Abstract.
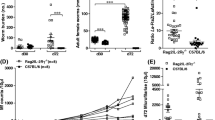
We compared the impact of IL-4 and IL-5 deficiency during the fully permissive infection of BALB/c mice with the rodent filaria Litomosoides sigmodontis. IL-5, in contrast to IL-4, is crucial for the containment of adult worms during short- and long-term infections. IL-5 KO mice allowed development of more larvae into adult worms and showed up to 200 times more adult worms persisting during chronic infection (day 60 until 200 post-infection). This increased persistence was accompanied by a reduction in inflammatory nodules around adult filariae. In contrast, adult worm survival and nodule formation did not differ between BALB/c wild-type mice and BALB/c IL-4 KO or BALB/c IL-4 receptor (IL-4R) α-chain KO mice. In both IL-4 and IL-5 KO mice microfilaraemia was greatly enhanced (160-fold) and prolonged compared to wild-type mice. This extent of susceptibility to microfilariae required the presence of adult worms in a full infection cycle since upon intraperitoneal injection of microfilariae alone they were removed from BALB/c, BALB/c IL-4 KO and BALB/c IL-4R α-chain KO mice with equivalent kinetics, and since microfilarial survival was only slightly increased in IL-5 KO mice (factor of 5 vs. factor of 160 in full infection). In conclusion, IL-4 and IL-5 dependent effector pathways operate against different stages of filarial worms, and IL-5 has a greater impact on parasite containment than IL-4.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkmann, L., Bain, O., Saeftel, M. et al. Murine filariasis: interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 lead to containment of different worm developmental stages. Med Microbiol Immunol 192, 23–31 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-002-0155-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-002-0155-9