Abstract
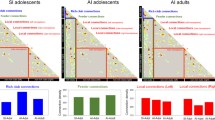
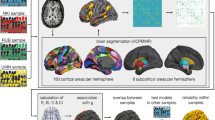
Gifted children learn more rapidly and effectively than others, presumably due to neurophysiological differences that affect efficiency in neuronal communication. Identifying the topological features that support its capabilities is relevant to understanding how the brain structure is related to intelligence. We proposed the analysis of the structural covariance network to assess which organizational patterns are characteristic of gifted children. The graph theory was used to analyse topological properties of structural covariance across a group of gifted children. The analysis was focused on measures of brain network integration, such as, participation coefficient and versatility, which quantifies the strength of specific modular affiliation of each regional node. We found that the gifted group network was more integrated (and less segregated) than the control group network. Brain regional nodes in the gifted group network had higher versatility and participation coefficient, indicating greater inter-modular communication mediated by connector hubs with links to many modules. Connector hubs of the networks of both groups were located mainly in association with neocortical areas (which had thicker cortex), with fewer hubs in primary or secondary neocortical areas (which had thinner cortex), as well as a few connector hubs in limbic cortex and insula. In the group of gifted children, a larger proportion of connector hubs were located in association cortex. In conclusion, gifted children have a more integrated and versatile brain network topology. This is compatible with the global workspace theory and other data linking integrative network topology to cognitive performance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander-Bloch A, Giedd JN, Bullmore E (2013) Imaging structural co-variance between human brain regions. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(5):322–336
Bassett DS, Bullmore E, Verchinski BA, Mattay VS, Weinberger DR, Meyer-Lindenberg A (2008) Hierarchical organization of human cortical networks in health and schizophrenia. J Neurosci 28(37):9239–9248
Bertolero MA, Yeo BTT, D’Esposito M (2015) The modular and integrative functional architecture of the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1510619112
Bethlehem RAI, Romero-Garcia R, Mak E, Bullmore ET, Baron-Cohen S (2017) Structural covariance networks in children with autism or ADHD. Cereb Cortex 27(8):4267–4276
Binet A, Simon T (1916) The development of intelligence in children (The Binet–Simon Scale). Psychol Sci 11:175
Binet A, Simon T (1948) The development of the Binet–Simon Scale, 1905–1908. In: Readings in the history of psychology, pp 412–424
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2012) The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(5):336–349
Cabeza R, Nyberg L (2000) Imaging cognition II: an empirical review of 275 PET and fMRI studies. J Cogn Neurosci 12(1):1–47
Chabris CF (2007) Cognitive and neurobiological mechanisms of the law of general intelligence. In: Integrating the mind: domain general versus domain specific processes in higher cognition, pp 449–491
Chevalier N, Kurth S, Doucette MR, Wiseheart M, Deoni SCL, Dean DC et al (2015) Myelination is associated with processing speed in early childhood: preliminary insights. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0139897
Colom R, Karama S, Jung RE, Haier RJ (2010) Human intelligence and brain networks. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 12(4):489–501
Davies G, Tenesa A, Payton A, Yang J, Harris SE, Liewald D et al (2011) Genome-wide association studies establish that human intelligence is highly heritable and polygenic. Molecular Psychiatry 16(10):996–1005
Dehaene S, Changeux JP (2011) Experimental and theoretical approaches to conscious processing. Neuron 70(2):200–227
Desikan RS, Ségonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D et al (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 3:968–980
Evans AC (2013) Networks of anatomical covariance. Neuroimage 80:489–504
Fields RD (2008) White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci 31(7):361–370
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(20):11050–11055
Fornito A, Zalesky A, Bullmore ET (2016) Fundamentals of brain network analysis. Academic Press, San Diego
Geake JG (2008) The neurobiology of giftedness. In: Wystąpienie na konferencji 10th Asia-Pacific conference on giftedness, Singapore
