Abstract
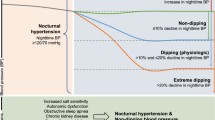
The aim of this study was to analyse the relationship between insulin–glucose metabolism, nocturnal blood pressure dipping and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in obese adolescents without diabetes. One hundred one consecutive children, with biopsy-proven NAFLD, were included in this study. Blood samples were drawn for the analyses of liver function tests, insulin–glucose metabolism and lipid profile appraisal. An ambulatory blood pressure measurement (ABPM) was performed. Seventy-six children (75.3 %) were systolic nondippers, and 23 of them were diastolic nondippers (30.3 %). No differences were found in the anthropometric parameters between the two groups. When compared to the systolic dippers, the systolic nondippers had higher medians of mean nocturnal blood pressure, glucose at 0, 60 and 120 min in the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), OGTT insulin at all time points and insulin-resistance values. No correlation of histopathological features with dipping/nondipping statuses was found. Conclusions: We found an association between a nocturnal blood pressure fall and measures of insulin levels, independent of obesity, or daytime blood pressure levels, among the obese patients with NAFLD. Although no association between nondipping profiles and NAFLD was observed in our study, further studies with a longer term follow-up are needed, to better elucidate the complex link between these particular entities.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine transferases
- AST:
-
Aspartate transferases
- ABPM:
-
Ambulatory blood pressure measurement
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- GGT:
-
Gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase
- HSC:
-
Hepatic stellate cells
- HOMA:
-
Homeostatic model assessment
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- ISI:
-
OGTT-derived insulin sensitivity index
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- NAFLD:
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- RAAS:
-
Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system
- NASH:
-
Steatohepatitis
- SNS:
-
Sympathetic nervous system
- TG:
-
Total triglycerides
References
Alisi A, Nobili V (2012) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children now: lifestyle changes and pharmacologic treatments. Nutrition 28:722–726
Benetos A, Thomas F, Safar ME, Bean KE, Guize L (2001) Should diastolic and systolic blood pressure be considered for cardiovascular risk evaluation: a study in middle-aged men and women. J Am Coll Cardiol 37:163–168
Berardis S, Sokal E. (2013) Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an increasing public health issue. Eur J Pediatr. in press
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. Br Med J 320:1240–1243
Corry DB, Tuck A (1999) Obesity, hypertension, and sympathetic nervous system activity. Curr Hypertens Rep 1:119–126
Fallo F, Dalla Pozza A, Sonino N, Federspil G, Ermani M, Baroselli S et al (2008) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, adiponectin and insulin resistance in dipper and nondipper essential hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 26:2191–2197
Framme J, Dangardt F, Mårild S, Osika W, Währborg P, Friberg P (2006) 24-h Systolic blood pressure and heart rate recordings in lean and obese adolescents. Clin Physiol Funct Image 26:235–239
Genovesi S, Giussani M, Pieruzzi F, Vigorita F, Arcovio C, Cavuto S, Stella A (2005) Results of blood pressure screening in a population of school-aged children in the province of Milan: role of overweight. J Hypertens 23:493–497
Gilardini L, Parati G, Sartorio A, Mazzilli G, Pontiggia B, Invitti C (2008) Sympathoadrenergic and metabolic factors are involved in ambulatory blood pressure rise in childhood obesity. J Hum Hypertens 22:75–82
Giordano U, Michielon G, Calò Carducci F, Ravà L, Alfieri S et al (2003) Cardiovascular hemodynamics: relationships with insulin resistance in obese children. Pediatr Cardiol 24:548–552
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S, Sturdivant RX (2013) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, Hoboken
Julius S, Valentini M, Palatini P (2000) Overweight and hypertension: a 2-way street? Hypertension 35:807–813
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW et al (2005) Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41:313–1321
