Abstract
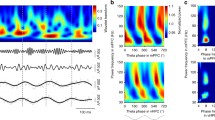
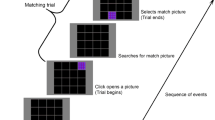
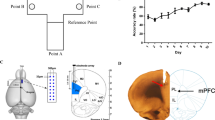
Spatial working memory (SWM) refers to a short-term system for temporary manipulation of spatial information and requires the cooperation of multiple brain regions. Despite evidence that the hippocampus (HPC) and prefrontal cortex (PFC) are involved in SWM, how the PFC and HPC interact during SWM remains puzzling. In this study, local field potentials (LFPs) were recorded simultaneously from rat ventral HPC and medial PFC during SWM tasks firstly. A cross-frequency coupling algorithm was used to test for functional connectivity in the PFC and HPC. Granger causality (GC) algorithm was used to test for effective connectivity in the PFC and HPC. Finally, concurrent interactions across two brain regions were analyzed based on functional connectivity and effective connectivity. Experimental results show that the LFPs power in the PFC and HPC decreased during the learning period and peaked before the rats’ behavioral selection during SWM. Moreover, the LFPs power mainly distributed in theta and gamma that are related to SWM. In relation to the functional connectivity, the effect of activity transmission during SWM in the PFC and HPC is the same; the phase–amplitude coupling (PAC) between gamma in the PFC and theta in the HPC is correlated with the formation of SWM and supports concurrent interactions between the PFC and HPC. In relation to the effective connectivity, the directed activity transmission in the HPC is greater than that in the PFC during SWM, indicating flow of activity from the HPC to the PFC.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data and materials used in this study are available on request, please contact the corresponding author.
Code availability
The code and analysis routines used in this study are available on request, please contact the corresponding author.
References
Anderson KL, Rajagovindan R, Ghacibeh GA, Meador KJ, Ding M (2010) Theta oscillations mediate interaction between prefrontal cortex and medial temporal lobe in human memory. Cereb Cortex 20(7):1604–1612. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp223
Andino-Pavlovsky V, Souza AC, Scheffer-Teixeira R, Tort AB, Etchenique R, Ribeiro S (2017) Dopamine modulates delta-gamma phase-amplitude coupling in the prefrontal cortex of behaving rats. Front Neural Circuits 11:29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2017.00029
Axmacher N, Henseler MM, Jensen O, Weinreich I, Elger CE, Fell J (2010) Cross-frequency coupling supports multi-item working memory in the human hippocampus. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107(7):3228–3233. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911531107
Babiloni F, Cincotti F, Babiloni C, Carducci F, Mattia D, Astolfi L, Basilisco A, Rossini PM, Ding L, Ni Y, Cheng J, Christine K, Sweeney J, He B (2005) Estimation of the cortical functional connectivity with the multimodal integration of high-resolution EEG and fMRI data by directed transfer function. Neuroimage 24(1):118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.09.036
Barrett AB, Murphy M, Bruno MA, Noirhomme Q, Boly M, Laureys S, Seth AK (2012) Granger causality analysis of steady-state electroencephalographic signals during propofol-induced anaesthesia. PLoS ONE 7:e29072. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029072
Blinowska KJ, Kus R, Kaminski M, Janiszewska J (2010) Transmission of brain activity during cognitive task. Brain Topogr 23:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0137-y
Bressler SL, Seth AK (2011) Wiener-Granger causality: a well established methodology. Neuroimage 58(2):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.059
Brockmann MD, Pöschel B, Cichon N, Hanganu-Opatz IL (2011) Coupled oscillations mediate directed interactions between prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of the neonatal rat. Neuron 71(2):332–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.041
Brzezicka A, Kaminski M, Kaminski J, Blinowska KJ (2010) Information transfer during transitive reasoning task. Brain Topogr 24:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0158-6
Buzsaki G, Draguhn A (2004) Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 304(5679):1926–1929. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1099745
Canal MR (2010) Comparison of wavelet and short time Fourier Transform methods in the analysis of EMG signals. J Med Syst 34(1):91–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9219-8
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2004) Dopaminergic modulation of visual attention and working memory in the rodent prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1628–1636. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300490
Colgin LL (2011) Oscillations and hippocampal–prefrontal synchrony. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21(3):467–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2011.04.006
Das A, Menon V (2021) Asymmetric frequency-specific feedforward and feedback information flow between hippocampus and prefrontal cortex during verbal memory encoding and recall. J Neurosci 41(40):8427–8440. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0802-21.2021
