Abstract
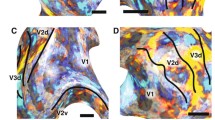
Previous studies have revealed modular projections from area V2 to area V4 in macaques. Specifically, V2 neurons in cytochrome oxidase (CO)-rich thin and CO-sparse pale stripes project to distinct regions in V4. However, how these modular projections relate to the functional subcompartments of V4 remains unclear. In this study, we injected retrograde fluorescent tracers into V4 regions with different functional properties (color, orientation, and direction) that were identified with intrinsic signal optical imaging (ISOI). We examined the labeled neurons in area V2 and their locations with respect to the CO patterns. Covariation was observed between the functional properties of the V4 injection sites and the numbers of labeled neurons in particular CO stripes. This covariation indicates that the color domains in V4 mainly received inputs from thin stripes in V2, whereas V4 orientation domains received inputs from pale stripes. Although motion-sensitive domains are present in both V2 and V4, our results did not reveal a functional specific feedforward projection between them. These results confirmed previous findings of modular projections from V2 to V4 and provided functional specificity for these anatomical projections. Together, these findings indicate that color and form remain separate in ventral mid-level visual processing.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data have been included in the manuscript and supporting information. Original data are available upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Codes are available upon reasonable request.
References
Chang C-C, Lin C-J (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol TIST 2:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1145/1961189.1961199
Chen G, Lu HD, Roe AW (2008) A map for horizontal disparity in monkey V2. Neuron 58:442–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.02.032
Chen M, Li P, Zhu S et al (2016) An orientation map for motion boundaries in macaque V2. Cereb Cortex 26:279–287. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu235
Conway BR, Moeller S, Tsao DY (2007) Specialized color modules in macaque extrastriate cortex. Neuron 56:560–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.10.008
De Yoe EA, Van Essen DC (1985) Segregation of efferent connections and receptive field properties in visual area V2 of the macaque. Nature 317:58–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/317058a0
De Yoe EA, Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC, McClendon E (1994) Multiple processing streams in occipitotemporal visual cortex. Nature 371:151–154. https://doi.org/10.1038/371151a0
Desimone R, Schein SJ (1987) Visual properties of neurons in area V4 of the macaque: sensitivity to stimulus form. J Neurophysiol 57:835–868. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1987.57.3.835
Fang Y, Chen M, Xu H et al (2019) An orientation map for disparity-defined edges in area V4. Cereb Cortex 29:666–679. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx348
Federer F, Williams D, Ichida JM et al (2013) Two projection streams from macaque V1 to the pale cytochrome oxidase stripes of V2. J Neurosci 33:11530–11539. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5053-12.2013
Felleman DJ, Xiao Y, McClendon E (1997) Modular organization of occipito-temporal pathways: cortical connections between visual area 4 and visual area 2 and posterior inferotemporal ventral area in macaque monkeys. J Neurosci 17:3185–3200. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-09-03185.1997
Ferrera VP, Nealey TA, Maunsell JH (1992) Mixed parvocellular and magnocellular geniculate signals in visual area V4. Nature 358:756–758. https://doi.org/10.1038/358756a0
Ferrera V, Rudolph K, Maunsell J (1994a) Responses of neurons in the parietal and temporal visual pathways during a motion task. J Neurosci 14:6171–6186. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-10-06171.1994
Ferrera VP, Nealey TA, Maunsell JH (1994b) Responses in macaque visual area V4 following inactivation of the parvocellular and magnocellular LGN pathways. J Neurosci 14:2080–2088. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-02080.1994
Franken TP, Reynolds JH (2021) Columnar processing of border ownership in primate visual cortex. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.06.455427
Gattass R, Sousa AP, Mishkin M, Ungerleider LG (1997) Cortical projections of area V2 in the macaque. Cereb Cortex 7:110–129. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/7.2.110
Gegenfurtner KR (2003) Cortical mechanisms of colour vision. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:563–572. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1138
Gegenfurtner KR, Kiper DC, Fenstemaker SB (1996) Processing of color, form, and motion in macaque area V2. Vis Neurosci 13:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0952523800007203
Ghose GM, Ts’o DY (1997) Form processing modules in primate area V4. J Neurophysiol 77:2191–2196. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1997.77.4.2191
Hu JM, Song XM, Wang Q, Roe AW (2020) Curvature domains in V4 of macaque monkey. Elife 9:e57261. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.57261
Hubel DH, Livingstone MS (1985) Complex–unoriented cells in a subregion of primate area 18. Nature 315:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/315325a0
Hubel DH, Livingstone MS (1987) Segregation of form, color, and stereopsis in primate area 18. J Neurosci 7:3378–3415. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03378.1987
Levitt JB, Kiper DC, Movshon JA (1994) Receptive fields and functional architecture of macaque V2. J Neurophysiol 71:2517–2542. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1994.71.6.2517
Li P, Zhu S, Chen M et al (2013) A Motion Direction Preference Map in Monkey V4. Neuron 78:376–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.024
Lu HD, Chen G, Tanigawa H, Roe AW (2010) A motion direction map in macaque V2. Neuron 68:1002–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.020
Maunsell JH, van Essen DC (1983) The connections of the middle temporal visual area (MT) and their relationship to a cortical hierarchy in the macaque monkey. J Neurosci 3:2563–2586. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-12-02563.1983
Maunsell JH, Nealey TA, DePriest DD (1990) Magnocellular and parvocellular contributions to responses in the middle temporal visual area (MT) of the macaque monkey. J Neurosci 10:3323–3334. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-10-03323.1990
