Abstract
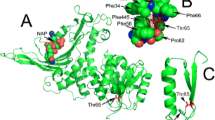
Biochemical and molecular genetic studies were performed on the enzyme variants of two patients compound heterozygous for glucose phosphate isomerase (GPI) deficiency, both suffering from severe haemolytic anaemia. The enzymes of case 1 (GPI `Zwickau') and case 2 (GPI `Nordhorn' [25]), revealed reduced GPI activity and remarkable thermolability. Glucose-6-phosphate (Gluc-6-P) concentration was elevated 2.3 times in case 1 and 3.8 times in case 2. Sequencing the patients' GPI genes showed four different point mutations, two of them involving highly conserved amino acids. The c1039 C→T substitution, found in the gene of GPI `Zwickau', has been described recently [30] and causes an Arg 347→Cys substitution close to the putative catalytic site. The second mutation in this case is a novel c1538 G→A substitution causing a Trp→stop mutation at position 513 apparently resulting in premature RNA degradation thus resulting either in a complete lack of protein or a protein which does not show GPI activity. In the gene of GPI `Nordhorn' a c1028 A→G mutation was discovered, also previously described [1, 9] causing a Gln 343→Trp substitution. The second mutation was a novel splice site mutation at the border of intron 15 to exon 16: IVS15-(-2) A→C which leads to an aberrant splicing of exon 16, thus resulting either in a truncated and most likely inactive enzyme or in no protein at all.
Conclusion Biochemical and molecular genetic studies performed with the enzyme variants GPI `Zwickau' and GPI `Nordhorn' showed that in both cases the simultaneous occurrence of a single amino acid sub‐stitution affecting the active site, together with a nonsense mutation leading to the loss of major parts of the enzyme probably explains the severe clinical course of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 August 1996 / Accepted: 17 January 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huppke, P., Wünsch, D., Pekrun, A. et al. Glucose phosphate isomerase deficiency: biochemical and molecular genetic studies on the enzyme variants of two patients with severe haemolytic anaemia. Eur J Pediatr 156, 605–609 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050674
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050674