotopic implantation of Lewis lung carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 90(11):1254–1261
Muto Y, Moriwaki H, Ninomiya M et al (1996) Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid, polyprenoic acid, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatoma Prevention Study Group. N Engl J Med 334(24):1561–1567
Muto Y, Moriwaki H, Saito A (1999) Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 340(13):1046–1047
Ohtani H, Yamazaki O, Matsuyama M et al (2005) Spontaneous regression of hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a case. Surg Today 35(12):1081–1086
Oikawa T (1998) Control of tumor-related angiogenesis. Hum Cell 11:201–206
Oikawa T, Murakami K, Sano M, Shibata J, Wierzba K, Yamada Y (2001) A potential use of a synthetic retinoid TAC-101 as an orally active agent that blocks angiogenesis in liver metastases of human stomach cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 92(11):1225–1234
Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Hong WK (1997) Retinoids in head and neck chemoprevention. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 216(2):283–290
Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J (1999a) Estimates of the worldwide incidence of 25 major cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer 80(6):827–841
Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J (1999b) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 49(1):33–64
Patt YZ, Hassan MM, Lozano RD et al (2005) Thalidomide in the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II trial. Cancer 103(4):749–755
Philip PA, Mahoney MR, Allmer C et al (2005) Phase II study of Erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(27):6657–6663
Posey J, Johnson P, Mok T, Hirmand M, Dahlberg S, Kwei L, Leung T (2005) Results of a phase 2/3 open-label, randomized trial of T138067 versus doxorubicin (DOX) in chemotherapy-naive, unresectable hepatocelular carcinoma (HC). 2005 ASCO Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, USA
Rizvi NA, Marshall JL, Ness E et al (2002) Initial clinical trial of oral TAC-101, a novel retinoic acid receptor-alpha selective retinoid, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 20(16):3522–3532
Sako T, Nakayama Y, Minagawa N et al (2005) 4-[3, 5-Bis(trimethylsily) benzamido] benzoic acid (TAC-101) induces apoptosis in colon cancer partially through the induction of Fas expression. In Vivo 19:125–132
Sankaranarayanan, Mathew RB (1996) Retinoids as cancer-preventive agents. IARC Sci Publ (139):47–59
Sano K, Takayama T, Murakami K, Saiki I, Makuuchi M (2003) Overexpression of retinoic acid receptor alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9(10 Pt 1):3679–3683
Satake K, Takagi E, Ishii A et al (2003) Anti-tumor effect of vitamin A and D on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 30(4):403–412
Shudo K, Kagechika H, Yamazaki N et al (2004) A synthetic retinoid Am80 (tamibarotene) rescues the memory deficit caused by scopolamine in a passive avoidance paradigm. Biol Pharm Bull 27:1887–1889
Simon R (1989) Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 10(1):1–10
Suzuki N, Aoki D, Oie S et al (2004) A novel retinoid, 4-[3, 5-bis (trimethylsilyl) venzamido] benzoic acid (TAC-101), induces apoptosis of human ocarian carcinoma cells and shows potential as a new antitumor agent for clear cell adneocarcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 94:643–649
Takai K, Okuno M, Yasuda I et al (2005) Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Updated analysis of the long-term follow-up data. Intervirology 48(1):39–45
Ventegodt S, Morad M, Hyam E, Merrick J (2004) Clinical holistic medicine: induction of spontaneous remission of cancer by recovery of the human character and the purpose of life (the life mission). Sci World J 4:362–377
Wang ZY, Sun GL, Lu JX, Gu LJ, Huang ME, Chen SR (1990) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid in China. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol 32(1):34–36
Yasuda I, Shiratori Y, Adachi S et al (2002) Acyclic retinoid induces partial differentiation, down-regulates telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression and telomerase activity, and induces apoptosis in human hepatoma-derived cell lines. J Hepatol 36(5):660–671
Yeo W, Mok TS, Zee B et al (2005) A randomized phase III study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon alpha-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 97(20):1532–1538
Yoshimura K, Uchida G, Okazaki M et al (2003) Differential expression of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) mRNA in normal human keratinocytes induced by a variety of natural and synthetic retinoids. Exp Cell Res 12(S2):28–34
Yuen MF, Wu PC, Lai VC, Lau JY, Lai CL (2001) Expression of c-Myc, c-Fos, and c-jun in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 91(1):106–112
Zhang JW, Wang JY, Chen SJ, Chen Z (2000) Mechanisms of all-trans retinoic acid-induced differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Biosci 25(3):275–284
Zhu AX, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP et al (2006) Phase II study of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in combination with bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24(12):1898–1903
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higginbotham, K.B., Lozano, R., Brown, T. et al. A phase I/II trial of TAC-101, an oral synthetic retinoid, in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134, 1325–1335 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0406-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0406-2