Abstract
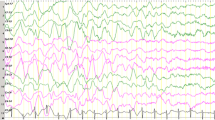
Deletions on the short arm of chromosome 4 cause Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) and Pitt-Rogers-Danks syndrome (PRDS). WHS is associated with severe growth and mental retardation, microcephaly, a characteristic facies and congenital malformations. The PRDS phenotype is similar to WHS but generally less severe. Seizures occur in the majority of WHS and PRDS patients. Sgrò et al. [17] described a stereotypic electroclinical pattern in four unrelated WHS patients, consisting of intermittent bursts of 2–3 Hz high voltage slow waves with spike wave activity in the parietal areas during drowsiness and sleep associated with myoclonic jerks. We report a patient with PRDS and the typical EEG pattern and review 14 WHS patients with similar EEG findings reported in the literature.
Conclusion Awareness and recognition of the characteristic electroclinical findings in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome and Pitt-Rogers-Danks syndrome might help in the early diagnosis of such patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 June 2000 and in revised form: 15 September 2000 / Accepted: 18 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zankl, A., Addor, MC., Maeder-Ingvar, M. et al. A characteristic EEG pattern in 4p-syndrome: case report and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr 160, 123–127 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310000679
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310000679