Abstract
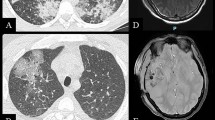
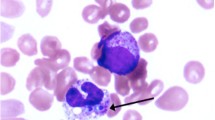
Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis (PDH) is thought to be on the top of the list of AIDS-defining illnesses in South America. Reported experience in children is very scarce. The aim of this study was to describe the clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of children living with HIV presenting with PDH in Ecuador. We did a retrospective study using collected data on medical records of children living with HIV attended in Francisco Icaza Bustamante Children’s Hospital (Guayaquil) between 1997 and 2019. The inclusion criteria consisted of patients under 18 years of age at admission with documented HIV infection and laboratory-confirmed diagnosis of PDH. Twenty-four children living with HIV were attended due to laboratory-confirmed PDH. Median CD4 cell count was 39 cells/mm³ (p25–p75 21–155) between 1 and 5 years and 22 cells/mm³ (p25–p75 10–57) for those aged 6 years and over. Fever (96%) was the most common clinical manifestation, followed by hepatomegaly (75%), cough (67%), weight loss (63%), diarrhea (63%), and abdominal distension (58%). Most significant laboratory findings were hypoalbuminemia (90%), hypertransaminasemia (78%), and pancytopenia (46%). Intravenous treatment with amphotericin B deoxycholate was started in all but one case in which diagnosis was postmortem. All these 23 patients were discharged after being hospitalized for a median of 68 days (p25–p75 48–90). Two children showed relapse during follow-up, one of whom died during the hospitalization of this second episode of PDH.
Conclusion: Clinical manifestations and laboratory findings of PDH in children living with HIV seem similar to those seen in adults, and low CD4 cell count appears to be the most important risk factor.
What is Known: • Since 1987, progressive disseminated histoplasmosis has been considered an AIDS-defining illness and, although underdiagnosis is frequent, is thought to be on the top of the list of AIDS-defining illnesses in South America. • Reported experience in children is very scarce. What is New: • Clinical manifestations and laboratory findings of progressive disseminated histoplasmosis in children living with HIV seem similar to those seen in adults. • Low CD4 cell count to be the most important risk factor. |

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PDH:
-
progressive disseminated histoplasmosis
- SD:
-
standard deviation
References
Wheat LJ, Freifeld AG, Kleiman MB, Baddley JW, DS MK, Lloyd JE, Kauffman CA, Infectious Diseases Society of America (2007) Clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with histoplasmosis: 2007 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 45:807–825
The neglected histoplasmosis in Latin America Group (2016) Disseminated histoplasmosis in central and South America, the invisible elephant: the lethal blind spot of international health organizations. AIDS 30:167–170
Nacher M, Adenis A, Mc Donald S, Mendonca M, Singh S, Lopes I, Malcher R, Hermelijn S, Wongsokarijo M, Van Eer M et al (2013) Disseminated histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients in South America: a neglected killer continues on its rampage. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e2319
Benedict K, Mody RK (2016) Epidemiology of histoplasmosis outbreaks, United States, 1938–2013. Emerg Infect Dis 22:370–378
Panel on Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Exposed and HIV-Infected Children. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-exposed and HIV-infected children. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/oi_guidelines_pediatrics.pdf. Accessed 31/12/2020
(2020) Subsecretaría Nacional de Vigilancia de la Salud Pública. Boletín anual VIH/SIDA y expuestos perinatales año 2019. https://www.salud.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/gaceta_vih_2019-1.pdf. (17 January 2021, date last accessed)
Adenis AA, Valdes A, Cropet C, McCotter O, Derado G, Couppie P, Chiller T, Nacher M (2018) Burden of HIV-associated histoplasmosis compared with tuberculosis in Latin America: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis 18:1150–1159
Wang TL, Cheah JS, Holmberg K (1996) Case report and review of disseminated histoplasmosis in South-East Asia: clinical and epidemiological implications. Tropical Med Int Health 1:35–42
