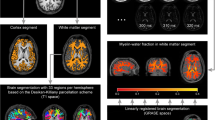
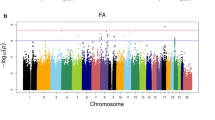
Abstract
The corpus callosum is the brain’s largest commissural fiber tract and is crucial for interhemispheric integration of neural information. Despite the high relevance of the corpus callosum for several cognitive systems, the molecular determinants of callosal microstructure are largely unknown. Recently, it was shown that genetic variations in the myelin-related proteolipid 1 gene PLP1 and the axon guidance related contactin 1 gene CNTN1 were associated with differences in interhemispheric integration at the behavioral level. Here, we used an innovative new diffusion neuroimaging technique called neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to quantify axonal morphology in subsections of the corpus callosum and link them to genetic variation in PLP1 and CNTN1. In a cohort of 263 healthy human adults, we found that polymorphisms in both PLP1 and CNTN1 were significantly associated with callosal microstructure. Importantly, we found a double dissociation between gene function and neuroimaging variables. Our results suggest that genetic variation in the myelin-related gene PLP1 impacts white matter microstructure in the corpus callosum, possibly by affecting myelin structure. In contrast, genetic variation in the axon guidance related gene CNTN1 impacts axon density in the corpus callosum. These findings suggest that PLP1 and CNTN1 gene variations modulate specific aspects of callosal microstructure that are in line with their gene function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboitiz F, Scheibel AB, Fisher RS, Zaidel E (1992a) Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res 598(1–2):143–153
Aboitiz F, Scheibel AB, Zaidel E (1992b) Morphometry of the Sylvian fissure and the corpus callosum, with emphasis on sex differences. Brain J Neurol 115(Pt 5):1521–1541
Alonso-Ortiz E, Levesque IR, Pike GB (2015) MRI-based myelin water imaging: a technical review. Magn Reson Med 73(1):70–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.25198
Banich MT, Belger A (1990) Interhemispheric interaction: how do the hemispheres divide and conquer a task? Cortex J Devot Stud Nerv Syst Behav 26(1):77–94
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson Ser B 111(3):209–219
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):435–455. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.782
Behrens TEJ, Berg HJ, Jbabdi S, Rushworth MFS, Woolrich MW (2007) Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: what can we gain? NeuroImage 34(1):144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.018
Berglund EO, Ranscht B (1994) Molecular cloning and in situ localization of the human contactin gene (CNTN1) on chromosome 12q11–q12. Genomics 21(3):571–582. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1994.1316
Billiet T, Vandenbulcke M, Mädler B, Peeters R, Dhollander T, Zhang H, Emsell L (2015) Age-related microstructural differences quantified using myelin water imaging and advanced diffusion MRI. Neurobiol Aging 36(6):2107–2121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.029
Bizzoca A, Corsi P, Polizzi A, Pinto MF, Xenaki D, Furley AJW, Gennarini G (2012) F3/Contactin acts as a modulator of neurogenesis during cerebral cortex development. Dev Biol 365(1):133–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.02.011
Boiko T, Winckler B (2006) Myelin under construction—teamwork required. J Cell Biol 172(6):799–801. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200602101
Caminiti R, Ghaziri H, Galuske R, Hof PR, Innocenti GM (2009) Evolution amplified processing with temporally dispersed slow neuronal connectivity in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(46):19551–19556. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907655106
Clarke JM, Zaidel E (1994) Anatomical-behavioral relationships: corpus callosum morphometry and hemispheric specialization. Behav Brain Res 64(1–2):185–202
Czopka T, Holst A von, Ffrench-Constant C, Faissner A (2010) Regulatory mechanisms that mediate tenascin C-dependent inhibition of oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation. J Neurosci 30(37):12310–12322. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4957-09.2010
Daducci A, Canales-Rodríguez EJ, Zhang H, Dyrby TB, Alexander DC, Thiran J-P (2015) Accelerated microstructure imaging via convex optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. NeuroImage 105:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.026
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 9(2):179–194. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0395
DeCarli C, Murphy DG, Tranh M, Grady CL, Haxby JV, Gillette JA, Rapoport SI (1995) The effect of white matter hyperintensity volume on brain structure, cognitive performance, and cerebral metabolism of glucose in 51 healthy adults. Neurology 45(11):2077–2084
Fabri M, Pierpaoli C, Barbaresi P, Polonara G (2014) Functional topography of the corpus callosum investigated by DTI and fMRI. World J Radiol 6(12):895–906. https://doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i12.895
