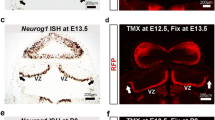
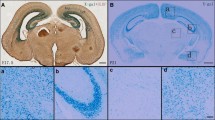
Abstract
Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain is restricted to specific regions, such as the dentate gyrus (DG) in the hippocampus and the subventricular zone (SVZ) in the walls of the lateral ventricles. Here, we used a mouse line carrying a knock-in of Cre recombinase in the Prss56 gene, in combination with two Cre-inducible fluorescent reporters (Rosa26 mTmG and Rosa26 tdTom), to perform genetic tracing of Prss56-expressing cells in the adult brain. We found reporter-positive cells in three neurogenic niches: the DG, the SVZ and the hypothalamus ventricular zone. In the prospective DG, Prss56 is expressed during embryogenesis in a subpopulation of radial glia. The pattern of migration and differentiation of reporter-positive cells during development recapitulates the successive steps of DG neurogenesis, including the formation of a subpopulation of adult neural stem cells (NSC). In the SVZ, Prss56 is expressed postnatally in a subpopulation of adult NSC mainly localized in the medial-ventral region of the lateral wall. This subpopulation preferentially gives rise to deep granule and Calbindin-positive periglomerular interneurons in the olfactory bulb. Finally, Prss56 is also expressed in a subpopulation of α2-tanycytes, which are potential adult NSCs of the hypothalamus ventricular zone. Our observations suggest that some α2-tanycytes translocate their soma into the parenchyma and may give rise to a novel cell type in this territory. Overall, this study establishes the Prss56 Cre line as an efficient and promising new tool to study multiple aspects of adult neurogenesis in the mouse.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen E (1912) The cessation of mitosis in the central nervous system of the albino rat. J Comp Neurol 22:547–568
Alonso M, Ortega-Pérez I, Grubb MS, Bourgeois J-P, Charneau P, Lledo P-M (2008) Turning astrocytes from the rostral migratory stream into neurons: a role for the olfactory sensory organ. J Neurosci 28:11089–11102
Altman J, Das GD (1965a) Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124:319–335
Altman J, Das GD (1965b) Post-natal origin of microneurones in the rat brain. Nature 207:953–956
Barraud P, Seferiadis AA, Tyson LD, Zwart MF, Szabo-Rogers HL, Ruhrberg C, Liu KJ, Baker CVH (2010) Neural crest origin of olfactory ensheathing glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:21040–21045
Batista-Brito R, Close J, Machold R, Fishell G (2008) The distinct temporal origins of olfactory bulb interneuron subtypes. J Neurosci 28:3966–3975
Beckervordersandforth R, Tripathi P, Ninkovic J, Bayam E, Lepier A, Stempfhuber B, Kirchhoff F, Hirrlinger J, Haslinger A, Lie DC, Beckers J, Yoder B, Irmler M, Götz M (2010) In vivo fate mapping and expression analysis reveals molecular hallmarks of prospectively isolated adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 7:744–758
Brill MS, Ninkovic J, Winpenny E, Hodge RD, Ozen I, Yang R, Lepier A, Gascón S, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Parras C, Guillemot F, Frotscher M, Berninger B, Hevner RF, Raineteau O, Götz M (2009) Adult generation of glutamatergic olfactory bulb interneurons. Nat Neurosci 12:1524–1533
Brunne B, Zhao S, Derouiche A, Herz J, May P, Frotscher M, Bock HH (2010) Origin, maturation, and astroglial transformation of secondary radial glial cells in the developing dentate gyrus. Glia 58:1553–1569
Coulpier F, Le Crom S, Maro GS, Manent J, Giovannini M, Maciorowski Z, Fischer A, Gessler M, Charnay P, Topilko P (2009) Novel features of boundary cap cells revealed by the analysis of newly identified molecular markers. Glia 57:1450–1457
Deshpande A, Bergami M, Ghanem A, Conzelmann K-K, Lepier A, Götz M, Berninger B (2013) Retrograde monosynaptic tracing reveals the temporal evolution of inputs onto new neurons in the adult dentate gyrus and olfactory bulb. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E1152–E1161
Enikolopov G, Overstreet-Wadiche L, Ge S (2015) Viral and transgenic reporters and genetic analysis of adult neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a018804
Ernst A, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Perl S, Tisdale J, Possnert G, Druid H, Frisén J (2014) Neurogenesis in the striatum of the adult human brain. Cell 156:1072–1083
Espósito MS, Piatti VC, Laplagne DA, Morgenstern NA, Ferrari CC, Pitossi FJ, Schinder AF (2005) Neuronal differentiation in the adult hippocampus recapitulates embryonic development. J Neurosci 25:10074–10086
