Abstract
Object
To investigate the influence of different microenvironments on tumor microcirculation patterns and invasiveness capability.
Methods
Melanoma B16 cells were injected into the abdominal cavity and skeletal muscle of C57 mice synchronously. CK-18 expression in melanoma was assessed to distinguish the malignant phenotype of tumors in the abdominal cavity from that in the skeletal muscle. HIF-1α, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and mRNA levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 was detected to compare the mRNA levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 from the two microenvironments. Cells positive for each immunohistochemical stain and the vessels representative of each type of microcirculation pattern were counted in two microenvironments.
Results
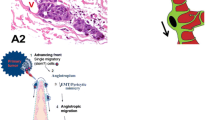
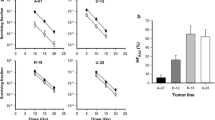
CK-18 and HIF-1α expression of melanoma were significantly higher in the skeletal muscle than in the abdominal cavity (P < 0.05). Compared with the abdominal cavity, melanoma cells in the skeletal muscle overexpressed MMP-2 and MMP-9 (P < 0.05). Real time-PCR results also showed that MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA levels of melanoma were higher in the skeletal muscle than in the abdominal cavity (P < 0.05). VM channels and endothelium-dependent vessels were the major microcirculation pattern in the skeletal muscle and in the abdominal cavity, respectively.
Conclusion
Different microenvironments affect invasiveness and blood supply patterns of melanoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Baruch A (2003) Host microenvironment in breast cancer development: inflammatory cells, cytokines and chemokines in breast cancer progression: reciprocal tumor-microenvironment interactions. Breast Cancer Res 5:31–36
Biju MP, Akai Y, Shrimanker N, Haase VH (2005) Protection of HIF-1-deficient primary renal tubular epithelial cells from hypoxia-induced cell death is glucose dependent. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1217–F1226
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Dai J, Keller J, Zhang J, Lu Y, Yao Z, Keller ET (2005) Bone morphogenetic protein-6 promotes osteoblastic prostate cancer bone metastases through a dual mechanism. Cancer Res 65:8274–8285
Dong D, Ko B, Baumeister P, Swenson S, Costa F, Markland F, Stiles C, Patterson JB, Bates SE, Lee AS (2005) Vascular targeting and antiangiogenesis agents induce drug resistance effector GRP78 within the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 65:5785–5791
Folberg R, Hendrix MJ, Maniotis AJ (2000) Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 156:361–381
Gutt CN, Kim ZG, Schemmer P, Krahenbuhl L, Schmedt CG (2002) Impact of laparoscopic and conventional surgery on Kupffer cells, tumor-associated CD44 expression, and intrahepatic tumor spread. Arch Surg 137:1408–1412
Hess AR, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Hendrix MJ (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates membrane Type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and MMP-2 activity during melanoma cell vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Res 63:4757–4762
Hess AR, Postovit LM, Margaryan NV (2005) Focal adhesion kinase promotes the aggressive melanoma phenotype. Cancer Res 65:9851–9860
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Kirschmann DA, Quaranta V, Seftor RE (2003) Remodeling of the microenvironment by aggressive melanoma tumor cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 995:151–161
Ishida H, Hashimoto D, Nakada H, Takeuchi I, Hoshino T, Murata N, Idezuki Y, Hosono M (2002) Increased insufflation pressure enhances the development of liver metastasis in a mouse laparoscopy model: possible mechanisms. Surg Endosc 16:331–335
Jacobi CA, Ordemann J, Zieren HU, Muller JM (1998) Effect of intra-abdominal pressure in laparoscopy on intraperitoneal tumor growth and development of trocar metastases. An animal experiment study in the rat model. Langenbecks Arch Chir Suppl Kongressbd 115:529–533
Jain RK (2001) Delivery of molecular medicine to solid tumors: lessons from in vivo imaging of gene expression and function. J Control Release 74:7–25
Jiang ZQ, Zhu FC, Qu JY, Zheng X, You CL (2003) Relationship between expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) and tumor angiogenesis, cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis in invasive carcinoma of cervix. Ai Zheng 22:178–184
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Ang LS, Sundaresan A (2006) Hypoxic damage to the periventricular white matter in neonatal brain: role of vascular endothelial growth factor, nitric oxide and excitotoxicity. J Neurochem 98:1200–1216
Karlsen TV, Karkkainen MJ, Alitalo K, Wiig H (2006) Transcapillary fluid balance consequences of missing initial lymphatics studied in a mouse model of primary lymphoedema. J Physiol 574:583–596
Kim SJ, Rabbani ZN, Dewhirst MW, Vujaskovic Z, Vollmer RT, Schreiber EG, Oosterwijk E, Kelley MJ (2005) Expression of HIF-1alpha, CA IX, VEGF, and MMP-9 in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 49:325–335
Krishnamachary B, Berg-Dixon S, Kelly B, Kelly B, Agani F, Feldser D, Ferreira G, Iyer N, LaRusch J, Pak B, Taghavi P, Semenza GL (2003) Regulation of colon carcinoma cell invasion by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cancer Res 63:1138–1143
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH, Kim KW (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med 36:1–12
