Abstract
Purpose
Carboxypeptidase-M (CPM) is a membrane-bound peptidase that metabolizes peptides, and is present in pneumocytes. CPM hydrolyses the C-terminal arginine of epidermal growth factor (EGF) resulting in des-Arg53-EGF which binds to the EGF receptor (EGFR) with an equal or greater affinity than native EGF. Therefore, this study focused on the possible presence of CPM in human lung adenocarcinomas (ADC) and evaluated the relationship between CPM and EGFR by assessing the impact of expressions on patient clinical outcome.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of 110 patients who underwent resection of the primary tumour (92) or metastatic tissues (18) for treatment or diagnosis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for CPM and EGFR was made in serial sections using standard methods.
Results
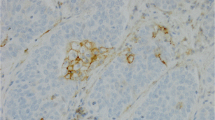
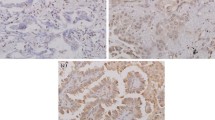
This study demonstrates for the first time that 23.6% of ADCs express carboxypeptidase-M (26/110), mainly in membrane-bound forms. The amounts and the extent of CPM within tumours vary from low levels to obviously overexpressed forms. The immunohistochemical positivity (+) for CPM in ADCs negatively correlated with disease survival. In addition, 80% of CPM+ adenocarcinomas (21/26) showed a coexpression with EGFR suggesting a high prevalence for coexistence. The follow up data indicated a significantly shorter 5-year survival time for patients with CPM+–EGFR+ (double-positive) tumours compared to those harbouring neoplasias negative for both proteins (9.5 vs. 60.4% survivals, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The fact that CPM+ ADCs often co-express with EGFR suggests a functional-regulatory link between these proteins which might have therapeutical consequences. The present novel data could lead to improved IHC tests in lung adenocarcinomas for EGFR expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco-Aparicio C, Molina MA, Fernandez-Salas E et al (1998) Potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor, a T-knot protein is an epidermal growth factor antagonist that inhibits tumor cell growth. J Biol Chem 273:12370–12377
Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B Shimosato Y (2001) Histologic typing of tumours of lung and pleura: the new World Health Organization classification of tumours. Eur Respir J 18:1059–1068
Ciardiello F (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in cancer treatment. Future Oncol 1:221–234
Cohen AJ, Skidgel RA, Gilman LB et al (1997) Carboxypeptidase M: variable expression in normal human lung and inactivation in lung cancer. Chest 11:149S
Dacic S, Flanagan M, Cieply K et al (2006) Significance of EGFR protein expression and gene amplification in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 125:860–865
Dezso B, Haas PG, Hamzavi F et al (1996) The mechanism of local tumor irradiation combined with interleukin 2 therapy in murine renal carcinoma: histological evaluation of pulmonary metastases. Clin Cancer Res 2:1543–1552
Dragovic T, Schraufnagel DE, Becker RP, Sekosan M, Votta-Velis EG, Erdős EG (1995) Carboxypeptidase M activity is increased in bronchoalveolar lavage in human lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:760–764
Erdos EG, Deddish PA (2002) The kinin system: suggestions to broaden some prevailing concepts. Int Immunopharmacol 2:1741–1746
Ferrer Soler L, Cedano J, Querol E, de Liorens R (2003) Cloning, expression and purification of human epidermal growth factor using different expression systems. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 788:113–123
Gogolak P, Rethi B, Szatmári I, Lanyi A, Dezso B, Nagy L, Rajnavolgyi E (2007) Differentiation of CD1a− and CD1a+ monocyte-derived dendritic cells is biased by lipid enviroment and PPARγ. Blood 109:641–652
Herbst RS, Prager D, Herman R et al (2005) TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:5892–5899
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA, Di Maria MV, Veve R, Bremnes RM, Baron AE, Zeng C, Franklin W (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol 21:3798–3807
Hoffman PC, Mauer AM, Vokes EE (2000) Lung cancer. Lancet 355:479–485
Hollenberg MD, Gregorz H (1980) Epidermal growth factor-urogastrone: biological activity and receptor binding of derivatives. Mol Pharmacol 17:314–320
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A (2003) Cancer statistics. CA-Cancer J Clin 53:5–26
Kelly K, Hanna N, Rosenberg A, Bunn PA, Needle MN (2003) Multicentered phase I/II study of cetuximab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in untreated patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:644–644
Leeb-Lundberg LMF, Marceau F, Müller-Esterl W, Pettibone DJ, Zuraw BJ (2005) International Union of Pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: from molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol Rev 57:27–77
Li J, Rehli M, Timblin B, Tan F, Krause SW, Skidgel RA (2002) Structure of the human carboxypeptidase M gene. Identification of a proximal GC-rich promoter and a unique distal promoter that consists of repetitive elements. Gene 284:189–202
Maione P, Gridelli C, Troiani T, Ciardiello F (2006) Combining targeted therapies and drugs with multiple targets in the treatment of NSCLC. Oncologist 11:274–284
Massarelli E, Herbst RS (2006) A novel second-line targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Oncol 33(S1):9–16
McGwire GB, Skidgel RA (1995) Extracellular conversion of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to des-Arg53-EGF by carboxypeptidase M. J Biol Chem 270:17154–17158
McGwire GB, Becker RP, Skidgel RA (1999) Carboxypeptidase M, a glycosylphos-phatidylinositol-anchored protein, is localized on both the apical and the basolateral domains of polarized Madin-Darby Canine Kidney cells. J Biol Chem 274:31632–31640