Ghosh SS, Kakunoori S, Augustinack J, Nieto-Castanon A, Kovelman I, Gaab N et al (2010) Evaluating the validity of volume-based and surface-based brain image registration for developmental cognitive neuroscience studies in children 4 to 11 years of age. Neuroimage 53(1):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.075
Goh S, Bansal R, Xu D, Hao X, Liu J, Peterson BS (2011) Neuroanatomical correlates of intellectual ability across the life span. Dev Cogn Neurosci 1(3):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2011.03.001
Gong G, He Y, Concha L, Lebel C, Gross DW, Evans AC, Beaulieu C (2009) Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb Cortex 19(3):524–536
Gross MUM (2006) Exceptionally gifted children: long-term outcomes of academic acceleration and nonacceleration. J Educ Gifted 29(4):404–429
He Y, Chen Z, Gong G, Evans A (2009) Neuronal networks in Alzheimer’s disease. The Neuroscientist 15(4):333–350
Irimia A, Van Horn JD (2013) The structural, connectomic and network covariance of the human brain. Neuroimage 66:489–499
Jung RE, Haier RJ (2007) The Parieto-Frontal integration theory (P-FIT) of intelligence: converging neuroimaging evidence. Behav Brain Sci 30(02):135–154
Karama S, Colom R, Johnson W, Deary IJ, Haier R, Waber DP et al (2011) Cortical thickness correlates of specific cognitive performance accounted for by the general factor of intelligence in healthy children aged 6 to 18. Neuroimage 55(4):1443–1453
Khundrakpam BS, Reid A, Brauer J, Carbonell F, Lewis J, Ameis S et al (2013) Developmental changes in organization of structural brain networks. Cereb Cortex 23(9):2072–2085
Khundrakpam BS, Lewis JD, Reid A, Karama S, Zhao L, Chouinard-Decorte F, Evans AC (2016) Imaging structural covariance in the development of intelligence. Neuroimage 144(Pt A):227–240
Kim DJ, Davis EP, Sandman CA, Sporns O, O’Donnell BF, Buss C, Hetrick WP (2016) Children’s intellectual ability is associated with structural network integrity. Neuroimage 124:550–556
Kitzbichler MG, Henson RN, Smith ML, Nathan PJ, Bullmore ET (2011) Cognitive effort drives workspace configuration of human brain functional networks. J Neurosci 31(22):8259–8270. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0440-11.2011
Li Y, Liu Y, Li J, Qin W, Li K, Yu C, Jiang T (2009) Brain anatomical network and intelligence. PLoS Comput Biol 5(5):e1000395. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000395
Maslov S, Sneppen K (2002) Specificity and stability in topology of protein networks. Science 296(5569):910–913
Menary K, Collins PF, Porter JN, Muetzel R, Olson EA, Kumar V et al (2013) Associations between cortical thickness and general intelligence in children, adolescents and young adults. Intelligence 41(5):597–606
Meunier D, Lambiotte R, Bullmore ET (2010) Modular and hierarchically modular organization of brain networks. Front Neurosci 4:200. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2010.00200
Mukherjee P, Chung SW, Berman JI, Hess CP, Henry RG (2008) Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: technical considerations. Am J Neuroradiol 29(5):843–852. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1052
Naghavi HR, Nyberg L (2005) Common fronto-parietal activity in attention, memory, and consciousness: shared demands on integration? Conscious Cogn 14(2):390–425
Navas-Sánchez FJ, Alemán-Gómez Y, Sánchez-Gonzalez J, Guzmán-De-Villoria JA, Franco C, Robles O et al (2014) White matter microstructure correlates of mathematical giftedness and intelligence quotient. Hum Brain Mapp 35(6):2619–2631
Navas-Sánchez FJ, Carmona S, Alemán-Gómez Y, Sánchez-González J, Guzmán-de-Villoria J, Franco C et al (2016) Cortical morphometry in frontoparietal and default mode networks in math-gifted adolescents. Hum Brain Mapp 37(5):1893–1902
Romero-Garcia R, Atienza M, Clemmensen LH, Cantero JL (2012) Effects of network resolution on topological properties of human neocortex. Neuroimage 59(4):3522–3532
Romero-Garcia R, Whitaker KJ, Váša F, Seidlitz J, Shinn M, Fonagy P et al (2018) Structural covariance networks are coupled to expression of genes enriched in supragranular layers of the human cortex. Neuroimage 171:256–267
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010) Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52(3):1059–1069
Santamaría P, Arribas D, Pereña J, Seisdedos N (2005) EFAI, Evaluación Factorial de las Aptitudes Intelectuales. Departamento I + D TEA Ediciones, Madrid
Schnack HG, van Haren NEM, Brouwer RM, Evans A, Durston S, Boomsma DI et al (2014) Changes in thickness and surface area of the human cortex and their relationship with intelligence. Cereb Cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 10:1608–1617
