Abstract
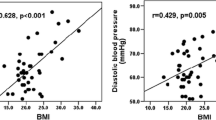
There is a tendency to adiposity in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) despite physiological corticosteroid doses. This study investigated body fatness in children with CAH under corticosteroid replacement therapy. Seventeen children with CAH (female:male, 9:8; age range 1.6–10.5 years) and 18 controls (female:male, 9:9; age range 1.4–10.2 years) were studied. Serum lipids, leptin, insulin, anthropometry, body circumferences, skinfold thickness, and body fat ratio as measured with bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) were the study parameters. Weight standard deviation scores (SDS), body mass index (BMI), BMI–SDS, body circumferences, skinfold thickness, and body fat ratio were higher and leptin was positively correlated with all of the body circumference and skinfold thickness parameters as well as body fat ratio in the study group. Waist/hip ratio was lower in the study group. Body fatness is a serious problem starting in early childhood in CAH patients and further refinement of the glucocorticoid replacement regimens as well as lifestyle measures are needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BC:
-
Body circumference(s)
- BFR:
-
Body fat ratio
- BIA:
-
Bioelectrical impedance analysis
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CAH:
-
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- SDS:
-
Standard deviation score(s)
- ST:
-
Skinfold thickness
References
Charmandari E, Weise M, Bornstein SR, Eisenhofer G, Keil MF, Chrousos GP, Merke DP (2002) Children with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia have elevated serum leptin concentratins and insulin resistance: potential clinical implications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2114–2120
Cornean RE, Hindmarsh PC, Brook CG (1998) Obesity in 21-hydroxylase deficient patients. Arc Dis Child 78:261–263
Lukert BP (2006) Glucocorticoid replacement—how much is enough. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:793–794
Elimam A, Knutson U, Brönnegard M, Stierna P, Albertsson-Wikland K, Marcus C (1998) Variations in glucocorticoid levels within the physiological range affect plasma leptin levels. Eur J Endocrine 139:615–620
Freedman DS, Serdula MK, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS (1999) Relation of circumferences and skinfold thicknesses to lipid and insulin concentrations in children and adolescents: the Bogalusa heart study. Am J Clin Nutr 69:308–317
Hagenfeldt K, Ritzen EM, Ringertz H, Helleday J, Carlström K (2000) Bone mass and body composition of adult women with congenital virilizing 21-hydroxylase deficiency after glucocorticoid treatment since infancy. Eu J Endocrinol 143:667–671
Khaled MA, McCutcheon MJ, Reddy S, Pearman PL, Hunter GR, Weinsier RL (1988) Electrical impedance in assessing human body composition: the BIA method. Am J Clin Nutr 47:789–792
King JA, Wisniewski AB, Bankowski BJ, Carson KA, Zacur HA, Migeon CJ (2006) Long-term corticosteroid replacement and bone mineral density in adult women with classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:865–869
Marshall W, Tanner J (1969) Variation in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch Dis Child 44:291–303
Marshall W, Tanner J (1970) Variation in pattern of pubertal changes in boys. Arch Dis Child 45:13–23
Nanbu A, Kumamoto Y, Tachiki H, Itoh N, Mikuma N, Tsunekawa T, Tagaki Y, Maruta H (1989) A clinical study of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Hinyokika Kiyo Nov 35:1831–1837
New MI, Ghizzoni L, Lin-Su K (2007) An update on congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In: Lifshitz F (ed) Pediatric endocrinology. Informa Healthcare USA, Inc., New York, pp 227–245
Neyzi O, Binyildiz P, Alp H (1979) Growth standards for Turkish children. Courrier 29:553–558
Poyrazoglu S, Gunoz H, Darendeliler F (2003) Serum leptin levels in patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency before and after treatment. Turk J Pediatr 45:33–38
Rolland-Cachera MF, Cole T, Sempe M, Tichet J, Rossignol C, Charraud A (1991) Body mass index variatons. Eur J Clin Nutr 45:13–21
Silva IN, Kater CE, Cunha CF, Viana MB (1997) Randomized controlled trial of growth effect of hydrocortisone in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Arch Dis Child 77:214–220
Slieker LJ, Sloop KW, Surface PL, Kriauciunas A, LaQuier F, Manetta J, Bue-Valleskey J, Stephens TW (1996) Regulation of expression of ob mRNA and protein by glucocorticoids and cAMP. J Biol Chem 271:5301–5304
Tan JTT, Patel KB, Kaplan LM, Koening JI, Hooi SC (1998) Regulation of leptin expression and secretion by corticosteroids and insulin. Endocrine 8:85–92
Taylor WT, Jones IE, Williams SM, Goulding A (2000) Evaluation of waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and the conicity index as screening tools for high trunk fat mass, as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorpsiometry, in children aged 3–19 y. Am J Clin Nutr 72:490–495
Völkl TMK, Simm D, Beier C, Dörr HG (2006) Obesity among children and adolescents with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Pediatrics 117:98–105
Widjaja A, Schürmeyer TH, Von Zur Mühlen A, Brabant G (1998) Determinants of serum leptin levels in Cushing’s syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:600–603
Yu AC, Grant DB (1995) Adult height in women with early-treated congenital adrenal hyperplasia: relation to body mass index in earlier childhood. Acta Pediatr 84:899–903
Zakrzewska K, Cusin I, Stricker-Krongrad A, Boss O, Ricquier D, Jeanrenaud B, Bohner-Jeanrenaud F (1999) Induction of obesity and hyperleptinemia by central glucocorticoid infusions in the rat. Diabetes 48:365–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isguven, P., Arslanoglu, I., Mesutoglu, N. et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis of body fatness in childhood congenital adrenal hyperplasia and its metabolic correlates. Eur J Pediatr 167, 1263–1268 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-007-0665-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-007-0665-y