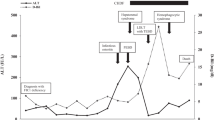
Abstract
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) can cause intense pruritus that is refractory to medical therapy. Surgical biliary diversion techniques, including partial internal biliary diversion (PIBD), have been developed over the years to relieve pruritus without requiring liver transplantation. No clinical or genetic features can currently predict postoperative pruritus response. We present three PFIC type 2 (PIFC 2) patients who underwent transient endoscopic nasobiliary drainage (NBD) prior to PIBD surgery. Two patients repeatedly responded to NBD and presented with complete pruritus resolution after subsequent PIBD. NBD failed technically in the third patient, and PIBD was partially successful. Mild post-endoscopic biological pancreatitis occurred in 2/6 NBD procedures and resolved spontaneously. The only adverse effect observed within 7 years post-PIBD was very mild transient osmotic diarrhea.
Conclusion: Our limited data suggest that NBD is a safe and effective way to predict pruritus response before performing permanent biliary diversion surgery in PFIC patients.
What is Known: • Surgical biliary diversion techniques have been developed to relieve intractable pruritus in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC). • No clinical or genetic features can currently predict pruritus response to surgery. | |
What is New: • Our data suggest that nasobiliary drainage could be a safe and effective tool to predict pruritus response to biliary diversion and avoid unnecessary surgery in PFIC patients. |

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERCP:
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- MARS:
-
Molecular adsorbents recirculating system
- NBD:
-
Nasobiliary drainage
- PEBD:
-
Partial external biliary diversion
- PFIC:
-
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
- PIBD:
-
Partial internal biliary diversion
- TBA:
-
Serum total bile acids
References
Wanty C, Joomye R, Van Hoorebeek N, Paul K, Otte JB, Reding R, Sokal EM (2004) Fifteen years single center experience in the management of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis of infancy. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 67(4):313–319
Ismail H, Kalicinski P, Markiewicz M, Jankowska I, Pawlowska J, Kluge P, Eliadou E, Kaminski A, Szymczak M, Drewniak T, Revillon Y (1999) Treatment of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: liver transplantation or partial external biliary diversion. Pediatr Transplant 3(3):219–224
Davis AR, Rosenthal P, Newman TB (2009) Nontransplant surgical interventions in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Surg 44(4):821–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.07.018
Ramachandran P, Shanmugam NP, Sinani SA, Shanmugam V, Srinivas S, Sathiyasekaran M, Tamilvanan V, Rela M (2014) Outcome of partial internal biliary diversion for intractable pruritus in children with cholestatic liver disease. Pediatr Surg Int 30(10):1045–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3559-x
Erginel B, Soysal FG, Durmaz O, Celik A, Salman T (2018) Long-term outcomes of six patients after partial internal biliary diversion for progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Surg 53(3):468–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.10.055
Nicastro E, Stephenne X, Smets F, Fusaro F, de Magnee C, Reding R, Sokal EM (2012) Recovery of graft steatosis and protein-losing enteropathy after biliary diversion in a PFIC 1 liver transplanted child. Pediatr Transplant 16(5):E177–E182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3046.2011.01514.x
Hegade VS, Krawczyk M, Kremer AE, Kuczka J, Gaouar F, Kuiper EM, van Buuren HR, Lammert F, Corpechot C, Jones DE (2016) The safety and efficacy of nasobiliary drainage in the treatment of refractory cholestatic pruritus: a multicentre European study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(2):294–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13449
Stapelbroek JM, van Erpecum KJ, Klomp LW, Venneman NG, Schwartz TP, van Berge Henegouwen GP, Devlin J, van Nieuwkerk CM, Knisely AS, Houwen RH (2006) Nasobiliary drainage induces long-lasting remission in benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology 43(1):51–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20998
Appleby VJ, Hutchinson JM, Davies MH (2015) Safety and efficacy of long-term nasobiliary drainage to treat intractable pruritus in cholestatic liver disease. Frontline Gastroenterol 6(4):252–254. https://doi.org/10.1136/flgastro-2014-100489
Jacquemin E (2012) Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 36(Suppl 1):S26–S35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2210-7401(12)70018-9
Whitington PF, Whitington GL (1988) Partial external diversion of bile for the treatment of intractable pruritus associated with intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology 95(1):130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(88)90301-0
Bustorff-Silva J, Sbraggia Neto L, Olimpio H, de Alcantara RV, Matsushima E, De Tommaso AM, Brandao MA, Hessel G (2007) Partial internal biliary diversion through a cholecystojejunocolonic anastomosis--a novel surgical approach for patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Surg 42(8):1337–1340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.03.029
Kremer AE, van Dijk R, Leckie P, Schaap FG, Kuiper EM, Mettang T, Reiners KS, Raap U, van Buuren HR, van Erpecum KJ, Davies NA, Rust C, Engert A, Jalan R, Oude Elferink RP, Beuers U (2012) Serum autotaxin is increased in pruritus of cholestasis, but not of other origin, and responds to therapeutic interventions. Hepatology 56(4):1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.25748