Forni PE, Taylor-Burds C, Melvin VS, Williams T, Wray S (2011) Neural crest and ectodermal cells intermix in the nasal placode to give rise to GnRH-1 neurons, sensory neurons, and olfactory ensheathing cells. J Neurosci 31:6915–6927
Fukuda S, Kato F, Tozuka Y, Yamaguchi M, Miyamoto Y, Hisatsune T (2003) Two distinct subpopulations of nestin-positive cells in adult mouse dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 23:9357–9366
Gage FH, Temple S (2013) Neural stem cells: generating and regenerating the brain. Neuron 80:588–601
Gal A, Rau I, El Matri L, Kreienkamp H-J, Fehr S, Baklouti K, Chouchane I, Li Y, Rehbein M, Fuchs J, Fledelius HC, Vilhelmsen K, Schorderet DF, Munier FL, Ostergaard E, Thompson DA, Rosenberg T (2011) Autosomal-recessive posterior microphthalmos is caused by mutations in PRSS56, a gene encoding a trypsin-like serine protease. Am J Hum Genet 88:382–390
Ge S, Yang C-H, Hsu K-S, Ming G-L, Song H (2007) A critical period for enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated neurons of the adult brain. Neuron 54:559–566
Gould E (2007) How widespread is adult neurogenesis in mammals? Nat Rev Neurosci 8:481–488
Gresset A, Coulpier F, Gerschenfeld G, Jourdon A, Matesic G, Richard L, Vallat J-M, Charnay P, Topilko P (2015) Boundary caps give rise to neurogenic stem cells and terminal glia in the skin. Stem Cell Rep 5:1–13
Guo C, Eckler MJ, McKenna WL, McKinsey GL, Rubenstein JLR, Chen Bin (2013) Fezf2 expression identifies a multipotent progenitor for neocortical projection neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Neuron 80:1167–1174
Haan N, Goodman T, Najdi-Samiei A, Stratford CM, Rice R, El Agha E, Bellusci S, Hajihosseini MK (2013) Fgf10-expressing tanycytes add new neurons to the appetite/energy-balance regulating centers of the postnatal and adult hypothalamus. J Neurosci 33:6170–6180
Hodge RD, Nelson BR, Kahoud RJ, Yang R, Mussar KE, Reiner SL, Hevner RF (2012) Tbr2 is essential for hippocampal lineage progression from neural stem cells to intermediate progenitors and neurons. J Neurosci 32:6275–6287
Ihrie RA, Álvarez-Buylla A (2011) Lake-front property: a unique germinal niche by the lateral ventricles of the adult brain. Neuron 70:674–686
Ihrie RA, Shah JK, Harwell CC, Levine JH, Guinto CD, Lezameta M, Kriegstein AR, Álvarez-Buylla A (2011) Persistent Sonic Hedgehog signaling in adult brain determines neural stem cell positional identity. Neuron 71:250–262
Iwano T, Masuda A, Kiyonari H, Enomoto H, Matsuzaki F (2012) Prox1 postmitotically defines dentate gyrus cells by specifying granule cell identity over CA3 pyramidal cell fate in the hippocampus. Development 139:3051–3062
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Batteur S, Mao XO, Smelick C, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) Neurogenesis and aging: FGF-2 and HB-EGF restore neurogenesis in hippocampus and subventricular zone of aged mice. Aging Cell 2:175–183
Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G (2004) Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 27:447–452
Kohwi M, Petryniak MA, Long JE, Ekker M, Obata K, Yanagawa Y, Rubenstein JLR, Alvarez-Buylla A (2007) A subpopulation of olfactory bulb GABAergic interneurons is derived from Emx1- and Dlx5/6-expressing progenitors. J Neurosci 27:6878–6891
Kokoeva MV, Yin H, Flier JS (2005) Neurogenesis in the hypothalamus of adult mice: potential role in energy balance. Science 310:679–683
Kuhn HG, Winkler J, Kempermann G, Thal LJ, Gage FH (1997) Epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 have different effects on neural progenitors in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci 17:5820–5829
Lee DA, Blackshaw S (2012) Functional implications of hypothalamic neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 30:615–621
Lee DA, Bedont JL, Pak T, Wang H, Song J, Miranda-Angulo A, Takiar V, Charubhumi V, Balordi F, Takebayashi H, Aja S, Ford E, Fishell G, Blackshaw S (2012) Tanycytes of the hypothalamic median eminence form a diet-responsive neurogenic niche. Nat Neurosci 15:700–702
Lepousez G, Nissant A, Bryant AK, Gheusi G, Greer CA, Lledo PM (2014) Olfactory learning promotes input-specific synaptic plasticity in adult-born neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:13984–13989