Dashtestani H, Zaragoza R, Pirsiavash H, Knutson KM, Kermanian R, Cui J, Harrison JD, Halem M, Gandjbakhche A (2019) Canonical correlation analysis of brain prefrontal activity measured by functional near infra-red spectroscopy (fNIRS) during a moral judgment task. Behav Brain Res 359:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.10.022
Daume J, Gruber T, Engel AK, Friese U (2017) Phase–amplitude coupling and long-range phase synchronization reveal frontotemporal interactions during visual working memory. J Neurosci 37(2):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2130-16.2016
Deacon RMJ, Rawlins GNP (2006) T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat Protoc 1:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.2
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Meth 134(1):9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009
Fell J, Axmacher N (2011) The role of phase synchronization in memory processes. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:105–118
Gao Q, Duan X, Chen H (2011) Evaluation of effective connectivity of motor areas during motor imagery and execution using conditional Granger causality. Neuroimage 54(2):1280–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.071
Goodman MS, Kumar S, Zomorrodi R, Ghazala Z, Cheam ASM, Barr MS, Daskalakis ZJ, Blumberger DM, Fischer C, Flint A, Mah L, Herrmann N, Bowie CR, Mulsant BH, Rajji TK (2018) Theta-gamma coupling and working memory in Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Front Aging Neurosci 10:101. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00101
Hallock HL, Wang A, Griffin AL (2016) Ventral midline thalamus is critical for hippocampal–prefrontal synchrony and spatial working memory. J Neurosci 36(32):8372–8389. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0991-16.2016
Hardoon DR, Szedmak S, Shawe-Taylor J (2004) Canonical correlation analysis: an overview with application to learning methods. Neural Comput 16(12):2639–2664. https://doi.org/10.1162/0899766042321814
Haupt M, Eccard JA, Winter Y (2010) Does spatial learning ability of common voles (Microtus arvalis) and bank voles (Myodes glareolus) constrain foraging efficiency? Anim Cogn 13(6):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-010-0327-8
Hoover WB, Vertes RP (2007) Anatomical analysis of afferent projections to the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat. Brain Struct Funct 212:149–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-007-0150-4
Hurtado JM, Rubchinsky LL, Sigvardt KA (2004) Statistical method for detection of phase-locking episodes in neural oscillations. J Neurophysiol 91(4):1883–1898
Hyman JM, Zilli EA, Paley AM, Hasselmo ME (2010) Working memory performance correlates with prefrontal–hippocampal theta interactions but not with prefrontal neuron firing rates. Front Integr Neurosci 4:2. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.07.002.2010
Hyvarinen A, Ramkumar P, Parkkonen L, Hari R (2010) Independent component analysis of short-time Fourier transforms for spontaneous EEG/MEG analysis. Neuroimage 49(1):257–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.028
Jafakesh S, Jahromy FZ, Daliri MR (2016) Decoding of object categories from brain signals using cross frequency coupling methods. Biomed Signal Proces 27:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2016.01.013
Jay TM, Glowinski J, Thierry AM (1990) Selectivity of the hippocampal projection to the prelimbic area of the prefrontal cortex in the rat. Brain Res 505(2):337–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)91464-9
Jones MW, Wilson MA (2005) Theta rhythms coordinate hippocampal–prefrontal interactions in a spatial memory task. PLoS Biol 3(12):e402. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0030402
Liao W, Mantini D, Zhang Z, Pan Z, Ding J, Gong Q, Yang Y, Chen H (2010) Evaluating the effective connectivity of resting state networks using conditional Granger causality. Biol Cybern 102(1):57–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0350-5
Liu T, Bai W, Xia M, Tian X (2018) Directional hippocampal–prefrontal interactions during working memory. Behav Brain Res 338:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.10.003
Lu Y, Yang L, Worrell GA, He B (2012) Seizure source imaging by means of fine spatio-temporal dipole localization and directed transfer function in partial epilepsy patients. Clin Neurophysiol 123:1275–1283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2011.11.007
Mitra P, Bokil H (2008) Observed brain dynamics. Oxford University Press
Nicolai CV, Engler G, Sharott A, Engel AK, Moll CK, Siegel M (2014) Corticostriatal coordination through coherent phase–amplitude coupling. J Neurosci 34(17):5938–5948. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5007-13.2014
Oehrn CR, Fell J, Baumann C, Rosburg T, Ludowig E, Kessler H, Hanslmayr S, Axmacher N (2018) Direct electrophysiological evidence for prefrontal control of hippocampal processing during voluntary forgetting. Curr Biol 28(18):3016–3022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.042