Pares A, Herrera M, Aviles J, Sanz M, Mas A (2010) Treatment of resistant pruritus from cholestasis with albumin dialysis: combined analysis of patients from three centers. J Hepatol 53(2):307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.02.031
Kremer AE, Martens JJ, Kulik W, Rueff F, Kuiper EM, van Buuren HR, van Erpecum KJ, Kondrackiene J, Prieto J, Rust C, Geenes VL, Williamson C, Moolenaar WH, Beuers U, Oude Elferink RP (2010) Lysophosphatidic acid is a potential mediator of cholestatic pruritus. Gastroenterology 139(3):1008–1018, e1001. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.05.009
Arnell H, Papadogiannakis N, Zemack H, Knisely AS, Nemeth A, Fischler B (2010) Follow-up in children with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis after partial external biliary diversion. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 51(4):494–499. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181df99d5
Schukfeh N, Metzelder ML, Petersen C, Reismann M, Pfister ED, Ure BM, Kuebler JF (2012) Normalization of serum bile acids after partial external biliary diversion indicates an excellent long-term outcome in children with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Surg 47(3):501–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.08.010
Verkade HJ, Bezerra JA, Davenport M, Schreiber RA, Mieli-Vergani G, Hulscher JB, Sokol RJ, Kelly DA, Ure B, Whitington PF, Samyn M, Petersen C (2016) Biliary atresia and other cholestatic childhood diseases: advances and future challenges. J Hepatol 65(3):631–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.032
Tong JL, Ran ZH, Shen J, Fan GQ, Xiao SD (2008) Association between fecal bile acids and colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Yonsei Med J 49(5):792–803. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.5.792
Li T, Chiang JY (2014) Bile acid signaling in metabolic disease and drug therapy. Pharmacol Rev 66(4):948–983. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.113.008201
Jansen PL, Strautnieks SS, Jacquemin E, Hadchouel M, Sokal EM, Hooiveld GJ, Koning JH, De Jager-Krikken A, Kuipers F, Stellaard F, Bijleveld CM, Gouw A, Van Goor H, Thompson RJ, Muller M (1999) Hepatocanalicular bile salt export pump deficiency in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology 117(6):1370–1379. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70287-8
Bull LN, Pawlikowska L, Strautnieks S, Jankowska I, Czubkowski P, Dodge JL, Emerick K, Wanty C, Wali S, Blanchard S, Lacaille F, Byrne JA, van Eerde AM, Kolho KL, Houwen R, Lobritto S, Hupertz V, McClean P, Mieli-Vergani G, Sokal E, Rosenthal P, Whitington PF, Pawlowska J, Thompson RJ (2018) Outcomes of surgical management of familial intrahepatic cholestasis 1 and bile salt export protein deficiencies. Hepatol Commun 2(5):515–528. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1168
Davit-Spraul A, Fabre M, Branchereau S, Baussan C, Gonzales E, Stieger B, Bernard O, Jacquemin E (2010) ATP8B1 and ABCB11 analysis in 62 children with normal gamma-glutamyl transferase progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC): phenotypic differences between PFIC1 and PFIC2 and natural history. Hepatology 51(5):1645–1655. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23539
van Wessel DBE, Thompson RJ, Gonzales E, Jankowska I, Sokal E, Grammatikopoulos T, Kadaristiana A, Jacquemin E, Spraul A, Lipinski P, Czubkowski P, Rock N, Shagrani M, Broering D, Algoufi T, Mazhar N, Nicastro E, Kelly DA, Nebbia G, Arnell H, Bjorn F, Hulscher JBF, Serranti D, Arikan C, Polat E, Debray D, Lacaille F, Goncalves C, Hierro L, Munoz Bartolo G, Mozer-Glassberg Y, Azaz A, Brecelj J, Dezsofi A, Calvo PL, Grabhorn E, Sturm E, van der Woerd WJ, Kamath BM, Wang JS, Li L, Durmaz O, Onal Z, Bunt TMG, Hansen BE, Verkade HJ, course NA, Prognosis of P, Effect of biliary Diversion c (2020) Genotype correlates with the natural history of severe bile salt export pump deficiency. J Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.02.007
Zellos A, Lykopoulou L, Polydorou A, Tanou K, Jirsa M, Roma E, Knisely AS (2012) Nasobiliary drainage in an episode of intrahepatic cholestasis in a child with mild ABCB11 disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 55(1):88–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e31822f2bda
Funding
GJ is supported by the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique et Médicale (FNRS, Belgium) through an FRIA grant (number FC29559). IS is supported by FNRS and Fondation contre le Cancer grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GJ contributed to study conception and design, to data collection and analysis, drafted the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. XS contributed to study conception and design and to material preparation, revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. IS contributed to study conception and design and to material preparation, revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. FS contributed to study conception and design and to material preparation, revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. CDM contributed to study conception and design and to material preparation, revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. RR contributed to study conception and design and to material preparation, revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. ES contributed to study conception and design and to material preparation, revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
These procedures were considered as standard medical care and did not require prior ethical committee approval.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jannone, G., Stephenne, X., Scheers, I. et al. Nasobiliary drainage prior to surgical biliary diversion in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type II. Eur J Pediatr 179, 1547–1552 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-020-03646-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-020-03646-z