Abstract
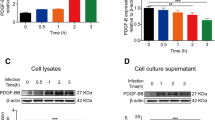
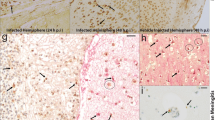
Escherichia coli K1 is the most common Gram-negative bacteria causing neonatal meningitis. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) transmigration across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is the hallmark of bacterial meningitis. Reportedly, the deletion of virulence factor cglD (E44:ΔcglD) from E44 is responsible for a less efficient PMN transendothelial migration ability. In the present study, we found that complementation of the cglD gene into E44:ΔcglD mutant strain might restore the PMN count and myeloperoxidase level in a neonatal mouse meningitis. Using human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs), the main model of the BBB in vitro, we found that E44:ΔcglD mutant strain induced a less efficient PMN adhesion to HBMECs and down-regulated chemokines CXCL1, CXCL6 and CXCL8 and adhesion molecule E-selectin, compared with the E44 strain. Complementation of cglD restored the PMN adhesion to HBMECs and the level of these proteins. E44:ΔcglD mutant strain also induced a less efficient NF-κB pathway activation in HBMECs and reduced the soluble p65 (sp65) level in the cerebral spinal fluid of newborn mice, compared with the E44 strain. Complementation of cglD restored the NF-κB pathway activation and increased the sp65 levels. This suggests that cglD in E44 contributes to NF-κB pathway activation in the brain endothelium to promote PMN adhesion to HBMECs and transendothelial migration. Our identified novel requirement of cglD for immune activation and subsequent PMN entry into the central nervous system suggests that therapies directed at neutralising this molecule will be beneficial in preventing bacterial meningitis progression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grandgirard D, Leib SL (2006) Strategies to prevent neuronal damage in paediatric bacterial meningitis. Curr Opin Pediatr 18:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mop.0000193292.09894.b7
Korhonen TK, Valtonen MV, Parkkinen J, Vaisanen-Rhen V, Finne J, Orskov F, Orskov I, Svenson SB, Makela PH (1985) Serotypes, hemolysin production, and receptor recognition of Escherichia coli strains associated with neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Infect Immun 48:486–491
Huang SH, Stins MF, Kim KS (2000) Bacterial penetration across the blood-brain barrier during the development of neonatal meningitis. Microbes Infect 2:1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1286-4579(00)01277-6
Kim KS (2008) Mechanisms of microbial traversal of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:625–634. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1952
Zhang K, Zhao WD, Li Q, Fang WG, Zhu L, Shang DS, Chen YH (2009) Tentative identification of glycerol dehydrogenase as Escherichia coli K1 virulence factor cglD and its involvement in the pathogenesis of experimental neonatal meningitis. Med Microbiol Immunol 198(3):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-009-0119-4
Huang SH, Chen YH, Kong G, Chen S, Besemer J, Borodovsky M, Jong A (2001) A novel genetic island of meningitic Escherichia coli K1 containing the ibeA invasion gene (GimA): functional annotation and carbon-source-regulated invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Funct Integr Genom 1:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s101420100039
Wang S, Peng L, Gai Z, Zhang L, Jong A, Cao H, Huang SH (2016) Pathogenic triad in bacterial meningitis: pathogen invasion, NF-κB activation, and leukocyte transmigration that occur at the blood-brain barrier. Front Microbiol 7:148. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00148
Doulet N, Donnadieu E, Laran-Chich MP, Niedergang F, Nassif X, Couraud PO, Bourdoulous S (2006) Neisseria meningitidis infection of human endothelial cells interferes with leukocyte transmigration by preventing the formation of endothelial docking structures. J Cell Biol 173(4):627–637. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200507128
Banerjee A, Van Sorge NM, Sheen TR, Uchiyama S, Mitchell TJ, Doran KS (2010) Activation of brain endothelium by pneumococcal neuraminidase NanA promotes bacterial internalization. Cell Microbiol 12(11):1576–1588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01490.x
Doran KS, Liu GY, Nizet V (2003) Group B streptococcal beta-hemolysin/cytolysin activates neutrophil signaling pathways in brain endothelium and contributes to development of meningitis. J Clin Invest 112(5):736–744. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI17335
