Abstract
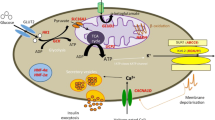
Two cases of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia associated with persistent hyperammonaemia in unrelated infants of 7 days and 4 months of age are reported. Blood ammonia levels were 100–300 μmol/l (normal values<40 μmol/l). The hyperammonaemia was asymptomatic and not associated with any of the abnormalities of amino acids or organic acids observed in urea cycle enzyme defects. Orotic aciduria was normal. The hyperammonaemia was not influenced by the levels of blood glucose nor by subtotal pancreatectomy. On admission blood glucose was ca. 1.2 mmol/l (21.6 mg/dl) corresponding to blood insulin levels of 35 and 22 mU/l respectively in both infants. Continuous intravenous glucose perfusion was necessary to prevent hypoglycaemia. Furthermore 2-oxoglutaric acid in urine was increased in the second infant to 3.15 mg/mg creatinine (normal 0.41 +/−0.12). This may point to mutations in the glutamate dehydrogenase gene.
Conclusion 2-Oxoglutaric aciduria may be an important clue to the diagnose in this syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 January 1998 / Accepted: 25 November 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitaura, J., Miki, Y., Kato, H. et al. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia associated with persistent hyperammonaemia. Eur J Pediatr 158, 410–413 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310051103
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310051103