Meert AP, Martin B, Delmotte P et al (2001) The role of EGF-R expression on patient survival in lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 20:975–981
Morgillo F, Lee H-Y (2005) Resistence to epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy. Drug Resist Updat 8:298–310
Mountain CF (1997) Revisions in the international system for staging lung cancer. Chest 111:1710–1717
Nagae A, Abe M, Becker RP, Deddish PA, Skidgel RA, Erdös EG (1993) High concentration of carboxypeptidase M in lungs: presence of the enzyme in alveolar type I cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 9:221–229
Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME (2001) EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer 37/4:S9–S15
Niemiec J, Kolodziejski L, Dyczek S (2005) EGFR LI and Ki-67 LI are independent prognostic parameters influencing survivals of surgically treated squamous cell lung cancer patients. Neoplasma 52:231–237
Normanno N, De Luca A, Bianco C, Strizzi L, Mancino M, Maiello M et al (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signalling in cancer. Gene 366:2–16
Ohsaki Y, Tanno S, Fujita Y et al (2000) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with p53 overexpression. Oncol Rep 7:603–607
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J et al (2004) EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smoker” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13306–13311
Parries G, Chen K, Misono KS, Cohen S (1995) The human urinary epidermal growth factor (EGF) precursor. J Biol Chem 270:27954–27960
Pessoa LG, da Silva ID, Baptista HA, Pesquero JL, Paiva AC, Bader M, Pesquero JB (2002) Molecular structure and alternative splicing of the human carboxypeptidase M gene. Biol Chem 383:263–269
Rao RK, Koldovski O, Kore M, Pollack PF, Wright S, Davis TP (1990) Processing and transfer of epidermal growth factor in developing jejunum and ileum. Peptides 11:1093–1102
Renfrew CA, Hubbard AL (1991) Sequential processing of epidermal growth factor in early and late endosomes of rat liver. J Biol Chem 266:4348–4356
Reverter D, Maskos K, Tan F, Skidgel RA, Bode W (2004) Crystal structure of human carboxypeptidase M, a membrane-bound enzyme that regulates peptide hormone activity. J Mol Biol 338:257–269
Rusch V, Klimstra D, Venkatraman E et al (1997) Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligand transforming growth factor alpha is frequent in resectable non-small cell lung cancer but does not predict tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 3:515–522
Sasaki H, Shimizu S, Endo K et al (2006) EGFR and erB2 mutation status in Japanese lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer 118:180–184
Schaudies RP, Savage CR (1986) Intracellular modification of 125I-labeled epidermal growth factor by normal human foreskin fibroblasts. Endocrinology 118:875–882
Selvaggi G, Novello S, Torri V, Leonardo E, De Giuli P, Borasio P, Mossetti C, Ardissone F, Lausi P, Scagliotti GV (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression correlates with a poor prognosis in completely resected non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 15:28–32
Sitja-Arnau M, Molina MA, Blanco-Aparicio C et al (2005) Mechanism of action of potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor (PCI) as an EGF blocker. Cancer Lett 26:169–184
Skidgel RA, Erdős EG (1998) Cellular carboxypeptidases. Immunol Rev 161:129–141
Skidgel RA, Davis RM, Tan F (1989) Human carboxypeptidase M. Purification and characterization of a membrane-bound carboxypeptidase that cleaves peptide hormones. J Biol Chem 264:2236–2241
Skidgel RA, McGwire GB, Li XY (1996) Membrane anchoring and release of carboxypeptidase M: implications for extracellular hydrolysis of peptide hormones. Immunopharmacology 32:48–52
Skidgel RA, Stanisavljevic S, Erdös EG (2006) Kinin- and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor-mediated nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. Biol Chem 387:159–165
Sonnweber B, Diaska M, Skvortsov S et al (2006) High predictive value of epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation but not of EGFRvIII mutation in resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Pathol 59:255–259
Sporn MB, Robert AB (1985) Autocrine growth factors and cancer. Nature 313:745–747
Suzuki M, Shigematsu H, Lizasa T et al (2006) Exclusive mutation in epidermal growth factor receptor gene, HER-2, and KRAS, and synchronous methylation of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 106:2200–2207
Szatmari I, Gogolak P, Im SJ, Dezso B et al (2004) Activation of PPARγ specifies a dendritic cell subtype capable of enhaced induction of iNKT cell expansion. Immunity 21:95–106
Szatmari I, Pap A, Rühl R, Ma JX, Rajnavolgyi E, Dezso B, Nagy L (2006) PPAR-gamma controls CD1d expression by turning on retionic acid synthesis in developing human dendritic cell. J Exp Med 203:2351–2362
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Drs. Ervin G. Erdös and Randal A. Skidgel (University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA) for suggestions and comments on the manuscript. The authors acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Maria Besenyei. This work was supported by Feichtinger’s cancer foundation (Balazs Dezso) and the university research fund for Ph.D. program (Ioannis Tsakiris). A part of the morphological aspects of CPM immunostainings on lung cancers was presented (Balazs Dezso) at the 65th Annual Congress of the Hungarian Society of Pathologists held in Hajduszoboszlo (Hungary), 5–7 October, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsakiris, I., Soos, G., Nemes, Z. et al. The presence of carboxypeptidase-M in tumour cells signifies epidermal growth factor receptor expression in lung adenocarcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134, 439–451 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0304-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0304-z