O’Neill PK, Gordon JA, Sigurdsson T (2013) Theta oscillations in the medial prefrontal cortex are modulated by spatial working memory and synchronize with the hippocampus through its ventral subregion. J Neurosci 33(35):14211–14224. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2378-13.2013
Onslow A, Bogacz R, Jones MW (2011) Quantifying phase–amplitude coupling in neuronal network oscillations. Prog Biophys Mol Bio 105(1–2):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2010.09.007
Park HJ, Friston K (2013) Structural and functional brain networks: from connections to cognition. Science 342(6158):1238411. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1238411
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Rajan A, Siegel SN, Liu Y, Bengson J (2018) Theta oscillations index frontal decision-making and mediate reciprocal frontal–parietal interactions in willed attention. Cereb Cortex 29(7):2832–2843. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy149
Recasens M, Gross J, Uhlhaas PJ (2018) Low-frequency oscillatory correlates of auditory predictive processing in cortical–subcortical networks: a MEG-study. Sci Rep 8(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32385-3
Seth AK (2005) Causal connectivity of evolved neural networks during behavior. Network Comp Neural 16(1):35–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/09548980500238756
Sirota A, Montgomery S, Fujisawa S, Isomura Y, Zugaro M, Buzsáki G (2008) Entrainment of neocortical neurons and gamma oscillations by the hippocampal theta rhythm. Neuron 60(4):683–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.09.014
Spellman T, Rigotti M, Ahmari SE, Fusi S, Gogos JA, Gordon JA (2015) Hippocampal-prefrontal input supports spatial encoding in working memory. Nature 522(7556):309–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14445
Squire LR, Stark CE, Clark RE (2004) The medial temporal lobe. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:279–306. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144130
Stevenson RF, Zheng J, Mnatsakanyan L, Vadera S, Knight RT, Lin JJ, Yassa MA (2018) Hippocampal CA1 gamma power predicts the precision of spatial memory judgments. P Natl Acad Sci USA 115(40):10148–10153. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1805724115
Tamura M, Spellman TJ, Rosen AM, Gogos GA, Gordon JA (2017) Hippocampal-prefrontal theta-gamma coupling during performance of a spatial working memory task. Nat Commun 8(1):2182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02108-9
Thierry AM, Gioanni Y, Dégénétais E, Glowinski J (2000) Hippocampo-prefrontal cortex pathway: anatomical and electrophysiological characteristics. Hippocampus 10(4):411–419. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-1063(2000)10:43.0.CO;2-A
Tort ABL, Komorowski RW, Manns JR, Kopell NJ, Eichenbaume H (2009) Theta-gamma coupling increases during the learning of item–context associations. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106(49):20942–20947. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911331106
Wimmer K, Nykamp DQ, Constantinidis C, Compte A (2014) Bump attractor dynamics in prefrontal cortex explains behavioral precision in spatial working memory. Nat Neurosci 17(3):431–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3645
Xia M, Liu T, Bai W, Zheng X, Tian X (2019) Information transmission in HPC-PFC network for spatial working memory in rat. Behav Brain Res 356:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.024
Yamamoto J, Suh J, Takeuchi D, Tonegawa S (2014) Successful execution of working memory linked to synchronized high-frequency gamma oscillations. Cell 157(4):845–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.009
Zhang D, Zhao H, Bai W, Tian X (2016) Functional connectivity among multi-channel EEGs when working memory load reaches the capacity. Brain Res 1631:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.11.036
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yu H, Yang Y, Li W, Qian Z (2017) Theta-gamma coupling in hippocampus during working memory deficits induced by low frequency electromagnetic field exposure. Physiol Behav 179:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.05.033
Zhang W, Guo L, Liu D, Xu G (2020) The dynamic properties of a brain network during working memory based on the algorithm of cross-frequency coupling. Cogn Neurodynamics 14(2):215–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-019-09562-9
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 52077056 and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province under Grant E2020202033.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the Guideline for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Approval was granted by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Hebei University of Technology (No. HEBUTaCUC2019002).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Guo, L. & Liu, D. Concurrent interactions between prefrontal cortex and hippocampus during a spatial working memory task. Brain Struct Funct 227, 1735–1755 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-022-02469-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-022-02469-y