Abstract
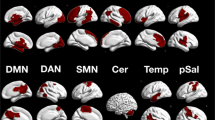
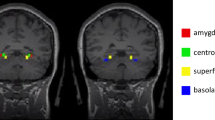
Social anxiety (SA) comprises a multitude of persistent fears around the central element of dreaded negative evaluation and exclusion. This very common anxiety is spectrally distributed among the general population and associated with social perception biases deemed causal in its maintenance. Here, we investigated cerebral resting state markers linking SA and biased social perception. To this end, resting state functional connectivity (RSFC) was assessed as the neurobiological marker in a study population with greatly varying SA using fMRI in the first step of the experiment. One month later the impact of unattended laughter—exemplifying social threat—on a face rating task was evaluated as a measure of biased social perception. Applying a dimensional approach, SA-related cognitive biases tied to the valence, dominance and arousal of the threat signal and their underlying RSFC patterns among central nodes of the cerebral emotion, voice and face processing networks were identified. In particular, the connectivity patterns between the amygdalae and the right temporal voice area met all criteria for a cerebral mediation of the association between SA and the laughter valence-related interpretation bias. Thus, beyond this identification of non-state-dependent cerebral markers of biased perception in SA, this study highlights both a starting point and targets for future research on the causal relationships between cerebral connectivity patterns, SA and biased perception, potentially via neurofeedback methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amir N, Taylor CT (2012) Interpretation training in individuals with generalized social anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol 80(3):497–511. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026928
Amir N, Beard C, Taylor CT, Klumpp H, Elias J, Burns M, Chen X (2009) Attention training in individuals with generalized social phobia: a randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol 77(5):961–973
Banos RM, Quero S, Botella C (2008) Detection and distraction effects for threatening information in social phobia and change after treatment. Depress Anxiety 25(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.20269
Beard C, Amir N (2008) A multi-session interpretation modification program: changes in interpretation and social anxiety symptoms. Behav Res Ther 46(10):1135–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2008.05.012
Belin P, Zatorre RJ, Lafaille P, Ahad P, Pike B (2000) Voice-selective areas in human auditory cortex. Nature 403(6767):309–312
Boehme S, Ritter V, Tefikow S, Stangier U, Strauss B, Miltner WH, Straube T (2015) Neural correlates of emotional interference in social anxiety disorder. PLoS One 10(6):e0128608. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128608
Browning M, Holmes EA, Murphy SE, Goodwin GM, Harmer CJ (2010) Lateral prefrontal cortex mediates the cognitive modification of attentional bias. Biol Psychiatry 67(10):919–925
Brück C, Kreifelts B, Wildgruber D (2011) Emotional voices in context: a neurobiological model of multimodal affective information processing. Phys Life Rev 8(4):383–403
Brühl AB, Delsignore A, Komossa K, Weidt S (2014) Neuroimaging in social anxiety disorder-a meta-analytic review resulting in a new neurofunctional model. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:260–280
Chiao JY, Adams RB, Tse PU, Lowenthal L, Richeson JA, Ambady N (2008) Knowing who’s boss: fMRI and ERP investigations of social dominance perception. Group Process Intergroup Relat GPIR 11(2):201–214. https://doi.org/10.1177/1368430207088038
Clark DM, McManus F (2002) Information processing in social phobia. Biol Psychiatry 51(1):92–100
Clark DM, Wells A (1995) A cognitive model of social phobia. In: Heimberg RG, Liebowitz MR, Hope DA, Schneier FR (eds) Social phobia: diagnosis, assessment, and treatment. Guilford Press, New York, pp 69–93
Davila Ross M, Owren MJ, Zimmermann E (2009) Reconstructing the evolution of laughter in great apes and humans. Curr Biol 19(13):1106–1111
Eibl-Eibesfeldt I (1970) Ethology: the biology of behavior. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York
Epstein R, Harris A, Stanley D, Kanwisher N (1999) The parahippocampal place area: recognition, navigation, or encoding? Neuron 23(1):115–125
Ethofer T, Bretscher J, Wiethoff S, Bisch J, Schlipf S, Wildgruber D, Kreifelts B (2013) Functional responses and structural connections of cortical areas for processing faces and voices in the superior temporal sulcus. NeuroImage 76C:45–56
Gilboa-Schechtman E, Foa EB, Amir N (1999) Attentional biases for facial expressions in social phobia: the effects of target and distractor in “face-in-the-crowd” task. Cogn Emot 13:305–318