Li G, Kataoka H, Coughlin SR, Pleasure SJ (2009) Identification of a transient subpial neurogenic zone in the developing dentate gyrus and its regulation by Cxcl12 and reelin signaling. Development 136:327–335
Li J, Tang Y, Cai D (2012) IKKβ/NF-κB disrupts adult hypothalamic neural stem cells to mediate a neurodegenerative mechanism of dietary obesity and pre-diabetes. Nat Cell Biol 14:999–1012
Li G, Fang L, Fernández G, Pleasure SJ (2013) The ventral hippocampus is the embryonic origin for adult neural stem cells in the dentate gyrus. Neuron 78:658–672
Lie DC, Dziewczapolski G, Willhoite AR, Kaspar BK, Shults CW, Gage FH (2002) The adult substantia nigra contains progenitor cells with neurogenic potential. J Neurosci 22:6639–6649
Liu Y, Namba T, Liu J, Suzuki R, Shioda S, Seki T (2010) Glial fibrillary acidic protein-expressing neural progenitors give rise to immature neurons via early intermediate progenitors expressing both glial fibrillary acidic protein and neuronal markers in the adult hippocampus. Neuroscience 166:241–251
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A (1994) Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264:1145–1148
Madisen L, Zwingman TA, Sunkin SM, Oh SW, Zariwala HA, Gu H, Ng LL, Palmiter RD, Hawrylycz MJ, Jones AR, Lein ES, Zeng H (2010) A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain. Nat Neurosci 13:133–140
Marín-Burgin A, Mongiat LA, Pardi MB, Schinder AF (2012) Unique processing during a period of high excitation/inhibition balance in adult-born neurons. Science 335:1238–1242
Markakis EA, Palmer TD, Randolph-Moore L, Rakic P, Gage FH (2004) Novel neuronal phenotypes from neural progenitor cells. J Neurosci 24:2886–2897
Merkle FT, Tramontin AD, Garcia-Verdugo J-M, Álvarez-Buylla A (2004) Radial glia give rise to adult neural stem cells in the subventricular zone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17528–17532
Merkle FT, Mirzadeh Z, Alvarez-Buylla A (2007) Mosaic organization of neural stem cells in the adult brain. Science 317:381–384
Merkle FT, Fuentealba LC, Sanders TA, Magno L, Kessaris N, Álvarez-Buylla A (2014) Adult neural stem cells in distinct microdomains generate previously unknown interneuron types. Nat Neurosci 17:207–214
Ming G-L, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70:687–702
Mirzadeh Z, Merkle FT, Soriano-Navarro M, Garcia-Verdugo J-M, Álvarez-Buylla A (2008) Neural stem cells confer unique pinwheel architecture to the ventricular surface in neurogenic regions of the adult brain. Cell Stem Cell 3:265–278
Mirzadeh Z, Doetsch F, Sawamoto K, Wichterle H, Álvarez-Buylla A (2010) The subventricular zone en-face: wholemount staining and ependymal flow. J Vis Exp 39:1–8
Muzumdar MD, Tasic B, Miyamichi K, Li L, Luo L (2007) A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. Genesis 45:593–605
Nair KS, Hmani-Aifa M, Ali Z, Kearney AL, Salem SB, Macalinao DG, Cosma IM, Bouassida W, Hakim B, Benzina Z, Soto I, Söderkvist P, Howell GR, Smith RS, Ayadi H, John SWM (2011) Alteration of the serine protease PRSS56 causes angle-closure glaucoma in mice and posterior microphthalmia in humans and mice. Nat Genet 43:579–584
Nolte C, Matyash M, Pivneva T, Schipke CG, Ohlemeyer C, Hanisch UK, Kirchhoff F, Kettenmann H (2001) GFAP promoter-controlled EGFP-expressing transgenic mice: a tool to visualize astrocytes and astrogliosis in living brain tissue. Glia 33:72–86
Nunes MC, Roy NS, Keyoung HM, Goodman RR, McKhann G, Jiang L, Kang J, Nedergaard M, Goldman SA (2003) Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain. Nat Med 9:439–447
Palmer TD, Ray J, Gage FH (1995) FGF-2-responsive neuronal progenitors reside in proliferative and quiescent regions of the adult rodent brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 6:474–486
Pencea V, Bingaman KD, Wiegand SJ, Luskin MB (2001) Infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor into the lateral ventricle of the adult rat leads to new neurons in the parenchyma of the striatum, septum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. J Neurosci 21:6706–6717
Pierce AA, Xu AW (2010) De novo neurogenesis in adult hypothalamus as a compensatory mechanism to regulate energy balance. J Neurosci 30:723–730
Reynolds BA, Tetzlaff W, Weiss S (1992) A multipotent EGF-responsive striatal embryonic progenitor cell produces neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci 12:4565–4574
Rivers LE, Young KM, Rizzi M, Jamen F, Psachoulia K, Wade A, Kessaris N, Richardson WD (2008) PDGFRA/NG2 glia generate myelinating oligodendrocytes and piriform projection neurons in adult mice. Nat Neurosci 11:1392–1401