Seidlitz J, Váša F, Shinn M, Romero-Garcia R, Whitaker KJ, Vértes PE et al (2018) Morphometric similarity networks detect microscale cortical organization and predict inter-individual cognitive variation. Neuron 97(1):231–247
Sharda M, Khundrakpam BS, Evans AC, Singh NC (2016) Disruption of structural covariance networks for language in autism is modulated by verbal ability. Brain Struct Funct 221(2):1017–1032
Shine JM, Bissett PG, Bell PT, Koyejo O, Balsters JH, Gorgolewski KJ et al (2016) The dynamics of functional brain networks: integrated network states during cognitive task performance. Neuron 1:21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.018
Shinn M, Romero-Garcia R, Seidlitz J, Váša F, Vértes PE, Bullmore E (2017) Versatility of nodal affiliation to communities. Sci Rep 7(1):4273
van den Heuvel MP, Stam CJ, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE (2009) Efficiency of functional brain networks and intellectual performance. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29(23):7619–7624
van Wijk BCM, Stam CJ, Daffertshofer A (2010) Comparing brain networks of different size and connectivity density using graph theory. PLoS ONE 5(10):e13701. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013701
Váša F, Seidlitz J, Romero-Garcia R, Whitaker KJ, Rosenthal G, Vértes PE et al (2018) Adolescent tuning of association cortex in human structural brain networks. Cereb Cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 28(1):281–294. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx249
Vértes PE, Rittman T, Whitaker KJ, Romero-Garcia R, Váša F, Kitzbichler MG et al (2016) Gene transcription profiles associated with inter-modular hubs and connection distance in human functional magnetic resonance imaging networks. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 371(1705):5. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0362
von Economo C (1929) The cytoarchitectonics of the human cerebral cortex. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Vuoksimaa E, Panizzon MS, Chen CH, Fiecas M, Eyler LT, Fennema-Notestine C et al (2016) Is bigger always better? The importance of cortical configuration with respect to cognitive ability. Neuroimage 129:356–366
Wang L, Song M, Jiang T, Zhang Y, Yu C (2011) Regional homogeneity of the resting-state brain activity correlates with individual intelligence. Neurosci Lett 488(3):275–278
Wechsler D (1939) The measurement of adult intelligence. Williams & Wilkins Co, Baltimore
Whitaker KJ, Vértes PE, Romero-Garcia R, Váša F, Moutoussis M, Prabhu G et al (2016) Adolescence is associated with genomically patterned consolidation of the hubs of the human brain connectome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(32):9105–9110
Wu K, Taki Y, Sato K, Sassa Y, Inoue K, Goto R et al (2011) The overlapping community structure of structural brain network in young healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19608. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019608
Yang JJ, Yoon U, Yun HJ, Im K, Choi YY, Lee KH et al (2013) Prediction for human intelligence using morphometric characteristics of cortical surface: partial least square analysis. Neuroscience 246:351–361
Zatorre RJ, Fields RD, Johansen-Berg H (2012) Plasticity in gray and white: neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nat Neurosci 15(4):528–536
Zhang L, Gan JQ, Wang H (2017) Neurocognitive mechanisms of mathematical giftedness: a literature review. Appl Neuropsychol Child 6(1):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2015.1119692
Zielinski BA, Gennatas ED, Zhou J, Seeley WW (2010) Network-level structural covariance in the developing brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(42):18191–18196
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Ministerio de Economía y Competividad (PSI2013-47216-P) to JMSG. JSC was partially supported by a mobility grant from the Ministerio de Educación, Cultura y Deporte (MINECO, ref. PRX15/00127) and by the Ministerio de Economía y Competividad through the grant TEC2016-77791-C4-2-R. RRG was supported by a strategic award from the Wellcome Trust to the University of Cambridge and University College London (095844/Z/11/Z) and the Guarantors of Brain Charity (264139). The authors would like to thank M. Shinn for his useful comments on the versatility parameter and for providing the code to calculate it.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solé-Casals, J., Serra-Grabulosa, J.M., Romero-Garcia, R. et al. Structural brain network of gifted children has a more integrated and versatile topology. Brain Struct Funct 224, 2373–2383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01914-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01914-9