Fischl B, Sereno MI, Dale AM (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage 9(2):195–207. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0396
Flint J, Munafò MR (2013) Candidate and non-candidate genes in behavior genetics. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23(1):57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2012.07.005
Froeling M, Tax CMW, Vos SB, Luijten PR, Leemans A (2017) “MASSIVE” brain dataset: multiple acquisitions for standardization of structural imaging validation and evaluation. Magn Reson Med 77(5):1797–1809. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26259
Garde E, Mortensen EL, Krabbe K, Rostrup E, Larsson HB (2000) Relation between age-related decline in intelligence and cerebral white-matter hyperintensities in healthy octogenarians: a longitudinal study. Lancet 356(9230):628–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02604-0
Ge Y, Grossman RI, Babb JS, Rabin ML, Mannon LJ, Kolson DL (2002) Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: Volumetric MR imaging analysis. Am J Neuroradiol 23(8):1327–1333
Genç E, Ocklenburg S, Singer W, Güntürkün O (2015) Abnormal interhemispheric motor interactions in patients with callosal agenesis. Behav Brain Res 293:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.07.016
Genç E, Fraenz C, Schlüter C, Friedrich P, Hossiep R, Voelkle MC, Ling JM, Güntürkün O, Jung RE (2018) Diffusion markers of dendritic density and arborization in gray matter predict differences in intelligence. Nat Commun 9:1905. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04268-8
Grussu F, Schneider T, Tur C, Yates RL, Tachrount M, Ianuş A, Yiannakas MC, Newcombe J, Zhang H, Alexander DC, DeLuca GC, Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott CAM (2017) Neurite dispersion: a new marker of multiple sclerosis spinal cord pathology? Ann Clin Transl Neurol 4(9):663–679. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.445
Hofer S, Frahm J (2006) Topography of the human corpus callosum revisited—comprehensive fiber tractography using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 32(3):989–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.044
Inoue K (2005) PLP1-related inherited dysmyelinating disorders: Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease and spastic paraplegia type 2. Neurogenetics 6(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-004-0207-y
Jahanshad N, Ganjgahi H, Bralten J, den Braber A, Faskowitz J, Knodt A, Sprooten E (2017) Do candidate genes affect the brain’s white matter microstructure? Large-scale evaluation of 6165 diffusion MRI scans. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/107987
Jespersen SN, Bjarkam CR, Nyengaard JR, Chakravarty MM, Hansen B, Vosegaard T, Vestergaard-Poulsen P (2010) Neurite density from magnetic resonance diffusion measurements at ultrahigh field: comparison with light microscopy and electron microscopy. NeuroImage 49(1):205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.053
Jespersen SN, Leigland LA, Cornea A, Kroenke CD (2012) Determination of axonal and dendritic orientation distributions within the developing cerebral cortex by diffusion tensor imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(1):16–32. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2011.2162099
Lamprianou S, Chatzopoulou E, Thomas J-L, Bouyain S, Harroch S (2011) A complex between contactin-1 and the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPRZ controls the development of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(42):17498–17503. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108774108
Le Bihan D (2003) Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(6):469–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1119
Mädler B, Drabycz SA, Kolind SH, Whittall KP, MacKay AL (2008) Is diffusion anisotropy an accurate monitor of myelination? Correlation of multicomponent T2 relaxation and diffusion tensor anisotropy in human brain. Magn Reson Imaging 26(7):874–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2008.01.047
Martínez-Montero P, Muñoz-Calero M, Vallespín E, Campistol J, Martorell L, Ruiz-Falcó MJ, Molano J (2013) PLP1 gene analysis in 88 patients with leukodystrophy. Clin Genet 84(6):566–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12103
Mayer AR, Ling JM, Dodd AB, Meier TB, Hanlon FM, Klimaj SD (2017) A prospective microstructure imaging study in mixed-martial artists using geometric measures and diffusion tensor imaging: methods and findings. Brain Imaging Behav 11(3):698–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9546-1
Mori S, Zhang J (2006) Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron 51(5):527–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.012
Nam Y, Lee J, Hwang D, Kim D-H (2015) Improved estimation of myelin water fraction using complex model fitting. NeuroImage 116:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.03.081
Ocklenburg S, Hugdahl K, Westerhausen R (2013) Structural white matter asymmetries in relation to functional asymmetries during speech perception and production. NeuroImage 83:1088–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.076
