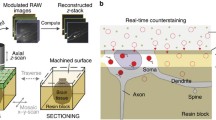
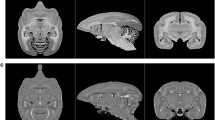
Abstract
We describe our connectomics pipeline for processing anterograde tracer injection data for the brain of the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Brain sections were imaged using a batch slide scanner (NanoZoomer 2.0-HT) and we used artificial intelligence to precisely segment the tracer signal from the background in the fluorescence images. The shape of each brain was reconstructed by reference to a block-face and all data were mapped into a common 3D brain space with atlas and 2D cortical flat map. To overcome the effect of using a single template atlas to specify cortical boundaries, brains were cyto- and myelo-architectonically annotated to create individual 3D atlases. Registration between the individual and common brain cortical boundaries in the flat map space was done to absorb the variation of each brain and precisely map all tracer injection data into one cortical brain space. We describe the methodology of our pipeline and analyze the accuracy of our tracer segmentation and brain registration approaches. Results show our pipeline can successfully process and normalize tracer injection experiments into a common space, making it suitable for large-scale connectomics studies with a focus on the cerebral cortex.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, Brevdo E, Chen Z, Citro C, Corrado G, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M, Ghemawat S, Goodfellow I, Harp A, Irving G, Isard M, Jia Y, Jozefowicz R, Kaiser L, Kudlur M, Levenberg J, Mané D, Monga R, Moore S, Murray D, Olah C, Schuster M, Shlens J, Steiner B, Sutskever I, Talwar K, Tucker P, Vanhoucke V, Vasudevan V, Viégas F, Vinyals O, Warden P, Wattenberg M, Wicke M, Yu Y, Zheng X (2015) TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. https://research.google.com/pubs/pub45166.html. Accessed 20 May 2019
Abe H, Tani T, Mashiko H, Kitamura N, Miyakawa N, Mimura K, Sakai K, Suzuki W, Kurotani T, Mizukami H, Watakabe A, Yamamori T, Ichinohe N (2017) 3D reconstruction of brain section images for creating axonal projection maps in marmosets. J Neurosci Methods 286:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.04.016
Abe H, Tani T, Mashiko H, Kitamura N, Hayami T, Watanabe S, Sakai K, Suzuki W, Mizukami H, Watakabe A, Yamamori T, Ichinohe N (2018) Axonal projections from the middle temporal area in the common marmoset. Front Neuroanat 12:89. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00089
Avants BB, Epstein CL, Grossman M, Gee JC (2008) Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med Image Anal 12(1):26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2007.06.004
Avants BB, Tustison NJ, Song G, Cook PA, Klein A, Gee JC (2011) A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. Neuroimage 54(3):2033–2044
Bakker R, Wachtler T, Diesmann M (2012) Cocomac 2.0 and the future of tract-tracing databases. Front Neuroinform 6:30
Bota M, Sporns O, Swanson LW (2015) Architecture of the cerebral cortical association connectome underlying cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(16):E2093–E2101. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504394112
Bradski G (2000) The opencv library. Dr Dobb's J. Softw Tools 25:120–125
Chollet F et al (2015) Keras. https://keras.io. Accessed 20 May 2019
Dunn OJ (1964) Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6(3):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1964.10490181
Gaffling S, Daum V, Steidl S, Maier A, Köstler H, Hornegger J (2015) A gauss-seidel iteration scheme for reference-free 3-D histological image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(2):514–530
Geyer S, Schleicher A, Zilles K (1999) Areas 3a, 3b, and 1 of human primary somatosensory cortex: 1. Microstructural organization and interindividual variability. Neuroimage 10(1):63–83. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1999.0440
Gorgolewski K, Burns CD, Madison C, Clark D, Halchenko YO, Waskom ML, Ghosh SS (2011) Nipype: a flexible, lightweight and extensible neuroimaging data processing framework in python. Front Neuroinform 5:13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2011.00013
