Abstract
Purpose
Inter individual variation in lung cancer susceptibility may be modulated in part through genetic polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes, especially the genes involved in the Base Excision Repair (BER) and nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. Two of the genetic polymorphisms, XRCC1Arg399Gln and XPD Lys751Gln have been extensively studied in the association with lung cancer risk, although published studies have been inconclusive.
Methods
In order to verify the role of the common variant alleles in the XPD gene, we have genotyped 211 lung cancer patients and 211 healthy controls using PCR-RFLP assays in a hospital based, case-control study in an Indian population. Logistic regression models were fit to examine the relationship between the log odds of lung cancer and each covariate. Overall Survival in relation to various genotypes and clinicopathological factors were analyzed using Kaplan Meier estimates and hazard ratios were calculated using Cox Regression analysis.
Results
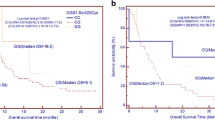
The carriers of XRCC1 399 AA genotypes were at higher risk of lung cancer (OR = 2.1, 95% CI:1.224–3.669, P = 0.007) than carriers of GG genotype. Subjects carrying 751 AC genotype were at an increased risk of carcinoma of the lung (OR = 1.8; 95% CI:1.233–2.807, P = 0.003) than subjects with AA genotypes. Compared to the XRCC1 399 GG/ XPD 751 AA reference genotype, the combined variants, XRCC1 399 GG/ XPD 751 AC+CC (OR = 1.9, 95% CI: 1.037–3.481), P = 0.03), XRCC1 399 GA+AA/ XPD 751 AA (OR = 1.7, 95% CI: 1.020–2.833, P = 0.04), XRCC1 399 GA+AA/XPD 751 AC+CC (OR = 2.7, 95% CI: 1.582–4.864, P = 0.01), had significantly higher odds ratios. Increasing numbers of either XPD or XRCC1 variant alleles were associated with shorter overall survival, the risk being significant for the XRCC1 gene polymorphism (P = 0.01 by log-rank test). The hazard of dying was significant for the XRCC1 399 AA genotype (HR = 3.04, 95%CI: 1.393–6.670, P = 0.005). Higher tumour stage also came out as significant predictors of patient death.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that genetic polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes may modulate overall lung cancer susceptibility and that pathological stage and XRCC1 Arg399Gln independently predicted overall survival among Indian lung cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman SZ, El Zein RA (2000) The 399Gln polymorphism in the DNA repair gene XRCC1 modulates the genotoxic response induced in human lymphocytes by the tobacco-specific nitrosamine NNK. Cancer Lett 159:63–71
Ahrendt AS, Hu Y, Buta M, McDermot P, Benoit N, Yang SC, Sidransky D (2003) P53 mutations and survival in stage I non small cell Lung Cancer: results of a prospective study. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:926–927
Benhamou S, Sarasin A (2000) Variability in nucleotide excision repair and cancer risk: a review. Mutat Res 462:149–158
Butkiewicz D, Rusin M, Enewold L, Shields PG, Chorazy M, Harris CC (2001) Genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair genes and risk of lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 22:593–597
Caldecott KW (2003) XRCC1 and DNA strand break repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 2:955–969
Casse C, Hu YC, Ahrendt SA (2003) The XRCC1 codon 399 Gln allele is associated with adenine to guanine p53 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Mutat Res 528:19–27
Chacko P, Rajan B, Joseph T, Mathew BS, Pillai MR (2005) Polymorphisms in DNA repair gene XRCC1 and increased genetic susceptibility to breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 89:15–21
Chen S, Tang D, Xue K, Xu L, Ma G, Hsu Y, Cho SS (2002) DNA repair gene XRCC1 and XPD polymorphisms and risk of lung cancer in a Chinese population. Carcinogenesis 23:1321–1325
Coin F, Marinoni JF, Rodolfo C, Fribourg S, Pedrini AM, Egly JM (1998) Mutations in the XPD helicase gene result in XP and TTD phenotypes, preventing interaction between XPD and the p44 subunit of TFIIH. Nat Genet 20:184–188
De Ruyck K, Szaumkessel M, De Rudder I, Dehoorne A, Vral A, Claes K, Velghe A, Van Meerbeeck J, Thierens H (2007) Polymorphisms in base-excision repair and nucleotide-excision repair genes in relation to lung cancer risk. Mutat Res 631:101–110