Goldin PR, Ziv M, Jazaieri H, Hahn K, Heimberg R, Gross JJ (2013) Impact of cognitive behavioral therapy for social anxiety disorder on the neural dynamics of cognitive reappraisal of negative self-beliefs: randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 70(10):1048–1056. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.234
Goldin PR, Ziv M, Jazaieri H, Weeks J, Heimberg RG, Gross JJ (2014) Impact of cognitive-behavioral therapy for social anxiety disorder on the neural bases of emotional reactivity to and regulation of social evaluation. Behav Res Ther 62:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2014.08.005
Hautzinger M (1991) The Beck Depression Inventory in clinical practice. Der Nervenarzt 62(11):689–696
Havranek MM, Volkart F, Bolliger B, Roos S, Buschner M, Mansour R, Chmielewski T, Gaudlitz K, Hattenschwiler J, Seifritz E, Ruch W (2017) The fear of being laughed at as additional diagnostic criterion in social anxiety disorder and avoidant personality disorder? PLoS One 12(11):e0188024. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188024
Jacobi F, Hofler M, Strehle J, Mack S, Gerschler A, Scholl L, Busch MA, Maske U, Hapke U, Gaebel W, Maier W, Wagner M, Zielasek J, Wittchen HU (2014) Mental disorders in the general population: study on the health of adults in Germany and the additional module mental health (DEGS1-MH). Der Nervenarzt 85(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00115-013-3961-y
Kanwisher N, McDermott J, Chun MM (1997) The fusiform face area: a module in human extrastriate cortex specialized for face perception. J Neurosci 17(11):4302–4311
Kim YK, Yoon HK (2018) Common and distinct brain networks underlying panic and social anxiety disorders. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 80(Pt B):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.06.017
Kreifelts B, Ethofer T, Grodd W, Erb M, Wildgruber D (2007) Audiovisual integration of emotional signals in voice and face: an event-related fMRI study. NeuroImage 37(4):1445–1456
Kreifelts B, Ethofer T, Shiozawa T, Grodd W, Wildgruber D (2009) Cerebral representation of non-verbal emotional perception: fMRI reveals audiovisual integration area between voice- and face-sensitive regions in the superior temporal sulcus. Neuropsychologia 47(14):3059–3066
Kreifelts B, Ethofer T, Huberle E, Grodd W, Wildgruber D (2010) Association of trait emotional intelligence and individual fMRI-activation patterns during the perception of social signals from voice and face. Humn Brain Mapp 31(7):979–991
Kreifelts B, Jacob H, Bruck C, Erb M, Ethofer T, Wildgruber D (2013) Non-verbal emotion communication training induces specific changes in brain function and structure. Front Hum Neurosci 7:648
Kreifelts B, Brück C, Ritter J, Ethofer T, Domin M, Lotze M, Jacob H, Schlipf S, Wildgruber D (2014) They are laughing at me: cerebral mediation of cognitive biases in social anxiety. PLoS One 9(6):e99815
Kreifelts B, Brück C, Ethofer T, Ritter J, Weigel L, Erb M, Wildgruber D (2017) Prefrontal mediation of emotion regulation in social anxiety disorder during laughter perception. Neuropsychologia 96:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.01.016
Laux L, Glanzmann P, Schaffner P, Spielberger CD (1981) Das State-Trait-Angstinventar. Beltz, Weinheim
Lehrl S (2005) Mehrfachwahl-Wortschatz-Intelligenztest MWT-B, 5th edn. Spitta, Balingen
Lipsitz JD, Schneier FR (2000) Social phobia. Epidemiology and cost of illness. Pharmacoeconomics 18(1):23–32
Liu F, Zhu C, Wang Y, Guo W, Li M, Wang W, Long Z, Meng Y, Cui Q, Zeng L, Gong Q, Zhang W, Chen H (2015) Disrupted cortical hubs in functional brain networks in social anxiety disorder. Clin Neurophysiol 126(9):1711–1716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2014.11.014
Machado-de-Sousa JP, Arrais KC, Alves NT, Chagas MH, de Meneses-Gaya C, Crippa JA, Hallak JE (2010) Facial affect processing in social anxiety: tasks and stimuli. J Neurosci Methods 193(1):1–6
Mendlowicz MV, Stein MB (2000) Quality of life in individuals with anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry 157(5):669–682
Minkova L, Sladky R, Kranz GS, Woletz M, Geissberger N, Kraus C, Lanzenberger R, Windischberger C (2017) Task-dependent modulation of amygdala connectivity in social anxiety disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 262:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.12.016
Miskovic V, Schmidt LA (2012) Social fearfulness in the human brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(1):459–478
Mogg K, Bradley BP (2002) Selective orienting of attention to masked threat faces in social anxiety. Behav Res Ther 40(12):1403–1414
Northoff G, Heinzel A, de Greck M, Bermpohl F, Dobrowolny H, Panksepp J (2006) Self-referential processing in our brain—a meta-analysis of imaging studies on the self. NeuroImage 31(1):440–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.12.002
Öhman A (1986) Face the beast and fear the face: animal and social fears as prototypes for evolutionary analyses of emotion. Psychophysiology 23(2):123–145