Grillner S, Ip N, Koch C, Koroshetz W, Okano H, Polachek M, Poo M, Sejnowski T (2016) Worldwide initiatives to advance brain research. Nat Neurosci 19(9):1118–1122. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4371
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Bach F, Blei D (eds) Proceedings of the 32nd international conference on international conference on machine learning (ICML 2015), vol 37. PMLR, Lille, France, pp 448–456
Jorgenson LA, Newsome WT, Anderson DJ, Bargmann CI, Brown EN, Deisseroth K, Donoghue JP, Hudson KL, Ling GSF, MacLeish PR, Marder E, Normann RA, Sanes JR, Schnitzer MJ, Sejnowski TJ, Tank DW, Tsien RY, Ugurbil K, Wingfield JC (2015) The brain initiative: developing technology to catalyse neuroscience discovery. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 370(1668):20140164. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0164
Kapur J, Sahoo P, Wong A (1985) A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 29(3):273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/0734-189X(85)90125-2
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Klein A, Andersson J, Ardekani BA, Ashburner J, Avants B, Chiang MC, Christensen GE, Collins DL, Gee J, Hellier P, Song JH, Jenkinson M, Lepage C, Rueckert D, Thompson P, Vercauteren T, Woods RP, Mann JJ, Parsey RV (2009) Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. Neuroimage 46(3):786–802
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1952) Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 47(260):583–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1952.10483441
Kuan L, Li Y, Lau C, Feng D, Bernard A, Sunkin SM, Zeng H, Dang C, Hawrylycz M, Ng L (2015) Neuroinformatics of the Allen Mouse brain connectivity atlas. Methods 73:4–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.12.013
Lin M, Takahashi Y, Huo B, Hanada M, Nagashima J, Hata J, Tolpygo A, Ram K, Lee B, Miller M, Rosa M, Sasaki E, Iriki A, Okano H, Mitra P (2019) A high-throughput neurohistological pipeline for brain-wide mesoscale connectivity mapping of the common marmoset. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40042
Lowekamp BC, Chen DT, Ibáñez L, Blezek D (2013) The design of SimpleITK. Front Neuroinform 7:45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2013.00045
Majka P, Chaplin TA, Yu HH, Tolpygo A, Mitra PP, Wójcik DK, Rosa MGP (2016) Towards a comprehensive atlas of cortical connections in a primate brain: mapping tracer injection studies of the common marmoset into a reference digital template. J Comp Neurol 524(11):2161–2181
Marcus D, Harwell J, Olsen T, Hodge M, Glasser M, Prior F, Jenkinson M, Laumann T, Curtiss S, Van Essen D (2011) Informatics and data mining tools and strategies for the human connectome project. Front Neuroinform 5:4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2011.00004
Markov NT, Ercsey-Ravasz MM, Ribeiro Gomes AR, Lamy C, Magrou L, Vezoli J, Misery P, Falchier A, Quilodran R, Gariel MA, Sallet J, Gamanut R, Huissoud C, Clavagnier S, Giroud P, Sappey-Marinier D, Barone P, Dehay C, Toroczkai Z, Knoblauch K, Van Essen DC, Kennedy H (2014) A weighted and directed interareal connectivity matrix for macaque cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 24(1):17–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhs270
Markram H, Meier K, Lippert T, Grillner S, Frackowiak R, Dehaene S, Knoll A, Sompolinsky H, Verstreken K, DeFelipe J, Grant S, Changeux JP, Saria A (2011) Introducing the human brain project. Procedia Comput Sci 7:39–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2011.12.015 (proceedings of the 2nd European Future Technologies Conference and Exhibition 2011 (FET 11))
Oh SW, Harris JA, Ng L, Winslow B, Cain N, Mihalas S, Wang Q, Lau C, Kuan L, Henry AM, Mortrud MT, Ouellette B, Nguyen TN, Sorensen SA, Slaughterbeck CR, Wakeman W, Li Y, Feng D, Ho A, Nicholas E, Hirokawa KE, Bohn P, Joines KM, Peng H, Hawrylycz MJ, Phillips JW, Hohmann JG, Wohnoutka P, Gerfen CR, Koch C, Bernard A, Dang C, Jones AR, Zeng H (2014) A mesoscale connectome of the mouse brain. Nature 508(7495):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13186
