Abstract
Purpose
Aromatase catalyzes the conversion of androgens to estrogens; its high expression in breast cancers may be responsible for the local high levels of estrogen and may promote tumor growth and progression; however, the clinical importance of aromatase remains unclear and needs to be further researched.
Methods
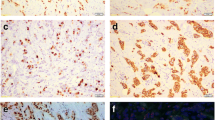
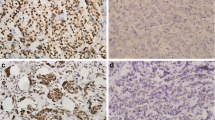
By immunochemistry, we detected aromatase, MMP2 and MMP9 immunoreactivity in 244 axillary lymph node negative breast cancers.
Results
Aromatase immunoreactivity was positively associated with co-expression of MMP2 and MMP9 (MMP2/9) in the estrogen receptor and/or progestin receptor- (ER/PR) positive patients (P < 0.05), but not in the ER and PR negative patients (P > 0.05); aromatase status positively associated with tumor size in the postmenopausal patients (P < 0.05) but not in the premenopausal patients (P > 0.05). The proportional hazards assumption was violated for aromatase status (global test, P < 0.05), and aromatase was an unfavorable prognostic factor for disease-free survival (DFS) (P = 0.04) in multivariate analysis of time-dependent non-proportional Cox regression. In the ER/PR-positive patients, positive aromatase staining was significantly associated with decreased overall survival (OS) (P = 0.04), but there was no such association in the ER and PR negative patients (P > 0.05).
Conclusions
Our study suggested that local estrogen production by aromatase plays important roles in the growth and invasiveness of breast cancer; tumor aromatase status may be indicative of breast cancer prognosis in some patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas Abidi SM, Howard EW, Dmytryk JJ, Pento JT (1997) Differential influence of antiestrogens on the in vitro release of gelatinases (type IV collagenases) by invasive and non-invasive breast cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 15:432–439
Bolufer P, Ricart E, Lluch A, Vazquez C, Rodriguez A, Ruiz A, Llopis F, Garcia-Conde J, Romero R (1992) Aromatase activity and estradiol in human breast cancer: its relationship to estradiol and epidermal growth factor receptors and to tumor-node-metastasis staging. J Clin Oncol 10:438–446
Brodie A, Long B, Lu Q (1998) Aromatase expression in the human breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 49(Suppl 1):S85–S91, discussion S109–S119
Brodie A, Lu Q, Long B (1999) Aromatase and its inhibitors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 69:205–210
Brodie A, Lu Q, Nakamura J (1997) Aromatase in the normal breast and breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 61:281–286
Brodie AH, Mouridsen HT (2003) Applicability of the intratumor aromatase preclinical model to predict clinical trial results with endocrine therapy. Am J Clin Oncol 26:S17–S26
Brodie AM, Lu Q, Long BJ, Fulton A, Chen T, Macpherson N, DeJong PC, Blankenstein MA, Nortier JW, Slee PH, van de Ven J, van Gorp JM, Elbers JR, Schipper ME, Blijham GH, Thijssen JH (2001) Aromatase and COX-2 expression in human breast cancers. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 79:41–47
Buzdar AU (2003) Advances in endocrine treatments for postmenopausal women with metastatic and early breast cancer. Oncologist 8:335–341
Dowsett M, Detre S, Rowlands M, Grimshaw R (1996) Oestrogen formation in breast: clinical and biological importance. J Endocrinol 150:S59–S63
Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, McDermott E, O’Higgins N (2000) Metalloproteinases: role in breast carcinogenesis, invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 2:252–257
Ellis MJ, Hayes DF, Lippman ME (2004) Treatment of metastastatic breast cancer In: Harris Jr, Lippmen Me, Morrow M, Osborne Ck (eds) Disease of the breast. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadephia, pp 1101–1159
Elston CW, Ellis IO (2002) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. C. W. Elston & I. O. Ellis. Histopathology 1991; 19:403–410. Histopathology 41:151
Eppenberger U, Levano S, Schoumacher F, Muller H, Eppenberger-Castori S (2001) Molecular epidemiology of aromatase expression in 1182 primary breast cancers. In: Miller W, Santen R (eds) Aromatase inhibition and breast cancer. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 199–212
Esteban JM, Warsi Z, Haniu M, Hall P, Shively JE, Chen S (1992) Detection of intratumoral aromatase in breast carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study with clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Pathol 140:337–343
Evans TR, Rowlands MG, Silva MC, Law M, Coombes RC (1993) Prognostic significance of aromatase and estrone sulfatase enzymes in human breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 44:583–587
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Speizer FE (1998) Plasma sex steroid hormone levels and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1292–1299
Hilsenbeck SG, Ravdin PM, de Moor CA, Chamness GC, Osborne CK, Clark GM (1998) Time-dependence of hazard ratios for prognostic factors in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 52:227–237
Hirvonen R, Talvensaari-Mattila A, Paakko P, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T (2003) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in T(1-2) no breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 77:85–91
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin–biotin–peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Iwata H, Kobayashi S, Iwase H, Masaoka A, Fujimoto N, Okada Y (1996) Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human breast carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 87:602–611
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam A, Dorgan JF, Longcope C, Stanczyk FZ, Stephenson HE Jr, Falk RT, Miller R, Schatzkin A, Allen DS, Fentiman IS, Key TJ, Wang DY, Dowsett M, Thomas HV, Hankinson SE, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, Koenig K, Shore RE, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Berrino F, Muti P, Micheli A, Krogh V, Sieri S, Pala V, Venturelli E, Secreto G, Barrett-Connor E, Laughlin GA, Kabuto M, Akiba S, Stevens RG, Neriishi K, Land CE, Cauley JA, Kuller LH, Cummings SR, Helzlsouer KJ, Alberg AJ, Bush TL, Comstock GW, Gordon GB, Miller SR, Longcope C (2003) Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:1218–1226
