Abstract
Purpose
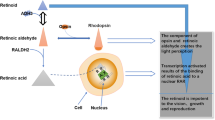
Acyclic retinoid (ACR) has been shown to be a promising chemopreventive agent for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after curative resection. The effects of retinoid are mediated by retinol-binding proteins (RBPs) through regulating cell proliferation and differentiation.
Patients and methods
This study investigated the clinical significance of RBP5 in HCC. RBP5 mRNA level was examined by real-time quantitative PCR on 52 matched tumor and adjacent non-tumor liver tissues, and on ten normal livers. Expression of RBP5 protein was examined using Western blotting analysis and immunohistochemistry.
Results
Down-regulation of RBP5 was found in HCC tissues at both mRNA and protein levels. Decreased RBP5 level was closely related to poor differentiation (P = 0.02) and large tumor size (P = 0.01). Low level of RPB5 was associated with poor overall survival (P = 0.02), and was an independent prognostic factor for HCC.
Conclusions
Our study revealed that RBP5 down-regulation in HCC was associated with aggressive tumor features, suggesting an important role of RPB5 in HCC progression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu J, Batuwangala M, Herbert K, Symonds P (2005) Retinoic acid and retinoid receptors: potential chemopreventive and therapeutic role in cervical cancer. Lancet Oncol 6:712–720
Ades L, Chevret S, De Botton S, Thomas X, Dombret H, Beve B, Sanz M, Guerci A, Miguel JS, Dela Serna J, Garo C, Stoppa AM, Reman O, Stamatoulas A, Fey M, Cahn JY, Sotto JJ, Bourhis JH, Parry A, Chomienne C, Degos L, Fenaux P (2005) Outcome of acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all trans retinoic acid and chemotherapy in elderly patients: the European group experience. Leukemia 19:230–233
Baba M, Iishi H, Yamamoto R, Tatsuta M (1991) Inhibition by retinoic acid of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N-nitrosomorpholine and of expression of myc oncogene protein in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Cancer 49:467–470
Brabender J, Metzger R, Salonga D, Danenberg KD, Danenberg PV, Holscher AH, Schneider PM (2005) Comprehensive expression analysis of retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors in non-small cell lung cancer: implications for tumor development and prognosis. Carcinogenesis 26:525–530
Chambon P (1996) A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J 10:940–954
Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, Fan ST, Barry C, Higgins J, Lai KM, Ji J, Dudoit S, Ng IO, Van De Rijn M, Botstein D, Brown PO (2002) Gene expression patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell 13:1929–1939
Chen YJ, Yeh SH, Chen JT, Wu CC, Hsu MT, Tsai SF, Chen PJ, Lin CH (2000) Chromosomal changes and clonality relationship between primary and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 119:431–440
Cheung ST, Ho JC, Leung KL, Chen X, Fong DY, So S, Fan ST (2005) Transcript AA454543 is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma after curative partial hepatectomy. Neoplasia 7:91–98
Cheung ST, Liu CL, Chow JPH, Lee YT, Ip YC, Ho JC, Fan ST (2006) Preoperative plasma transcript AA454543 level is an independent prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma after partial hepatectomy. Neoplasia 8:696–701
Cheung ST, Wong SY, Leung KL, Chen X, So S, Ng IO, Fan ST (2004) Granulin-epithelin precursor overexpression promotes growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:7629–7636
Cvetkovic D, Williams SJ, Hamilton TC (2003) Loss of cellular retinol-binding protein 1 gene expression in microdissected human ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:1013–1020
El-Metwally TH, Hussein MR, Pour PM, Kuszynski CA, Adrian TE (2005) High concentrations of retinoids induce differentiation and late apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Biol Ther 4:602–611
Farias EF, Marzan C, Mira-y-Lopez R (2005a) Cellular retinol-binding protein-I inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling through a retinoic acid receptor-dependent mechanism that regulates p85-p110 heterodimerization. Oncogene 24:1598–1606
Farias EF, Ong DE, Ghyselinck NB, Nakajo S, Kuppumbatti YS, Mira y Lopez R (2005b) Cellular retinol-binding protein I, a regulator of breast epithelial retinoic acid receptor activity, cell differentiation, and tumorigenicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:21–29
Fiore P, Castagnola E, Marchese N, Dufour C, Garaventa A, Mangraviti S, Cornaglia-Ferraris P (1997) Retinol (vitamin A) and retinal-binding protein serum levels in children with cancer at onset. Nutrition 13:17–20
Folli C, Calderone V, Ottonello S, Bolchi A, Zanotti G, Stoppini M, Berni R (2001) Identification, retinoid binding, and x-ray analysis of a human retinol-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:3710–3715
Ghyselinck NB, Bavik C, Sapin V, Mark M, Bonnier D, Hindelang C, Dierich A, Nilsson CB, Hakansson H, Sauvant P, Azais-Braesco V, Frasson M, Picaud S, Chambon P (1999) Cellular retinol-binding protein I is essential for vitamin A homeostasis. EMBO J 18:4903–4914