Ocklenburg S, Gerding WM, Arning L, Genç E, Epplen JT, Güntürkün O, Beste C (2017) Myelin genes and the corpus callosum: proteolipid protein 1 (PLP1) and Contactin 1 (CNTN1) gene variation modulates interhemispheric integration. Mol Neurobiol 54:7908–7916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0285-5
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36(6):893–906
Plecko B, Stöckler-Ipsiroglu S, Gruber S, Mlynarik V, Moser E, Simbrunner J. Prayer D (2003) Degree of hypomyelination and magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings in patients with Pelizaeus Merzbacher phenotype. Neuropediatrics 34(3):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-41276
Rosas HD, Lee SY, Bender AC, Zaleta AK, Vangel M, Yu P, Hersch SM (2010) Altered white matter microstructure in the corpus callosum in Huntington’s disease: implications for cortical “disconnection”. NeuroImage 49(4):2995–3004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.015
Ruest T, Holmes WM, Barrie JA, Griffiths IR, Anderson TJ, Dewar D, Edgar JM (2011) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging of fixed brain in a mouse model of Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease: comparison with quantitative measures of white matter pathology. NMR Biomed 24(10):1369–1379. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1700
Sarret C, Lemaire J-J, Tonduti D, Sontheimer A, Coste J, Pereira B, Boespflug-Tanguy O (2016) Time-course of myelination and atrophy on cerebral imaging in 35 patients with PLP1-related disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol 58(7):706–713. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13025
Schmahmann JD, Smith EE, Eichler FS, Filley CM (2008) Cerebral white matter: neuroanatomy, clinical neurology, and neurobehavioral correlates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1142:266–309. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1444.017
Sepehrband F, Alexander DC, Kurniawan ND, Reutens DC, Yang Z (2016) Towards higher sensitivity and stability of axon diameter estimation with diffusion-weighted MRI. NMR Biomed 29(3):293–308. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3462
Skoog I, Berg S, Johansson B, Palmertz B, Andreasson LA (1996) The influence of white matter lesions on neuropsychological functioning in demented and non-demented 85-year-olds. Acta Neurol Scand 93(2–3):142–148
Suárez R, Gobius I, Richards LJ (2014) Evolution and development of interhemispheric connections in the vertebrate forebrain. Front Hum Neurosci 8:497. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00497
Tariq M, Schneider T, Alexander DC, Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Zhang H (2016) Bingham-NODDI: mapping anisotropic orientation dispersion of neurites using diffusion MRI. NeuroImage 133:207–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.01.046
van der Knaap LJ, van der Ham IJM (2011) How does the corpus callosum mediate interhemispheric transfer? A review. Behav Brain Res 223(1):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.04.018
van der Knaap M, Valk J, Barkhof F (2005) Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Westerhausen R, Hugdahl K (2008) The corpus callosum in dichotic listening studies of hemispheric asymmetry: a review of clinical and experimental evidence. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32(5):1044–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.04.005
Wight PA (2017) Effects of intron 1 sequences on human PLP1 expression: implications for PLP1-related disorders. ASN Neuro 9(4):17590914–17720583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091417720583
Woodward K, Malcolm S (1999) Proteolipid protein gene: Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease in humans and neurodegeneration in mice. Trends Genet 15(4):125–128
Yool DA, Klugmann M, McLaughlin M, Vouyiouklis DA, Dimou L, Barrie JA, Griffiths IR (2001) Myelin proteolipid proteins promote the interaction of oligodendrocytes and axons. J Neurosci Res 63(2):151–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4547(20010115)63:2%3C151::AID-JNR1007%3E3.0.CO;2-Y
Zatorre RJ, Fields RD, Johansen-Berg H (2012) Plasticity in gray and white: neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nat Neurosci 15(4):528–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3045
Zhang H, Schneider T, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Alexander DC (2012) NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage 61(4):1000–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.072
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Gu227/16-1, GE2777/2-1 and BE4045/26-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, C., Gerding, W.M., Fraenz, C. et al. PLP1 and CNTN1 gene variation modulates the microstructure of human white matter in the corpus callosum. Brain Struct Funct 223, 3875–3887 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-1729-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-1729-7