Loulergue P, Bastides F, Baudouin V, Chandenier J, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Dupont B, Viard JP, Dromer F, Lortholary O (2007) Literature review and case histories of Histoplasma capsulatum var. duboisii infections in HIV-infected patients. Emerg Infect Dis 13:1647–1652
Nacher M, Adenis A, Adriouch L, Dufour J, Papot E, Hanf M, Vantilcke V, Calvez M, Aznar C, Carme B et al (2011) What is AIDS in the Amazon and the Guianas? Establishing the burden of disseminated Histoplasmosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84:239–240
Murphy RA, Gounder L, Manzini TC, Ramdial PK, Castilla C, Moosa MY (2015) Challenges in the management of disseminated progressive histoplasmosis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in resource-limited settings. Open Forum Infect Dis 2:ofv025
World Health Organization (2019) Second WHO model list of essential in vitro diagnostics. World Health Organization, Geneva
Bongomin F, Kwizera R, Denning DW (2019) Getting histoplasmosis on the map of international recommendations for patients with advanced HIV disease. J Fungi 5:80
Colombo AL, Tobón A, Restrepo A, Queiroz-Telles F, Nucci M (2011) Epidemiology of endemic systemic fungal infections in Latin America. Med Mycol 49:785–798
Vega W, Almeida R, Miño G, Gené J, Guarro J (2007) A quick and cost-effective method for diagnosing disseminated histoplasmosis in children. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 57:405–408
Ollague Sierra JE, Ollague Torres JM (2013) New clinical and histological patterns of acute disseminated histoplasmosis in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Dermatopathol 35:205–212
Schutze GE, Tucker NC, Jacobs RF (1992) Histoplasmosis and perinatal human immunodeficiency virus. Pediatr Infect Dis J 11:501–502
Byers M, Feldman S, Edwards J (1992) Disseminated histoplasmosis as the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-defining illness in an infant. Pediatr Infect Dis J 11:127–128
Pillay T, Pillay DG, Bramdev A (1997) Disseminated histoplasmosis in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected African child. Pediatr Infect Dis J 16:417–418
Cimerman S, Sokolowski W, Gonçalves SE, Lins MS, Colombo AL (1999) Histoplasmosis in an AIDS paediatric patient. Mycoses 42:567–569
Saidinejad M, Burns MM, Harper MB (2004) Disseminated histoplasmosis in a nonendemic area. Pediatr Infect Dis J 23:781–782
Nandí-Lozano E, Newton-Sánchez O, Ávila-Figueroa C (2006) Reporte de cinco casos pediátricos de histoplasmosis diseminada. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex 63:47–54
Mosam A, Moodley V, Ramdial PK (2006) Persistent pyrexia and plaques: a perplexing puzzle. Lancet 368:551
Kalata KE, Osborne C, Willis A, Navarro K, Fenton LZ, Smith C (2019) Disseminated histoplasmosis as an AIDS-defining illness presenting as fever of unknown origin in an 11-year-old female. Case Rep Pediatr 2019:9417102
McKinsey DS, Spiegel RA, Hutwagner L, Stanford J, Driks MR, Brewer J, Gupta MR, Smith DL, O’Connor MC, Dall L (1997) Prospective study of histoplasmosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: incidence, risk factors, and pathophysiology. Clin Infect Dis 24:1195–1203
Kim SH, Gerver SM, Fidler S, Ward H (2014) Adherence to antiretroviral therapy in adolescents living with HIV: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS 28:1945–1956
Brilhante RS, Fechine MA, Mesquita JR, Cordeiro RA, Rocha M, Monteiro AJ, Lima R, Caetano EP, Pereira JF, Castelo-Branco D et al (2012) Histoplasmosis in HIV-positive patients in Ceará, Brazil: clinical-laboratory aspects and in vitro antifungal susceptibility of Histoplasma capsulatum isolates. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 106:484–488
Karimi K, Wheat LJ, Connolly P, Cloud G, Hajjeh R, Wheat E, Alves K, Lacaz C, Keath E (2002) Differences in histoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States and Brazil. J Infect Dis 186:1655–1660
Wheat LJ, Connolly-Stringfield PA, Baker RL, Curfman MF, Eads ME, Israel KS, Norris SA, Webb DH, Zeckel ML (1990) Disseminated histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical findings, diagnosis and treatment, and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 69:361–374