Kinoshita Y, Chen S (2003) Induction of aromatase (CYP19) expression in breast cancer cells through a nongenomic action of estrogen receptor alpha. Cancer Res 63:3546–3555
Kirma N, Gill K, Mandava U, Tekmal RR (2001) Overexpression of aromatase leads to hyperplasia and changes in the expression of genes involved in apoptosis, cell cycle, growth, and tumor suppressor functions in the mammary glands of transgenic mice. Cancer Res 61:1910–1918
Koyama H, Iwata H, Kuwabara Y, Iwase H, Kobayashi S, Fujii Y (2000) Gelatinolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and–9 in oesophageal carcinoma; a study using in situ zymography. Eur J Cancer 36:2164–2170
Kute TE, Shao ZM, Sugg NK, Long RT, Russell GB, Case LD (1992) Cathepsin D as a prognostic indicator for node-negative breast cancer patients using both immunoassays and enzymatic assays. Cancer Res 52:5198–5203
Lu Q, Nakmura J, Savinov A, Yue W, Weisz J, Dabbs DJ, Wolz G, Brodie A (1996) Expression of aromatase protein and messenger ribonucleic acid in tumor epithelial cells and evidence of functional significance of locally produced estrogen in human breast cancers. Endocrinology 137:3061–3068
Mandava U, Kirma N, Tekmal RR (2001) Aromatase overexpression transgenic mice model: cell type specific expression and use of letrozole to abrogate mammary hyperplasia without affecting normal physiology. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 79:27–34
Missmer SA, Eliassen AH, Barbieri RL, Hankinson SE (2004) Endogenous estrogen, androgen, and progesterone concentrations and breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1856–1865
Mitropoulou TN, Tzanakakis GN, Kletsas D, Kalofonos HP, Karamanos NK (2003) Letrozole as a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation and expression of metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) by human epithelial breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 104:155–160
Miyoshi Y, Ando A, Hasegawa S, Ishitobi M, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S (2003) High expression of steroid sulfatase mRNA predicts poor prognosis in patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:2288–2293
Pacheco MM, Nishimoto IN, Mourao Neto M, Mantovani EB, Brentani MM (2001) Prognostic significance of the combined expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9, urokinase type plasminogen activator and its receptor in breast cancer as measured by Northern blot analysis. Int J Biol Markers 16:62–68
Pasqualini JR, Chetrite G, Blacker C, Feinstein MC, Delalonde L, Talbi M, Maloche C (1996) Concentrations of estrone, estradiol, and estrone sulfate and evaluation of sulfatase and aromatase activities in pre–and postmenopausal breast cancer patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:1460–1464
Pasqualini JR, Chetrite GS (2005) Recent insight on the control of enzymes involved in estrogen formation and transformation in human breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 93:221–236
Sasano H, Suzuki T, Moriya T (2001) Immunohistochemistry of aromatase: a recent new development. In: Miller W, Santen R (eds) Aromatase inhibition and breast cancer. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 191–198
Shenton KC, Dowsett M, Lu Q, Brodie A, Sasano H, Sacks NP, Rowlands MG (1998) Comparison of biochemical aromatase activity with aromatase immunohistochemistry in human breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 49(Suppl 1):S101–S107, discussion S109–S119
Silva MC, Rowlands MG, Dowsett M, Gusterson B, McKinna JA, Fryatt I, Coombes RC (1989) Intratumoral aromatase as a prognostic factor in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 49:2588–2591
Talvensaari-Mattila A, Paakko P, Hoyhtya M, Blanco-Sequeiros G, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T (1998) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 immunoreactive protein: a marker of aggressiveness in breast carcinoma. Cancer 83:1153–1162
Tekmal RR, Ramachandra N, Gubba S, Durgam VR, Mantione J, Toda K, Shizuta Y, Dillehay DL (1996) Overexpression of int-5/aromatase in mammary glands of transgenic mice results in the induction of hyperplasia and nuclear abnormalities. Cancer Res 56:3180–3185
Turner KJ, Macpherson S, Millar MR, McNeilly AS, Williams K, Cranfield M, Groome NP, Sharpe RM, Fraser HM, Saunders PT (2002) Development and validation of a new monoclonal antibody to mammalian aromatase. J Endocrinol 172:21–30
van Landeghem AA, Poortman J, Nabuurs M, Thijssen JH (1985) Endogenous concentration and subcellular distribution of estrogens in normal and malignant human breast tissue. Cancer Res 45:2900–2906
Wolczynski S, Surazynski A, Swiatecka J, Palka J (2001) Estrogenic and antiestrogenic effects of raloxifene on collagen metabolism in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Gynecol Endocrinol 15:225–233
Zhou C, Zhou D, Esteban J, Murai J, Siiteri PK, Wilczynski S, Chen S (1996) Aromatase gene expression and its exon I usage in human breast tumors. Detection of aromatase messenger RNA by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 59:163–171
Acknowledgments
Funded by Outstanding Young Investigator Award of National Natural Science Foundation of China (30025015), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China (32R14021) and Science Research Foundation for Youths of Fudan University, Shanghai, China (EXF000312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Li, H., Cao, D. et al. Clinical significance of aromatase protein expression in axillary node negative breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133, 401–409 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0186-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0186-5