Leo C, Giaccia AJ, Denko NC (2004) The hypoxic tumor microenvironment and gene expression. Semin Radiat Oncol 14:207–214
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA, Gardner LM, Pe’er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS, Hendrix MJ (1999) Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol 155:739–752
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, Nicholls LG, Harris AL, Stratford IJ, Hankinson O, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (1997) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8104–8109
Milkiewicz M, Haas TL (2005) Effect of mechanical stretch on HIF-1{alpha} and MMP-2 expression in capillaries isolated from overloaded skeletal muscles: laser capture microdissection study. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H1315–H1320
Milosevic MF, Fyles AW, Wong R, Pintilie M, Kavanagh MC, Levin W, Manchul LA, Keane TJ, Hill RP (1998) Interstitial fluid pressure in cervical carcinoma: within tumor heterogeneity, and relation to oxygen tension. Cancer 82:2418–2426
Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Ide T, Ohtaka K, Nagasawa H, Uto Y, Hori H, Miyazaki K (2006) Hypoxia accelerates cancer invasion of hepatoma cells by upregulating MMP expression in an HIF-1alpha-independent manner. Int J Oncol 29:1533–1539
Munoz-Najar UM, Neurath KM, Vumbaca F, Claffey KP (2006) Hypoxia stimulates breast carcinoma cell invasion through MT1-MMP and MMP-2 activation. Oncogene 25:2379–2392
Nguyen QD, De Wever O, Bruyneel E, Hendrix A, Xie WZ, Lombet A, Leibl M, Mareel M, Gieseler F, Bracke M, Gespach C (2005) Commutators of PAR-1 signaling in cancer cell invasion reveal an essential role of the Rho-Rho kinase axis and tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 24:8240–8251
Pietras K, Ostman A, Sjoquist M, Buchdunger E, Reed RK, Heldin CH, Rubin K (2001) Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptors reduces interstitial hypertension and increases transcapillary transport in tumors. Cancer Res 61:2929–2934
Rofstad EK, Tunheim SH, Mathiesen B, Graff BA, Halsor EF, Nilsen K, Galappathi K (2002) Pulmonary and lymph node metastasis is associated with primary tumor interstitial fluid pressure in human melanoma xenografts. Cancer Res 62:661–664
Salnikov AV, Iversen VV, Koisti M, Sundberg C, Johansson L, Stuhr LB, Sjoquist M, Ahlstrom H, Reed RK, Rubin K (2003) Lowering of tumor interstitial fluid pressure specifically augments efficacy of chemotherapy. FASEB J 17:1756–1758
Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Koshikawa N, Meltzer PS, Gardner LM, Bilban M, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Quaranta V, Hendrix MJ (2001) Cooperative interactions of laminin 5 gamma2 chain, matrix metalloproteinase-2, and membrane type-1-matrix/metalloproteinase are required for mimicry of embryonic vasculogenesis by aggressive melanoma. Cancer Res 61:6322–6327
Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Kirschmann DA, Hendrix MJ (2002) Targeting the tumor microenvironment with chemically modified tetracyclines: inhibition of laminin 5 gamma2 chain promigratory fragments and vasculogenic mimicry. Mol Cancer Ther 1:1173–1179
Semenza GL (2000) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: mechanisms and consequences. Biochem Pharmacol 59:47–53
Shams I, Avivi A, Nevo E (2004) Hypoxic stress tolerance of the blind subterranean mole rat: expression of erythropoietin and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9698–9703
Zhang S, Zhang D, Sun B (2007) Vasculogenic mimicry: current status and future prospects. Cancer Lett 14 (Epub ahead of print)
Sun B, Zhang S, Zhang D, Du J, Guo H, Zhao X, Zhang W, Hao X (2006) Vasculogenic mimicry is associated with high tumor grade, invasion and metastasis, and short survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 16:693–698
Sun B, Zhang D, Zhang S, Zhang W, Guo H, Zhao X (2007) Hypoxia influences vasculogenic mimicry channel formation and tumor invasion-related protein expression in melanoma. Cancer Lett 249:188–197
Van de Broek I, Leleu X, Schots R, Facon T, Vanderkerken K, Van Camp B, Van Riet I (2006) Clinical significance of chemokine receptor (CCR1, CCR2 and CXCR4) expression in human myeloma cells: the association with disease activity and survival. Haematologica 91:200–206
Vordermark D, Brown JM (2003) Evaluation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) as an intrinsic marker of tumor hypoxia in U87 MG human glioblastoma: in vitro and xenograft studies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:1184–1193
Yagmurdur MC, Basaran O, Ozdemir H, Gur G, Tran M, Karakayali H, Haberal M (2004) The impact of transient elevation of intra-abdominal pressure on liver regeneration in the rat. J Invest Surg 17:315–322
Zhang Y, Wu XH, Cao GH, Li S (2004) Relationship between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and angiogenesis in renal cell carcinoma. Ai Zheng 23:326–329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Baocun Sun, Shiwu Zhang and Danfang Zhang are equally contributed for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, B., Zhang, S., Zhang, D. et al. The influence of different microenvironments on melanoma invasiveness and microcirculation patterns: an animal experiment study in the mouse model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133, 979–985 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0245-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0245-6