Robins SC, Stewart I, McNay DE, Taylor V, Giachino C, Goetz M, Ninkovic J, Briancon N, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS, Kokoeva MV, Placzek M (2013a) α-Tanycytes of the adult hypothalamic third ventricle include distinct populations of FGF-responsive neural progenitors. Nat Commun 4:2049
Robins SC, Trudel E, Rotondi O, Liu X, Djogo T, Kryzskaya D, Bourque CW, Kokoeva MV (2013b) Evidence for NG2-glia derived, adult-born functional neurons in the hypothalamus. PLoS ONE 8:e78236
Rodríguez EM, Blázquez JL, Pastor FE, Peláez B, Peña P, Peruzzo B, Amat P (2005) Hypothalamic tanycytes: a key component of brain-endocrine interaction. Int Rev Cytol 247:89–164
Seki T, Sato T, Toda K, Osumi N, Imura T, Shioda S (2013) Distinctive population of Gfap-expressing neural progenitors arising around the dentate notch migrate and form the granule cell layer in the developing hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 522:261–283
Seri B, García-Verdugo JM, McEwen BS, Alvarez-Buylla A (2001) Astrocytes give rise to new neurons in the adult mammalian hippocampus. J Neurosci 21:7153–7160
Sousa-Ferreira L, de Almeida LP, Cavadas C (2014) Role of hypothalamic neurogenesis in feeding regulation. Trends Endocrin Met 25:80–88
Spassky N, Merkle FT, Flames N, Tramontin AD, Garcia-Verdugo J-M, Álvarez-Buylla A (2005) Adult ependymal cells are postmitotic and are derived from radial glial cells during embryogenesis. J Neurosci 25:10–18
Stenman J, Toresson H, Campbell K (2003) Identification of two distinct progenitor populations in the lateral ganglionic eminence: implications for striatal and olfactory bulb neurogenesis. J Neurosci 23:167–174
Tramontin AD, Garcia-Verdugo J-M, Lim DA, Álvarez-Buylla A (2003) Postnatal development of radial glia and the ventricular zone (VZ): a continuum of the neural stem cell compartment. Cereb Cortex 13:580–587
Urbán N, Guillemot F (2014) Neurogenesis in the embryonic and adult brain: same regulators, different roles. Front Cell Neurosci 8:396
Xu Y, Tamamaki N, Noda T, Kimura K, Itokazu Y, Matsumoto N, Dezawa M, Ide C (2005) Neurogenesis in the ependymal layer of the adult rat 3rd ventricle. Exp Neurol 192:251–264
Young KM, Fogarty M, Kessaris N, Richardson WD (2007) Subventricular zone stem cells are heterogeneous with respect to their embryonic origins and neurogenic fates in the adult olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 27:8286–8296
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132:645–660
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the IBENS Imaging Facility, which received the support of grants from the “Région Ile-de-France” (NERF No. 2009-44 and NERF No. 2011-45), the “Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale” (No. DGE 20111123023) and the “Fédération pour la Recherche sur le Cerveau—Rotary International France” (2011). The IBENS Imaging Facility also received support implemented by the ANR under the program «Investissements d’Avenir» , with the references: ANR-10-LABX-54 MEMO LIFE, ANR-11-IDEX-0001-02 PSL* Research University and ANR‐10‐INSB‐04‐01 France‐BioImaging infrastructure. We are also grateful to the IBENS mouse facility, in particular A. Boudjouher and C. Auger. We thank Nathalie Rouach and Annette Koulakoff (College de France, France) for the gift of the hGfAP::GFP line. The P.C. laboratory was financed by the Institut National de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), the Ministère de la Recherche et Technologie (MRT), the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM), the Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM), and the Association de Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC). It has received support under the program “Investissements d’Avenir” launched by the French Government and implemented by the ANR, with the references: ANR-10-LABX-54 MEMOLIFE and ANR-11-IDEX-0001-02 PSL* Research University. A.J. was supported by a doctoral grant from Sorbonne Universités and by the MEMOLIFE program. A.G. was supported by the Fondation Pierre Gilles de Gennes, FRM (SPF20101221087), MRT and the MEMOLIFE program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jourdon, A., Gresset, A., Spassky, N. et al. Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. Brain Struct Funct 221, 4411–4427 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1171-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1171-z