Divine KK, Gilliland FD, Crowell RE, Stidley CA, Bocklage TJ, Cook DL, Belinsky SA (2001) The XRCC1 399 glutamine allele is a risk factor for adenocarcinoma of the lung. Mutat Res 461:273–278
Duell EJ, Wiencke JK, Cheng TJ, Varkonyi A, Zuo ZF, Ashok TD, Mark EJ, Wain JC, Christiani DC, Kelsey KT (2000) Polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and ERCC2 and biomarkers of DNA damage in human blood mononuclear cells. Carcinogenesis 21:965–971
Gao WM, Romkes M, Siegfried JM, Luketich JD, Keohavong P (2006) Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes XPD and XRCC1 and p53 mutations in lung carcinomas of never-smokers. Mol Carcinog 45:828–832
Gurubhagavatula S, Liu G, Park S, Zhou W, Su L, Wain JC, Lynch TJ, Neuberg DS, Christiani DC (2004) XPD and XRCC1 genetic polymorphisms are prognostic factors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 22:2594–2601
Helzlsouer KJ, Harris EL, Parshad R, Perry HR, Price FM, Sanford KK (1996) DNA repair proficiency: potential susceptiblity factor for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:754–755
Hoeijmakers JH, Egly JM, Vermeulen W (1996) TFIIH: a key component in multiple DNA transactions. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6:26–33
Hou SM, Falt S, Angelini S, Yang K, Nyberg F, Lambert B, Hemminki K (2002) The XPD variant alleles are associated with increased aromatic DNA adduct level and lung cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 23:599–603
Hou SM, Ryk C, Kannio A, Angelini S, Falt S, Nyberg F, Husgafvel- Pursiainen K (2003) Influence of common XPD and XRCC1 variant alleles on p53 mutations in lung tumors. Environ Mol Mutagen 41:37–42
Hu JJ, Smith TR, Miller MS (2001) Amino acid substitution variants of APE1 and XRCC1 genes associated with ionizing radiation sensitivity. Carcinogenesis 22:917–922
Hu Z, Ma H, Chen F, Wei Q, Shen H (2005) XRCC1 polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 38 case-control studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:1810–1818
Kubota Y, Nash RA, Klungland A, Schar P, Barnes DE, Lindahl T (1996) Reconstitution of DNA base excision-repair with purified human proteins: interaction between DNA polymerase beta and the XRCC1 protein. EMBO J 15:6662–6670
Leadon SA, Cooper PK (1993) Preferential repair of ionizing radiation-induced damage in the transcribed strand of an active human gene is defective in Cockayne syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10499–10503
Lehmann AR (2001) The xeroderma pigmentosum group D (XPD) gene: one gene, two functions, three diseases. Genes Dev 15:15–23
Lei YC, Hwang SJ, Chang CC, Kuo HW, Luo JC, Chang MJ, Cheng TJ (2002) Effects on sister chromatid exchange frequency of polymorphisms in DNA repair gene XRCC1 in smokers. Mutat Res 519:93–101
Lunn RM, Langlois RG, Hsieh LL, Thompson CL, Bell DA (1999) XRCC1 polymorphisms: effects on aflatoxin B1-DNA adducts and glycophorin A variant frequency. Cancer Res 59:2557–2561
Lunn RM, Helzlsouer KJ, Parshad R, Umbach DM, Harris EL, Sanford KK, Bell DA (2000) XPD polymorphisms: effects on DNA repair proficiency. Carcinogenesis 21:551–555
Masson M, Niedergang C, Schreiber V, Muller S, Menissier-de Murcia J, de Murcia G (1998) XRCC1 is specifically associated with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and negatively regulates its activity following DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 18:3563–3571
Park JY, Lee SY, Jeon HS, Bae NC, Chae SC, Joo S, Kim CH, Park JH, Kam S, Kim IS, Jung TH (2002) Polymorphism of the DNA repair gene XRCC1 and risk of primary lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:23–27
Ramachandran S, Ramadas K, Hariharan R, Rejnish KR, Radhakrishna PM (2006) Single nucleotide polymorphisms of DNA repair genes XRCC1 and XPD and its molecular mapping in Indian oral cancer. Oral Oncol 42:350–362
Ratnasinghe D, Yao SX, Tangrea JA, Qiao YL, Andersen MR, Barrett MJ, Giffen CA, Erozan Y, Tockman MS, Taylor PR (2001) Polymorphisms of the DNA repair gene XRCC1 and lung cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10:119–123