Nacher M, Sarazin F, El Guedj M, Vaz T, Alvarez F, Nasser V, Randrianjohany A, Aznar C, Carme B, Couppié P (2006) Increased incidence of disseminated histoplasmosis following highly active antiretroviral therapy initiation. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 41:468–470
Daher EF, Silva GB Jr, Barros FA, Takeda C, Mota R, Ferreira MT, Oliveira SA, Martins JC, Araújo S, Gutiérrez-Adrianzén OA (2007) Clinical and laboratory features of disseminated histoplasmosis in HIV patients from Brazil. Tropical Med Int Health 12:1108–1115
Gutierrez ME, Canton A, Sosa N, Puga E, Talavera L (2005) Disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS in Panama: a review of 104 cases. Clin Infect Dis 40:1199–1202
Hughes WT (1984) Hematogenous histoplasmosis in the immunocompromised child. J Pediatr 105:569–575
Adderson EE (2004) Histoplasmosis in a pediatric oncology center. J Pediatr 144:100–106
Leggiadro RJ, Barrett FF, Hughes WT (1988) Disseminated histoplasmosis of infancy. Pediatr Infect Dis J 7:799–805
Odio CM, Navarrete M, Carrillo JM, Mora L, Carranza A (1999) Disseminated histoplasmosis in infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 18:1065–1068
Conces DJ Jr, Stockberger SM, Tarver RD, Wheat LJ (1993) Disseminated histoplasmosis in AIDS: findings on chest radiographs. AJR Am J Roentgenol 160:15–19
Wheat LJ, Chetchotisakd P, Williams B, Connolly P, Shutt K, Hajjeh R (2000) Factors associated with severe manifestations of histoplasmosis in AIDS. Clin Infect Dis 30:877–881
Hage CA, Ribes JA, Wengenack NL, Baddour LM, Assi M, McKinsey DS, Hammoud K, Alapat D, Babady NE, Parker M, Fuller D et al (2011) A multicenter evaluation of tests for diagnosis of histoplasmosis. Clin Infect Dis 53:448–454
Fojtasek MF, Kleiman MB, Connolly-Stringfield P, Blair R, Wheat LJ (1994) The Histoplasma capsulatum antigen assay in disseminated histoplasmosis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 13:801–805
Wheat LJ (2006) Antigen detection, serology, and molecular diagnosis of invasive mycoses in the immunocompromised host. Transpl Infect Dis 8:128–139
Baddley JW, Sankara IR, Rodriquez JM, Pappas PG, Many WJ Jr (2008) Histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients in a southern regional medical center: poor prognosis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 62:151–156
Couppié P, Sobesky M, Aznar C, Bichat S, Clyti BF, El Gudj M, Alvarez F, Demar M, Louvel D et al (2004) Histoplasmosis and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a study of prognostic factors. Clin Infect Dis 38:134–138
Goldman M, Zackin R, Fichtenbaum CJ, Skiest DJ, Koletar SL, Hafner R, Wheat LJ, Nyangweso PM, Yiannoutsos CT, Schnizlein-Bick CT, Owens S, Aberg JA, AIDS Clinical Trials Group A5038 Study Group (2004) Safety of discontinuation of maintenance therapy for disseminated histoplasmosis after immunologic response to antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 38:1485–1489
Myint T, Anderson AM, Sanchez A, Farabi A, Hage C, Baddley JW, Jhaveri M, Greenberg RN, Bamberger DM, Rodgers M, Crawford TN, Wheat LJ (2014) Histoplasmosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS): multicenter study of outcomes and factors associated with relapse. Medicine (Baltimore) 93:11–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. García-Boyano and Dr. Miño-León conceptualized and designed the study, collected data, drafted the initial manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. Dr. William Vega, Dr. Luis Prieto, Dr. Chávez-Solórzano, and Dr. Solís-Montiel made substantial contributions to the conception of the work and to the acquisition of data and reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest/competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This retrospective study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was authorized by the Ethics Committee of our institution.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Commnunicated by: Nicole Ritz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Boyano, M., Vega, W., Prieto, L. et al. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis in children living with HIV: a case series study. Eur J Pediatr 180, 1923–1931 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-03969-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-03969-5