Abstract
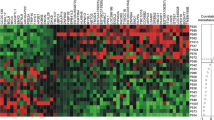
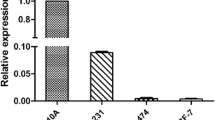
Purpose: The human CC3/TIP30 gene is a putative metastasis suppressor gene, based on the results of experimental studies using lung, colon and melanoma cell lines. However, there is very little evidence from studies on clinical material, in support of such a role for the gene. In this study, we evaluated the expression of CC3/TIP30 in human breast cancer tissue and investigated the possible associations with the clinicopathological parameters. Methods: Total RNA and proteins were extracted from the frozen breast tumor and matched normal tissues. Evaluation of CC3/TIP30 expression was assessed by reverse transcription (RT)-PCR and reverse phase protein array. Immunohistochemistry of CC3/TIP30 on breast tissue microarrays was also analyzed. Results: We have found that CC3/TIP30 expression is significantly associated with positive HER-2/neu status at both mRNA (P=0.023) and protein (P=0.016) levels. Immunohistochemical analysis on tissue microarrays also shows a positive correlation between CC3 expression and HER-2/neu status (P=0.0028). Conclusion: Our findings suggest a potential link between the expression of CC3/TIP30 gene and the HER-2/neu oncogene-mediated signal pathway.These findings could not have been predicted from previous experimental studies, and suggest that CC3/TIP30 may play a complex role in breast cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker ME, Yan L, Pear MR (2000) Three-dimensional model of human TIP30, a coactivator for HIV-1 Tat-activated transcription, and CC3, a protein associated with metastasis suppression. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:851–858
Hays DF, Thor AD (2002) c-erbB-2 in breast cancer: development of a clinically useful marker. Semin Oncol 29:231–245
Hewitt RE, Brown KE, Corcoran ML, Stetler-Stevenson WG (2000) Increased expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases type I (TIMP-I) in a more tumorigenic colon cancer cell line. J Path 192:455–459
Ito M, Jiang C, Krumm K, Zhang X, Pecha J, Zhao J, Guo Y, Roeder RG, Xiao H (2003) TIP30 deficiency increases susceptibility to tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 63:8763–8767
Jiang C, Ito M, Piening V, Bruck K, Roeder RG, Xiao H (2004) TIP30 interacts with an estrogen receptor α-interacting coactivator CIA and regulated c-myc transcription. J Biol Chem 279:27781–27789
King FW, Shtivelman E (2004) Inhibition of nuclear import by the proapoptotic protein CC3. Mol Cell Biol 24:7091–7101
Liu Y, Thor A, Shtivelman E, Cao Y, Tu G, Heath TD, Debs RJ (1999) Systemic gene delivery expands the repertoire of effective antiangiogenic agents sensitizing cell to apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:13338–13344
NicAmhlaoibh R, Shtivelman E (2001) Metastasis suppressor CC3 inhibits angiogenic properties of tumor cells in vitro. Oncogene 20:270–275
Schlessinger J (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211–225
Shtivelman E (1997) A link between metastasis and resistance to apoptosis of variant small cell lung carcinoma. Oncogene 14:2167–2173
Tsutsui S, Ohno S, Murakami S, Hachitanda Y, Odar S (2002) Prognostic value of c-erbB2 expression in breast cancer. J Surg Oncol 79:216–223
Whitman S, Wang X, Shalaby R, Shtivelman E (2000) Alternatively spliced products CC3 and TC3 have opposing effects on apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 20:583–593
Xiao H, Tao Y, Greenblatt J, Roeder RG (1998) A cofactor, TIP30, specifically enhances HIV-1 Tat-activated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2146–2151
Xiao H, Palhan V, Yang Y, Roeder RG (2000) TIP30 has an intrinsic kinase activity required for up-regulation of a subset of apoptotic genes. EMBO J 19:956–963
Yarden Y (2001) Biology of HER2 and its importance in breast cancer. Oncology 61(suppl 2):1–13
Zhang D-H, Salto-Tellez M, Do E, Putti TC, Koay ESC (2003a) Evaluation of HER-2/neu oncogene status in breast tumors on tissue microarrays. Hum Pathol 34:362–368
Zhang D-H, Salto-Tellez M, Putti TC, Do E, Koay ESC (2003b) Reliability of tissue microarrays in detecting protein expression and gene amplification in breast cancer. Mod Path 16:79–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
D.-H. Zhang and L.L. Wong contributed equally to this work..
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, DH., Wong, L.L., Tai, L.K. et al. Overexpression of CC3/TIP30 is associated with HER-2/neu status in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 603–608 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0674-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0674-z