Ryu JS, Hong YC, Han HS, Lee JE, Kim S, Park YM, Kim YC, Hwang TS (2004) Association between polymorphisms of ERCC1 and XPD and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with cisplatin combination chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 44:311–316
Shall S, de Murcia G (2000) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1: what have we learned from the deficient mouse model? Mutat Res 460:1–15
Shen MR, Jones IM, Mohrenweiser H (1998) Nonconservative amino acid substitution variants exist at polymorphic frequency in DNA repair genes in healthy humans. Cancer Res 58:604–608
Smith AG, Worrillow LJ, Allan JM (2007) A common genetic variant in XPD associates with risk of 5q- and 7q-deleted acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 109:1233–1236
Spitz MR, Wu X, Wang Y, Wang LE, Shete S, Amos CI, Guo Z, Lei L, Mohrenweiser H, Wei Q (2001) Modulation of nucleotide excision repair capacity by XPD polymorphisms in lung cancer patients. Cancer Res 61:1354–1357
Spitz MR, Wei Q, Dong Q (2003) Genetic susceptibility to lung cancer: the role of DNA damage and repair. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:689–698
Sung P, Bailly V, Weber C, Thompson LH, Prakash L, Prakash S (1993) Human xeroderma pigmentosum group D gene encodes a DNA helicase. Nature 365:852–855
Tang D, Cho S, Rundle A (2002) Polymorphisms in the DNA repair enzyme XPD are associated with increased levels of PAH-DNA adducts in a case-control study of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 75:159–166
Tomescu D, Kavanagh G, Ha T, Campbell H, Melton DW (2001) Nucleotide excision repair gene XPD polymorphisms and genetic predisposition to melanoma. Carcinogenesis 22:403–408
Wei Q, Spitz MR (1997) The role of DNA repair capacity in susceptibility to lung cancer: a review. Cancer Metastasis Rev 16:295–307
Wu X, Gu J, Wu TT, Swisher SG, Liao Z, Correa AM, Liu J, Etzel CJ, Amos CI, Huang M, Chiang SS, Milas L, Hittelman WN, Ajani JA (2006) Genetic variations in radiation and chemotherapy drug action pathways predict clinical outcomes in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:3789–3798
Xing D, Tan W, Wei Q, Lin D (2002) Polymorphisms of the DNA repair gene XPD and risk of lung cancer in a Chinese population. Lung Cancer 38:123–129
Yin J, Vogel U, Ma Y, Guo L, Wang H, Qi R (2006) Polymorphism of the DNA repair gene ERCC2 Lys751Gln and risk of lung cancer in a northeastern Chinese population. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 169:27–32
Zhou W, Liu G, Miller DP (2002a) Gene-environment interaction for the ERCC2 polymorphisms and cumulative cigarette smoking exposure in lung cancer. Cancer Res 62:1377–1381
Zhou W, Liu G, Miller DP, Thurston SW, Xu LL, Wain JC, Lynch TJ, Su L, Christiani DC (2002b) Gene-environment interaction for the ERCC2 polymorphisms and cumulative cigarette smoking exposure in lung cancer. Cancer Res 62:1377–1381
Zhou W, Liu G, Miller DP, Thurston SW, Xu LL, Wain JC, Lynch TG, Su L, Christiani DC (2003a) Polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and ERCC2, smoking, and lung cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:359–365
Zhou W, Liu G, Miller DP, Thurston SW, Xu LL, Wain JC, Lynch TJ, Su L, Christiani DC (2003b) Polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and ERCC2, smoking, and lung cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:359–365
Zienolddiny S, Campa D, Lind H, Ryberg D, Skaug V, Stangeland L, Phillips DH, Canzian F, Haugen A (2006) Polymorphisms of DNA repair genes and risk of non-small cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 27:560–567
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all the participants for their contribution. We also thank the support provided by the staff members of various clinical Departments of Regional Cancer Centre, Trivandrum. This work was supported by the grants from Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India and Indian Council of Medical Research, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sreeja, L., Syamala, V.S., Syamala, V. et al. Prognostic importance of DNA repair gene polymorphisms of XRCC1 Arg399Gln and XPD Lys751Gln in lung cancer patients from India. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134, 645–652 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0328-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0328-4