Koenker R (2005) Quantile regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lastra-Lastra G, Sowers JR, Restrepo-Erazo K, Manrique-Acevedo C, Lastra-González G (2009) Role of aldosterone and angiotensin II in insulin resistance: an update. Clin End 71:1–6
Latea L, Negrea S, Bolboaca S (2013) Primary non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in hypertensive patients. Australas Med J 6:325–330. doi:10.4066/AMJ.2013.1648
Lurbe E, Torro I, Aguilar F, Alvarez J, Alcon J, Pascual JM, Redon J (2008) Added impact of obesity and insulin resistance in nocturnal blood pressure elevation in children and adolescents. Hypertension 51:635–641
Martino F, Puddu PE, Pannarale G, Colantoni C, Martino E, Zanoni C, Barillà F. (2013) Hypertension in children and adolescents attending a lipid clinic. Eur J Pediatr. in press
Masuo K, Mikami H, Itoh M, Ogihara T, Tuck ML (2000) Sympathetic activity and body mass index contribute to blood pressure levels. Hypertens Res 23:303–310
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
McCarthy HD, Jarrett KV, Crawley HF (2001) The development of waist circumference percentiles in British children aged 5.0-16.9 y. Eur J Clin Nutr 55:902–907
Millar JA, Lever AF, Burke V (1999) Pulse pressure as a risk factor for cardiovascular events in the MRC mild hypertension trial. J Hypertens 17:1065–1072
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114(2 Suppl 4th Report):555–576
Nobili V, Svegliati-Baroni G, Alisi A, Miele L, Valenti L, Vajro P (2013) A 360-degree overview of paediatric NAFLD: recent insights. J Hepatol 58:1218–1229
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM (2012) Prevalence of obesity and trends in body mass index among US children and adolescents, 1999-2010. JAMA 307:483–449
Pietrobattista A, Fruwirth R, Natali G, Monti L, Devito R, Nobili V (2009) Is juvenile liver biopsy unsafe? Putting an end to a common misapprehension. Pediatr Radiol 39:959–961
Rosner B, Prineas RJ, Daniels SR, Loggie JMH (2000) Blood pressure differences between blacks and whites in relation to body size among US children and adolescents. Am J Epidemiol 151:1007–1019
Royston P, Sauerbrei W (2008) Multivariable model-building: a pragmatic approach to regression analysis based on fractional polynomials for modelling continuous variables. Wiley, Chichester
Sigala B, McKee C, Soeda J, Pazienza V, Morgan M, Lin CI et al (2013) Sympathetic nervous system catecholamines and neuropeptide Y neurotransmitters are upregulated in human NAFLD and modulate the fibrogenic function of hepatic stellate cells. PLoS One 8:e72928. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072928
Soergel M, Kirschstein M, Busch C, Danne T, Gellermann J, Holl R et al (1997) Oscillometric twenty-four-hour ambulatory blood pressure values in healthy children and adolescents: a multicenter trial including 1141 subjects. J Pediatr 130:178–184
Sorof J, Daniels S (2002) Obesity hypertension in children: a problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension 40:441–447
Sorof JM, Lai D, Turner J, Poffenbarger T, Portman RJ (2004) Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics 113(3 Pt 1):475–482
Vajro P, Lenta S, Socha P, Dhawan A, McKiernan P, Baumann U et al (2012) Diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: position paper of the ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54:700–713
Westerståhl M, Marcus C (2010) Association between nocturnal blood pressure dipping and insulin metabolism in obese adolescents. Int J Obes 34:472–477
Yokoyama H, Emoto M, Fujiwara S, Motoyama K, Morioka T, Komatsu M et al (2003) Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index and reciprocal index of homeostasis model assessment are useful indexes of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 26:2426–2432
Zhou MS, Schulman IH, Zeng Q (2012) Link between the renin–angiotensin system and insulin resistance: implications for cardiovascular disease. Vasc Med 17:330
Conflict of interest
No author has any conflict of interest, financial or otherwise related to the content of the paper.
Funding source
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Ugo Giordano and Claudia Della Corte have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giordano, U., Della Corte, C., Cafiero, G. et al. Association between nocturnal blood pressure dipping and insulin resistance in children affected by NAFLD. Eur J Pediatr 173, 1511–1518 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2342-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2342-2