Palomino DC, Marti LC (2015) Chemokines and immunity. Einstein 13(3):469–473. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-45082015RB3438
Carlos TM, Harlan JM (1994) Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood 84(7):2068–2101
van der Flier M, Geelen SP, Kimpen JL, Hoepelman IM, Tuomanen EI (2003) Reprogramming the host response in bacterial meningitis: how best to improve outcome? Clin Microbiol Rev 16(3):415–429. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.16.3.415-429.2003
Middleton J, Neil S, Wintle J, Clark-Lewis I, Moore H, Lam C, Auer M, Hub E, Rot A (1997) Transcytosis and surface presentation of IL-8 by venular endothelial cells. Cell 91:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80422-5
Kunsch C, Rosen CA (1993) NF-kappa B subunit-specific regulation of the interleukin-8 promoter. Mol Cell Biol 13(10):6137–6146. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.13.10.6137
Blackwell TS, Holden EP, Blackwell TR, DeLarco JE, Christman JW (1994) Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant mediates neutrophilic alveolitis in rats: association with nuclear factor kappa B activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11(4):464–472. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.11.4.7917314
Smith JB, Wadleigh DJ, Xia YR, Mar RA, Herschman HR, Lusis AJ (2002) Cloning and genomic localization of the murine LPS-induced CXC chemokine (LIX) gene, Scyb5. Immunogenetics 54(8):599–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-002-0501-5
Schindler U, Baichwal VR (1994) Three NF-kappa B binding sites in the human E-selectin gene required for maximal tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced expression. Mol Cell Biol 14(9):5820–5831. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.14.9.5820
Huang SH, Chi F, Peng L, Bo T, Zhang B, Liu LQ, Wu X, Mor-Vaknin N, Markovitz DM, Cao H, Zhou YH (2016) Vimentin, a Novel NF-κB regulator, is required for meningitic Escherichia coli K1-induced pathogen invasion and PMN transmigration across the blood-brain barrier. PLoS One 11(9):e0162641. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162641
Galanakis E, Di Cello F, Paul-Satyaseela M, Kim KS (2006) Escherichia coli K1 induces IL-8 expression in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Eur Cytokine Netw 17(4):260–265. https://doi.org/10.1684/ecn.2006.0042
Selvaraj SK, Periandythevar P, Prasadarao NV (2007) Outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli K1 selectively enhances the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microbes Infect 9(5):547–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2007.01.020
Che X, Chi F, Wang L, Jong TD, Wu CH, Wang X, Huang SH (2011) Involvement of IbeA in meningitic Escherichia coli K1-induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration across brain endothelial cells. Brain Pathol 21(4):389–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00463.x
Zou Y, He L, Wu CH, Cao H, Xie ZH, Ouyang Y, Wang Y, Jong A, Huang SH (2007) PSF is an IbeA-binding protein contributing to meningitic Escherichia coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Med Microbiol Immunol 196(3):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-006-0034-x
Neurath MF, Becker C, Barbulescu K (1998) Role of NF-kappaB in immune and inflammatory responses in the gut. Gut 43(6):856–860. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.43.6.856
Selvaraj SK, Prasadarao NV (2005) Escherichia coli K1 inhibits proinflammatory cytokine induction in monocytes by preventing NF-kappaB activation. J Leukoc Biol 78(2):544–554. https://dol.org/ https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0904516
Meeker RB, Williams K, Killebrew DA, Hudson LC (2012) Cell trafficking through the choroid plexus. Cell Adhes Migr 6(5):390–396. https://doi.org/10.4161/cam.21054
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81101225) and the Student’s Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (201710159000024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Shi, MJ., Niu, Z. et al. Activation of brain endothelium by Escherichia coli K1 virulence factor cglD promotes polymorphonuclear leukocyte transendothelial migration. Med Microbiol Immunol 208, 59–68 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-018-0560-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-018-0560-3