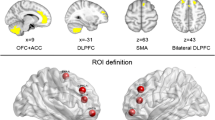
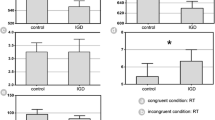
Abstract
Regardless of whether it is conceptualized as a behavioral addiction or an impulse-control disorder, internet gaming disorder (IGD) has been speculated to be associated with impaired cognitive control. Efficient cognitive behavior involves the coordinated activity of large-scale brain networks, however, whether the interactions among these networks during resting state modulated cognitive control behavior in IGD adolescents remain unclear. Twenty-eight IGD adolescents and twenty-five age-, gender-, and education-matched healthy controls participated in our study. Stroop color-word task was conducted to evaluate the cognitive control deficits in IGD adolescents. Functional connectivity and Granger Causal Analysis were employed to investigate the functional and effective connections within and between the salience, central executive, and default mode networks. Meanwhile, diffusion tensor imaging was used to assess the structural integrity of abnormal network connections. The abnormal functional connectivity within central executive networks and effective connectivity within salience network in IGD adolescents were detected. Moreover, the inefficient interactions between these two brain networks were observed. In addition, we identified reduced fractional anisotropy in salience network, right central executive network tracts, and between-network (the anterior cingulate cortex-right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex tracts) pathways in IGD individuals. Notably, we observed a significant correlation between the effective and structural connection from salience network to central executive network and the number of errors during incongruent condition in Stroop task in both IGD and control subjects. Our results suggested that impaired cognitive control in IGD adolescents is likely to be mediated through the abnormal interactions and structural connection between intrinsic large-scale brain networks.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboujaoude E (2010) Problematic internet use: an overview. World Psychiatry 9(2):85–90
Astill RG, Van der Heijden KB, Van Ijzendoorn MH, Van Someren EJ (2012) Sleep, cognition, and behavioral problems in school-age children: a century of research meta-analyzed. Psychol Bull 138(6):1109
Bavelier D, Green CS, Han DH, Renshaw PF, Merzenich MM, Gentile DA (2011) Brains on video games. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(12):763–768
Beard K, Wolf E (2001) Modification in the proposed diagnostic criteria for internet addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav 4(3):377–383
Beckmann CF, Smith SM (2004) Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23(2):137–152
Block JJ (2008) Issues for DSM-V: internet addiction. Am J Psychiatry 165(3):306–307
Bonnelle V, Ham TE, Leech R, Kinnunen KM, Mehta MA, Greenwood RJ, Sharp DJ (2012) Salience network integrity predicts default mode network function after traumatic brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(12):4690–4695
Brewer JA, Worhunsky PD, Carroll KM, Rounsaville BJ, Potenza MN (2008) Pretreatment brain activation during Stroop task is associated with outcomes in cocaine-dependent patients. Biol Psychiatry 64(11):998–1004
Casey B, Jones R, Hare T (2008) The adolescent brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1124(1):111–126
Chen G, Hamilton JP, Thomason ME, Gotlib IH, Saad ZS, Cox RW (2009) Granger causality via vector auto-regression tuned for FMRI data analysis. In: ISMRM 17th Scientific Meeting. Hawaii, 2009
Christakis D (2010) Internet addiction: a 21st century epidemic? BMC Med 8(1):61
Damoiseaux J, Rombouts S, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, Stam C, Smith SM, Beckmann C (2006) Consistent resting-state networks across healthy subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(37):13848–13853
Di X, Biswal BB (2013) Dynamic brain functional connectivity modulated by resting-state networks. Brain Struct Funct 1–10
Ding W-N, Sun J-H, Sun Y-W, Zhou Y, Li L, Xu J-R, Du Y-S (2013) Altered default network resting-state functional connectivity in adolescents with internet gaming addiction. PLoS One 8(3):e59902
Dong G, Zhou H, Zhao X (2011) Male internet addicts show impaired executive control ability: evidence from a color-word Stroop task. Neurosci Lett 499:114–118
Dong G, DeVito EE, Du X, Cui Z (2012) Impaired inhibitory control in “internet addiction disorder”: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 203:153–158
Dong G, Shen Y, Huang J, Du X (2013) Impaired Error-Monitoring Function in People with internet addiction disorder: an event-related fMRI study. Eur Addict Res 19(5):269–275
Duncan J (2001) An adaptive coding model of neural function in prefrontal cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(11):820–829
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(27):9673–9678
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Raichle ME (2007) Intrinsic fluctuations within cortical systems account for intertrial variability in human behavior. Neuron 56(1):171–184
Giedd JN, Blumenthal J, Jeffries NO, Castellanos FX, Liu H, Zijdenbos A, Paus T, Evans AC, Rapoport JL (1999) Brain development during childhood and adolescence: a longitudinal MRI study. Nat Neurosci 2(10):861–863
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND (2011) Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(11):652–669
Granger CW (1969) Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica J Econom Soc 37:424–438