Nakamura H, Gattass R, Desimone R, Ungerleider LG (1993) The modular organization of projections from areas V1 and V2 to areas V4 and TEO in macaques. J Neurosci 12:3681–3691. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03681.1993
Nascimento-Silva S, Gattass R, Fiorani M Jr, Sousa APB (2003) Three streams of visual information processing in V2 of Cebus monkey. J Comp Neurol 466:104–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10878
Nascimento-Silva S, Pinõn C, Soares JGM, Gattass R (2014) Feedforward and feedback connections and their relation to the cytox modules of V2 in Cebus monkeys. J Comp Neurol 522:3091–3105. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23571
Pasupathy A, Popovkina DV, Kim T (2020) Visual functions of primate area V4. Annu Rev vis Sci 6:363–385. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-vision-030320-041306
Peres R, Soares JGM, Lima B et al (2018) Neuronal response properties across cytochrome oxidase stripes in primate V2. J Comp Neurol 527:651–667. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24518
Peterhans E, von der Heydt R (1993) Functional organization of area V2 in the alert macaque. Eur J Neurosci 5:509–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00517.x
Rockland KS, Pandya DN (1979) Laminar origins and terminations of cortical connections of the occipital lobe in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 179:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(79)90485-2
Roe AW, Ts’o DY (1995) Visual topography in primate V2: multiple representation across functional stripes. J Neurosci 15:3689–3715. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03689.1995
Roe AW, Chelazzi L, Connor CE et al (2012) Toward a unified theory of visual area V4. Neuron 74:12–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.011
Schmid MC, Schmiedt JT, Peters AJ et al (2013) Motion-sensitive responses in visual area V4 in the absence of primary visual cortex. J Neurosci 33:18740–18745. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3923-13.2013
Shipp S, Zeki S (1985) Segregation of pathways leading from area V2 to areas V4 and V5 of macaque monkey visual cortex. Nature 315:322–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/315322a0
Shipp S, Zeki S (1989) The organization of connections between areas V5 and V2 in macaque monkey visual cortex. Eur J Neurosci 1:333–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00799.x
Shipp S, Zeki S (2002) The functional organization of area V2, I: specialization across stripes and layers. Vis Neurosci 19:187–210. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0952523802191164
Shipp S, Adams DL, Moutoussis K, Zeki S (2009) Feature binding in the feedback layers of area V2. Cereb Cortex 19:2230–2239. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhn243
Srinath R, Emonds A, Wang Q et al (2021) Early emergence of solid shape coding in natural and deep network vision. Curr Biol 31:51-65.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.09.076
Tanabe S, Doi T, Umeda K, Fujita I (2005) Disparity-tuning characteristics of neuronal responses to dynamic random-dot stereograms in macaque visual area V4. J Neurophysiol 94:2683–2699. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00319.2005
Tang R, Song Q, Li Y et al (2020) Curvature-processing domains in primate V4. Elife 9:e57502. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.57502
Tanigawa H, Lu HD, Roe AW (2010) Functional organization for color and orientation in macaque V4. Nat Neurosci 13:1542–1548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2676
Tso DY, Frostig RD, Lieke EE, Grinvald A (1990) Functional organization of primate visual cortex revealed by high resolution optical imaging. Science 249:417–420. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2165630
Ts’o DY, Roe AW, Gilbert CD (2001) A hierarchy of the functional organization for color, form and disparity in primate visual area V2. Vision Res 41:1333–1349. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6989(01)00076-1
Ungerleider LG, Galkin TW, Desimone R, Gattass R (2008) Cortical connections of area V4 in the macaque. Cereb Cortex 18:477–499. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhm061
Wang YI, Xiao Y, Felleman DJ (2007) V2 thin stripes contain spatially organized representations of achromatic luminance change. Cereb Cortex 17:116–129. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhj131
Wong-Riley M (1979) Changes in the visual system of monocularly sutured or enucleated cats demonstrable with cytochrome oxidase histochemistry. Brain Res 171:11–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(79)90728-5
Xiao Y, Zych A, Felleman DJ (1999) Segregation and convergence of functionally defined V2 Thin stripe and interstripe compartment projections to area V4 of macaques. Cereb Cortex 9:792–804. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/9.8.792
Xiao Y, Wang Y, Felleman DJ (2003) A spatially organized representation of colour in macaque cortical area V2. Nature 421:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01372
Xiao Y, Rao R, Cecchi G, Kaplan E (2008) Improved mapping of information distribution across the cortical surface with the support vector machine. Neural Netw 21:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2007.12.022
Zeki S, Shipp S (1989) Modular connections between areas V2 and V4 of macaque monkey visual cortex. Eur J Neurosci 1:494–506. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00356.x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31625012, 31530029, and 31371111). We thank Dr. Xiaohui Zhang and Dr. Yousheng Shu for their valuable technical support. We thank laboratory members (Rendong Tang, Heng Ma, Qianling Song, Pengcheng Li, Jie Lu, Yan Xiao, Peichao Li, Jiaming Hu, Haoran Xu, and Yang Fang) for providing technical assistance.
Funding
The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 31625012, 31530029, and 31371111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CF, KY, CL, JW, RZ and XC performed the experiments; CF, HDL and KY designed the research; all the authors participated in the analysis; CF and HDL interpreted the results and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Beijing Normal University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable. No human subjects.
Consent for publication
Not applicable. No human subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, C., Yan, K., Liang, C. et al. Function-specific projections from V2 to V4 in macaques. Brain Struct Funct 227, 1317–1330 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02440-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02440-3