Okano H, Sasaki E, Yamamori T, Iriki A, Shimogori T, Yamaguchi Y, Kasai K, Miyawaki A (2016) Brain/minds: a Japanese national brain project for marmoset neuroscience. Neuron 92(3):582–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.018
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9(1):62–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076
Paxinos G, Watson C, Petrides M, Rosa M, Tokuno H (2012) The marmoset brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 1st edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Poo M, Du J, Ip NY, Xiong ZQ, Xu B, Tan T (2016) China brain project: basic neuroscience, brain diseases, and brain-inspired computing. Neuron 92(3):591–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.050
Ragan T, Kadiri L, Umadevi Venkataraju K, Bahlmann K, Sutin J, Taranda J, Arganda-Carreras I, Kim Y, Seung H, Osten P (2012) Serial two-photon tomography for automated ex vivo mouse brain imaging. Nat Methods 9:255–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1854
Ronneberger O, PFischer, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), vol 9351. Springer, LNCS, pp 234–241. http://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/Publications/2015/RFB15a, (available on arXiv:1505.04597 [cs.CV])
Schleicher A, Palomero-Gallagher N, Morosan P, Eickhoff SB, Kowalski T, Vos Kd, Amunts K, Zilles K (2005) Quantitative architectural analysis: a new approach to cortical mapping. Anat Embryol 210(5):373–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-005-0028-2
Skibbe H, Watakabe A, Nakae K, Gutierrez CE, Tsukada H, Hata J, Kawase T, Gong R, Woodward A, Doya K, Okano H, Yamamori T, Ishii S (2019) Marmonet: a pipeline for automated projection mapping of the common marmoset brain from whole-brain serial two-photon tomography. arXiv:1908.00876
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R (2014) Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J Mach Learn Res 15:1929–1958
Steger C (1998) An unbiased detector of curvilinear structures. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(2):113–125. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.659930
Swanson LW, Hahn JD, Sporns O (2017) Organizing principles for the cerebral cortex network of commissural and association connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(45):E9692–E9701. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1712928114
Taashi-s (2018) Unet\(\_\)keras. https://github.com/taashi-s/UNet_Keras/tree/StationarySegmentation_cond1/src. Accessed 26 May 2019
Van Essen DC, Drury HA, Dickson J, Harwell J, Hanlon D, Anderson CH (2001) An integrated software suite for surface-based analyses of cerebral cortex. J Am Med Inform Assoc 8(5):443–459. https://doi.org/10.1136/jamia.2001.0080443
Woodward A, Hashikawa T, Maeda M, Kaneko T, Hikishima K, Iriki A, Okano H, Yamaguchi Y (2018) The brain/MINDS 3D digital marmoset brain atlas. Sci Data 5:180009
Acknowledgements
We thank Akiya Watakabe for sharing his expertise in marmoset tracer injection studies, Masahide Maeda for his technical support in maintaining the server used in this work, and Carlos Enrique Guiterrez and Hiromichi Tsukada for their participation and contribution in previous tracer study activities.
Funding
This research was supported by the program for Brain Mapping by Integrated Neurotechnologies for Disease Studies (Brain/MINDS) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, Grants JP19dm0207001 and JP19dm0207088.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All experimental procedures were approved by the Experimental Animal Committee of RIKEN, or by the Experimental Animal Committee of the National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry. The marmosets were handled in accordance with the “Guiding Principles of the Care and Use of Animals in the Field of Physiological Science” formulated by the Japanese Physiological Society.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woodward, A., Gong, R., Abe, H. et al. The NanoZoomer artificial intelligence connectomics pipeline for tracer injection studies of the marmoset brain. Brain Struct Funct 225, 1225–1243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02073-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02073-y