Abstract
Purpose
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) remains a clinical challenge because of the high rate of locoregional disease recurrence. Standard treatment includes surgery, radiation, chemoradiation or a combination of these approaches. New therapies are needed to achieve improved survival, quality of life and organ function in these patients. A novel molecular targeted therapy incorporated into our current treatment strategies may have a significant role in the treatment of HNSCC. The aim of this study was to evaluate the sensitivity of HNSCC cell lines to vinorelbine combined with gefitinib in vitro.
Methods
Six recently established cell lines were used: UT-SCC-9, -11, -19A, -29 and -34 (laryngeal SCC) and UT-SCC-33 (oral cavity SCC). Chemosensitivity was tested using the 96-well plate clonogenic assay. The vinorelbine concentrations used varied between 0.4 and 1.0 nM and the gefitinib concentrations varied between 0.05 and 1.6 μM. Survival data were fitted to the LQ model, and the area under the curve (AUC) value was obtained with numerical integration. The type of interaction was determined by comparing the AUC ratio of the two drugs to the survival fraction (SF) of gefitinib alone.
Results
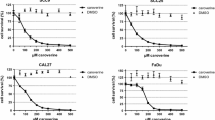
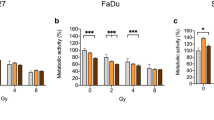
In the current study the combination of vinorelbine and gefitinib had a clear supra-additive or additive cytotoxic effect on the HNSCC cell lines.
Conclusions
This finding is encouraging as a proof of the possible benefit of combing an EGFR targeting compound with a cell cycle specific drug and warrants further studies of available combinations in vitro.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besenval M, Delgado M, Demarez JP, Krikorian A (1989) Safety and tolerance of Navelbine in phase I-II clinical trials. Semin Oncol 16(Suppl 4):37–40
Beulz-Riche D, Grunde P, Puozzo C, Sautel F, Filaquier C, Riche C, Ratanasavanh D (2005) Characterization of human cytochrome P450 isoenzymes involved in the metabolism of vinorelbine. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 19:545–553
Binet S, Fellous A, Lataste H, Krikorian A, Couzinier JP, Meniniger V (1989) In situ analysis of the action of Navelbine on microtubules using immunofluoresence. Semin Oncol 16(Suppl 4):5–8
Bourhis J, Pignon JP (1999) Meta-analysis head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. What is the role of chemotherapy? Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 13(4):769–775
Brizel DM, Albers ME, Fisher SR, Scher RL, Richtsmeier WJ, Hars V, George SL, Huang AT, Prosnitz LR (1998) Hyperfractionated irradiation with or without concurrent chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 338(25):1798–1804
Canobbio L, Boccardo F, Pastorini G, Brenna F, Martini C, Resasco M, Santi L (1989) Phase II study of Navelbine in advanced breast cancer. Semin Oncol 16(Suppl 4):33–36
Cohen EEW, Rosen F, Stadler WM, Recant W, Stenson K, Huo D, Vokes EE (2003) Phase II Trial of ZD1839 in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 21(10):1980–1987
Cohen MH, Williams GA, Sridhara R, Chen G, McGuinn WD, Morse D Jr, Abraham S, Rahman A, Liang C, Lostritto R, Baird A, Pazdur R (2004) Report from the FDA. United States food and drug administration drug approval summary: gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) tablets. Clin Cancer Res 10:1212–1218
Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, Jacobs J, Campbell BH, Saxman SB, Kish JA, Kim HE, Cmelak AJ, Rotman M, Machtay M, Ensley JF, Chao KS, Schultz CJ, Lee N, Fu KK (2004) Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 9501/Intergroup. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 6 350(19):1937–1944
Cros S, Wright M, Morimoto M, Lataste JP, Krikorian A (1989) Experimental anti-tumor activity of Navelbine. Semin Oncol 16:15–20
Degardin M, Oliveira J, Geoffrois L, Rolland F, Armand JP, Bastit P, Chauvergne J, Fargeot P, van Glabbeke M, Lentz MA, Tresca P, Boudillet J, Fumoleau P, Cappelaere P (1998) An EORTC-ECSG phase II study of vinorelbine in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann Oncol 9(10):1103–1107
Depenbrock H, Shirvani A, Rastetter J, Hanauske A-R (1995) Effects of vinorelbine on epidermal growth factor-receptor binding of human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Invest New Drugs 13:187–193