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Pernet CR, McAleer P, Latinus M, Gorgolewski KJ, Charest I, Bestelmeyer PE, Watson RH, Fleming D, Crabbe F, Valdes-Sosa M, Belin P (2015) The human voice areas: spatial organization and inter-individual variability in temporal and extra-temporal cortices. NeuroImage 119:164–174
Pourtois G, de Gelder B, Bol A, Crommelinck M (2005) Perception of facial expressions and voices and of their combination in the human brain. Cortex 41(1):49–59
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF (2008) Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 40(3):879–891
Provine RR (2013) Laughing, grooming, and pub science. Trends Cogn Sci 17(1):9–10
Quadflieg S, Wendt B, Mohr A, Miltner WH, Straube T (2007) Recognition and evaluation of emotional prosody in individuals with generalized social phobia: a pilot study. Behav Res Ther 45(12):3096–3103
Rapee RM, Heimberg RG (1997) A cognitive-behavioral model of anxiety in social phobia. Behav Res Ther 35(8):741–756
Ritter J, Brück C, Jacob H, Wildgruber D, Kreifelts B (2015) Laughter perception in social anxiety. J Psychiatr Res 60C:178–184
Robins DL, Hunyadi E, Schultz RT (2009) Superior temporal activation in response to dynamic audio-visual emotional cues. Brain Cogn 69(2):269–278
Sladky R, Hoflich A, Kublbock M, Kraus C, Baldinger P, Moser E, Lanzenberger R, Windischberger C (2015) Disrupted effective connectivity between the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex in social anxiety disorder during emotion discrimination revealed by dynamic causal modeling for FMRI. Cereb Cortex 25(4):895–903. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bht279
Stangier U, Heidenreich T (2003) Die Liebowitz Soziale Angst-Skala (LSAS). Collegium Internationale Psychiatriae Scalarum - Internationale Skalen für Psychiatrie. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Staugaard SR (2010) Threatening faces and social anxiety: a literature review. Clin Psychol Rev 30(6):669–690
Stein DJ, Ruscio AM, Lee S, Petukhova M, Alonso J, Andrade LH, Benjet C, Bromet E, Demyttenaere K, Florescu S, de Girolamo G, de Graaf R, Gureje O, He Y, Hinkov H, Hu C, Iwata N, Karam EG, Lepine JP, Matschinger H, Oakley Browne M, Posada-Villa J, Sagar R, Williams DR, Kessler RC (2010) Subtyping social anxiety disorder in developed and developing countries. Depress Anxiety 27(4):390–403
Szameitat DP, Alter K, Szameitat AJ, Darwin CJ, Wildgruber D, Dietrich S, Sterr A (2009) Differentiation of emotions in laughter at the behavioral level. Emotion 9(3):397–405
Trower P, Gilbert P (1989) New theoretical conceptions of social anxiety and social phobia. Clin Psychol Rev 9(1):19–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-7358(89)90044-5
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15(1):273–289
Watanabe T, Sasaki Y, Shibata K, Kawato M (2017) Advances in fMRI real-time neurofeedback. Trends Cogn Sci 21(12):997–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2017.09.010
Werner S, Noppeney U (2010) Superadditive responses in superior temporal sulcus predict audiovisual benefits in object categorization. Cereb Cortex 20(8):1829–1842
Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Nieto-Castanon A (2012) Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect 2(3):125–141. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2012.0073
Wittchen HU, Zaudig M, Fydrich T (1997) Strukturiertes Klinisches Interview für DSM-IV. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Worsley K, Marrett S, Neelin P, Vandal AC, Friston KJ, Evans A (1996) A unified statistical approach for determining significant signals in images of cerebral activation. Hum Brain Mapp 4(1):74–90
Wundt W (1905) Grundzüge der physiologischen Psychologie, 5th edn. Engelmann, Leipzig
Yuan M, Zhu H, Qiu C, Meng Y, Zhang Y, Shang J, Nie X, Ren Z, Gong Q, Zhang W, Lui S (2016) Group cognitive behavioral therapy modulates the resting-state functional connectivity of amygdala-related network in patients with generalized social anxiety disorder. BMC Psychiatry 16:198. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-0904-8
Yuan M, Zhu H, Qiu C, Meng Y, Zhang Y, Ren Z, Li Y, Yuan C, Gao M, Lui S, Gong Q, Zhang W (2018) Altered regional and integrated resting-state brain activity in general social anxiety disorder patients before and after group cognitive behavior therapy. Psychiatry Res 272:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.12.004
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants of the Fortüne-Program of the University of Tübingen (fortüne 1997-0-0, and fortüne 2140-0-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kreifelts, B., Weigel, L., Ethofer, T. et al. Cerebral resting state markers of biased perception in social anxiety. Brain Struct Funct 224, 759–777 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-1803-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-1803-1