Ho JC, Cheung ST, Patil M, Chen X, Fan ST (2006) Increased expression of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor attachment protein 1 (GPAA1) is associated with gene amplification in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 119:1330–1337
Hong WK, Lippman SM, Itri LM, Karp DD, Lee JS, Byers RM, Schantz SP, Kramer AM, Lotan R, Peters LJ et al (1990) Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 323:795–801
Kojima S, Okuno M, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Friedman SL, Moriwaki H (2004) Acyclic retinoid in the chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma (review). Int J Oncol 24:797–805
Kraemer KH, DiGiovanna JJ, Moshell AN, Tarone RE, Peck GL (1988) Prevention of skin cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum with the use of oral isotretinoin. N Engl J Med 318:1633–1637
Kuppumbatti YS, Bleiweiss IJ, Mandeli JP, Waxman S, Mira-Y-Lopez R (2000) Cellular retinol-binding protein expression and breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:475–480
Kuppumbatti YS, Rexer B, Nakajo S, Nakaya K, Mira-y-Lopez R (2001) CRBP suppresses breast cancer cell survival and anchorage-independent growth. Oncogene 20:7413–7419
Kurie JM, Lotan R, Lee JJ, Lee JS, Morice RC, Liu DD, Xu XC, Khuri FR, Ro JY, Hittelman WN, Walsh GL, Roth JA, Minna JD, Hong WK (2003) Treatment of former smokers with 9-cis-retinoic acid reverses loss of retinoic acid receptor-beta expression in the bronchial epithelium: results from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:206–214
Muto Y, Moriwaki H, Ninomiya M, Adachi S, Saito A, Takasaki KT, Tanaka T, Tsurumi K, Okuno M, Tomita E, Nakamura T, Kojima T (1996) Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid, polyprenoic acid, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatoma Prevention Study Group. N Engl J Med 334:1561–1567
Muto Y, Moriwaki H, Saito A (1999) Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 340:1046–1047
Napoli JL (1997) Retinoid binding-proteins redirect retinoid metabolism: biosynthesis and metabolism of retinoic acid. Semin Cell Dev Biol 8:403–415
Ng IO, Lai EC, Fan ST, Ng MM, So MK (1995) Prognostic significance of pathologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma. A multivariate analysis of 278 patients. Cancer 76:2443–2448
Pfahl M, Chytil F (1996) Regulation of metabolism by retinoic acid and its nuclear receptors. Annu Rev Nutr 16:257–283
Poon RT, Fan ST (2003) Evaluation of the new AJCC/UICC staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection in Chinese patients. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 12:35–50
Quadro L, Hamberger L, Colantuoni V, Gottesman ME, Blaner WS (2003) Understanding the physiological role of retinol-binding protein in vitamin A metabolism using transgenic and knockout mouse models. Mol Aspects Med 24:421–430
Reynolds CP, Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Maurer BJ (2003) Retinoid therapy of high-risk neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett 197:185–192
Roberts D, Williams SJ, Cvetkovic D, Weinstein JK, Godwin AK, Johnson SW, Hamilton TC (2002) Decreased expression of retinol-binding proteins is associated with malignant transformation of the ovarian surface epithelium. DNA Cell Biol 21:11–19
Schmitt-Graff A, Ertelt V, Allgaier HP, Koelble K, Olschewski M, Nitschke R, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G, Blum HE (2003) Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with beta-catenin, Ki-67 index, and patient survival. Hepatology 38:470–480
Sobin LH, Whitekind C (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Suzui M, Masuda M, Lim JT, Albanese C, Pestell RG, Weinstein IB (2002) Growth inhibition of human hepatoma cells by acyclic retinoid is associated with induction of p21(CIP1) and inhibition of expression of cyclin D1. Cancer Res 62:3997–4006
Takai K, Okuno M, Yasuda I, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Uematsu T, Tsurumi H, Shiratori Y, Muto Y, Moriwaki H (2005) Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Updated analysis of the long-term follow-up data. Intervirology 48:39–45
Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Miller WH Jr, Scheinberg DA, Itri LM, Hittelman WN, Vyas R, Andreeff M, Tafuri A, Jakubowski A et al (1991) Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). N Engl J Med 324:1385–1393
Yasuda I, Shiratori Y, Adachi S, Obora A, Takemura M, Okuno M, Shidoji Y, Seishima M, Muto Y, Moriwaki H (2002) Acyclic retinoid induces partial differentiation, down-regulates telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression and telomerase activity, and induces apoptosis in human hepatoma-derived cell lines. J Hepatol 36:660–667
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the grants from the Sun Chieh Yeh Research Foundation for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, and Seed Funding Program of the University of Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, J.C.Y., Cheung, S.T., Poon, W.S. et al. Down-regulation of retinol binding protein 5 is associated with aggressive tumor features in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133, 929–936 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0230-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0230-0