DePierre A, Lemarie E, Dapouis G, Gamier G, Jacoulet P, Dalphin JC (1991) A phase II study of Navelbine (vinorelbine) in the treatment of non small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 14:115–119
Engblom P, Pulkkinen JO, Rantanen V, Hirvonen H, Kulmala J, Grénman R, Grénman S (1999) Effects of paclitaxel with or without cremophor EL on cellular clonogenic survival and apoptosis. Eur J Cancer 35(2):284–288
Erjala K, Pulkkinen J, Kulmala J, Alanen K, Grénman R (2002) Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is highly sensitive to vinorelbine in vitro. Anticancer Res 22(6A):3135–3142
Erjala K, Pulkkinen J, Kulmala J, Grénman R (2004) Concomitant vinorelbine and radiation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Acta Oncol 43(2):169–174
Erjala K, Sundvall M, Junttila TT, Zhang N, Savisalo M, Mali P, Kulmala J, Pulkkinen J, Grénman R, Elenius K (2006) Signaling via ErbB2 and ErbB3 associates with resistance and EGFR amplification with sensitivity to EGFR-inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 12(13):4103–4111
Espinosa E, Zamora P, Milla A, Morales S, Molina R, Mira M, Gonzalez Baron M (2002) A phase II trial of cisplatin and vinorelbine in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck 24(12):1054–1059
Forastiere AA (2004) Is there a new role for induction chemotherapy in the treatment of head and neck cancer? J Natl Cancer Inst 96(22):1647–1649
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard J-Y,Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S, Rischin D, Eek R, Horai T, Noda K, Takata I, Smit E, Averbuch S, Macleod A, Wolf M, Feyereislova A, Dong R-P, Baselga J (2003) A multi-institutional randomised phase II trial of ZD1839 for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial). J Clin Oncol 21(12):2237–2246
Garden AS, Harris J, Vokes EE, Forastiere AA, Ridge JA, Jones C, Horwitz EM, Glisson BS, Nabell L, Cooper JS, Demas W, Gore E (2004) Preliminary results of radiation therapy oncology group 97–03: a randomized phase II trial of concurrent radiation and chemotherapy for advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 15:22(14):2856–2864
George MJ, Heron JF, Kerbrat P, Chauvergne J, Goupil A, Lebrun D, Guastalla JP, Namer M, Bugat R, Ayme Y, Toussaint C, L´homme C (1989) Navelbine in advanced ovarian epithelial cancer: a study of the French oncology centers. Semin Oncol 16(Suppl 4):30–32
Grandis JR, Melhem MF, Barnes EL, Tweardy DJ (1996) Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of transforming growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 78(6):1284–1292
Grénman R, Burk D, Virolainen E, Wagner JG, Lichter AS, Carey TE (1989) Clonogenic cell assay for anchorage-dependent squamous cell carcinoma cell lines using limiting dilution. Int J Cancer 44:131–136
Gridelli C, Perrone F, Gallo C, De Marinis F, Ianniello G, Gigolari S, Cariello S, Di Costanzo F, D’Aprile M, Rossi A, Migliorino R, Bartolucci R, Bianco AR, Pergola M, Monfardini S (1997) Vinorelbine is well tolerated and active in the treatment of elderly patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. A two-stage phase II study. Eur J Cancer 33:392–397
Kies MS, Haraf DJ, Athanasiadis I, Kozloff M, Mittal B, Pelzer H, Rademaker AW, Wenig B, Weichselbaum RR, Vokes EE (1998) Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiation for advanced head and neck cancer: Improved disease control and survival. J Clin Oncol 16(8):2715–2721
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H, Sandler A, Albain KS, Cella D, Wolf MK, Averbuch SD, Ochs JJ, Kay AC (2003) Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 290(16):2149–2158
Lansford CD, Grénman R, Bier H, Somers KD, Kim SY, Whiteside TL, Clayman GL, Welkoborsky H-J, Carey TE (1999) In: Masters JRW, Palsson B (eds) Human cell culture, vol. II, Chap. 28. Kluwer, Great Britain, pp 185–255
LoRusso PM, Herbst RS, Rischin D, Ranson M, Calvert H, Raymond E, Kieback D, Kaye S, Gianni L, Harris A, Bjork T, Maddox AM, Rothenberg ML, Small EJ, Rubin EH, Feyereislova A, Heyes A, Averbuch SD, Ochs J, Baselga J (2003) Improvements in quality of life and disease-related symptoms in phase I trials of the selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 in non-small cell lung cancer and other solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 9(6):2040–2048
Munro A (1995) An overview of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy in head and neck cancer. Br J Cancer 71(1):83–91
Orecchia R, Jereczek-Fossa BA, Catalano G, Chiesa F, De Pas T, Masci G, Krengli M, Vavassori A, De Paoli F, Robertson G, Marrocco E, De Braud F (2002) Phase II trial of vinorelbine, cisplatin and continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil followed by hyperfractionated radiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck cancer. Oncology 63:115–123
Pekkola-Heino K, Kulmala J, Grenman R (1992) Carboplatin-radiation interaction in squamous carcinoma cell lines. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118(12):1312–1315
Pignon JP, Bourhis J, Domenge C, Designe L (2000) Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: three meta-analyses of updated individual data. MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy on head and neck cancer. Lancet 18: 355(9208):949–955
Pulkkinen JO, Pekkola-Heino K, Grénman R (1996) Paclitaxel and irradiation induce apoptosis in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in an additive way. Anticancer Res 16:2923–2930
Raitanen M, Rantanen V, Kulmala J, Pulkkinen J, Klemi P, Grénman S, Grénman R (2002) Paclitaxel combined with fractionated radiation in vitro: a study with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 97:853–857
Ranson M, Hammond LA, Ferry D, Kris M, Tullo A, Murray PI, Miller V, Averbuch S, Ochs J, Morris C, Feyereislova A, Swaisland H, Rowinsky EK (2002) ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is well tolerated and active in patients with solid, malignant tumors: results of a phase I trial. J Clin Oncol 20(9):2217–2219
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N (1995) Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 19:183–232
Shintani S, Li C, Mihara M, Terakado N, Yano J, Nakashiro K, Hamakawa H (2003) Enhancement of tumor radioresponse by combined treatment with gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is accompanied by inhibition of DNA damage repair and cell growth in oral cancer. Int J Cancer 107:1030–1037
Shirasuna K, Hayashido Y, Sugiyama M, Yoshioka H, Matsuya T (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and EGF receptor in human oral mucosa and its malignancy. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 418:349–353
Sirotnak FM, Zakowski MF, Miller VA, Scher HI, Kris MG (2000) Efficacy of cytotoxic agents against human tumor xenografts is markedly enhanced by coadministration of ZD1839 (Iressa), an inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res 6:4885–4892
Sunwoo JB, Herscher LL, Kroog GS, Thomas GR, Ondrey FG, Duffey DC, Solomon BI, Boss C, Albert PS, McCullugh L, Rudy S, Muir C, Zhai S, Figg WD, Cook JA, Mitchell JB, Van Waes C (2001) Concurrent paclitaxel and radiation in the treatment of locally advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 19(3):800–811
Swaisland HC, Ranson M, Smith RP, Leadbetter J, Laight A, McKillop D, Wild MJ (2005) Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of gefitinib with rifampicin, itraconazole and metoprolol. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:1067–1081
Testolin A, Recher G, Gristoferi V, Gaspanni G (1994) Vinorelbine (NVB) in pretreated advanced head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: a phase II study. Invest N Drugs 12:231–234
Vokes EE, Haraf DJ, Kies MS (2000) The use of concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer. Semin Oncol 27(4 Suppl 8):34–38
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, Ashton SE, Curry BJ, Barker AJ, Gibson KH (2002) ZD1839 (Iressa): an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res 62:5749–5754
Yoshimura M, Imamura F, Ueno K, Yamamoto S (2004) Severe myelotoxicity in a combination of gefitinib and vinorelbine. Lung Cancer 45:121–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erjala, K., Raitanen, M., Kulmala, J. et al. Concurrent use of vinorelbine and gefitinib induces supra-additive effect in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133, 169–176 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0154-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0154-0