Greicius MD, Krasnow B, Reiss AL, Menon V (2003) Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(1):253–258
Hamilton JP, Chen G, Thomason ME, Schwartz ME, Gotlib IH (2010) Investigating neural primacy in major depressive disorder: multivariate Granger causality analysis of resting-state fMRI time-series data. Mol Psychiatry 16(7):763–772
Hampson M, Driesen N, Roth JK, Gore JC, Constable RT (2010) Functional connectivity between task-positive and task-negative brain areas and its relation to working memory performance. Magn Reson Imaging 28(8):1051–1057
Hesselmann G, Kell CA, Eger E, Kleinschmidt A (2008) Spontaneous local variations in ongoing neural activity bias perceptual decisions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(31):10984–10989
Holden C (2001) ‘Behavioral’ addictions: do they exist? Science 294(5544):980–982
Kelly A, Uddin LQ, Biswal BB, Castellanos FX, Milham MP (2008) Competition between functional brain networks mediates behavioral variability. Neuroimage 39(1):527–537
Kerns JG, Cohen JD, MacDonald AW, Cho RY, Stenger VA, Carter CS (2004) Anterior cingulate conflict monitoring and adjustments in control. Science 303(5660):1023–1026
Ko C, Liu G, Hsiao S, Yen J, Yang M, Lin W, Yen C, Chen C (2009) Brain activities associated with gaming urge of online gaming addiction. J Psychiatr Res 43(7):739–747
Ko C-H, Liu G-C, Yen J-Y, Chen C-Y, Yen C-F, Chen C-S (2013) Brain correlates of craving for online gaming under cue exposure in subjects with internet gaming addiction and in remitted subjects. Addict Biol 18(3):559–569
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2009) Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(1):217–238
Kühn S, Gallinat J (2014) Brains online: structural and functional correlates of habitual internet use. Addict Biol
Li B, Friston KJ, Liu J, Liu Y, Zhang G, Cao F, Su L, Yao S, Lu H, Hu D (2014) Impaired frontal-basal ganglia connectivity in adolescents with internet addiction. Sci Rep 4:5027
Matsumoto K, Tanaka K (2004) Conflict and cognitive control. Science 303(5660):969–970
Menon V (2011) Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model. Trends Cogn Sci 15(10):483–506
Moeller S, Tomasi D, Honorio J, Volkow N, Goldstein R (2012) Dopaminergic involvement during mental fatigue in health and cocaine addiction. Transl Psychiatry 2(10):e176
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Patel AX, Kundu P, Rubinov M, Jones PS, Vértes PE, Ersche KD, Suckling J, Bullmore ET (2014) A wavelet method for modeling and despiking motion artifacts from resting-state fMRI time series. NeuroImage 95:287–304
Petrides M (2005) Lateral prefrontal cortex: architectonic and functional organization. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360(1456):781–795
Petry NM, O’Brien CP (2013) Internet gaming disorder and the DSM-5. Addiction 108:1186–1187
Raichle ME, MacLeod AM, Snyder AZ, Powers WJ, Gusnard DA, Shulman GL (2001) A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(2):676–682
Ridderinkhof KR, van den Wildenberg WP, Segalowitz SJ, Carter CS (2004) Neurocognitive mechanisms of cognitive control: the role of prefrontal cortex in action selection, response inhibition, performance monitoring, and reward-based learning. Brain Cogn 56(2):129–140
Rosenberg J, Maximov II, Reske M, Grinberg F, Shah NJ (2014) “Early to bed, early to rise”: diffusion tensor imaging identifies chronotype-specificity. NeuroImage 84:428–434
Schmaal L, Goudriaan AE, Joos L, Kruse AM, Dom G, van den Brink W, Veltman DJ (2013) Modafinil modulates resting-state functional network connectivity and cognitive control in alcohol-dependent patients. Biol Psychiatry 73:789–795
Seeley WW, Menon V, Schatzberg AF, Keller J, Glover GH, Kenna H, Reiss AL, Greicius MD (2007) Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J Neurosci 27(9):2349–2356
Spreng RN, Stevens WD, Chamberlain JP, Gilmore AW, Schacter DL (2010) Default network activity, coupled with the frontoparietal control network, supports goal-directed cognition. Neuroimage 53(1):303–317
Sridharan D, Levitin DJ, Menon V (2008) A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(34):12569–12574
Steinberg L (2005) Cognitive and affective development in adolescence. Trends Cogn Sci 9(2):69–74
Stone R (2009) China reins in wilder impulses in treatment of ‘internet addiction’. Science 324(5935):1630–1631
Streeter CC, Terhune DB, Whitfield TH, Gruber S, Sarid-Segal O, Silveri MM, Tzilos G, Afshar M, Rouse ED, Tian H (2007) Performance on the Stroop predicts treatment compliance in cocaine-dependent individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(4):827–836
Stroop JR (1935) Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol 18(6):643–662
Uddin LQ, Supekar KS, Ryali S, Menon V (2011) Dynamic reconfiguration of structural and functional connectivity across core neurocognitive brain networks with development. J Neurosci 31(50):18578–18589
Volkow N, Fowler J, Wang G (2003) The addicted human brain: insights from imaging studies. J Clin Investig 111(10):1444–1451
Wolniczak I, Cáceres-DelAguila JA, Palma-Ardiles G, Arroyo KJ, Solís-Visscher R, Paredes-Yauri S, Mego-Aquije K, Bernabe-Ortiz A (2013) Association between facebook dependence and poor sleep quality: a study in a sample of undergraduate students in Peru. PLoS One 8(3):e59087
Xu J, Mendrek A, Cohen MS, Monterosso J, Simon S, Jarvik M, Olmstead R, Brody AL, Ernst M, London ED (2006) Effect of cigarette smoking on prefrontal cortical function in nondeprived smokers performing the Stroop Task. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(6):1421–1428
Yen CF, Yen JUYU, Ko CH (2010) Internet addiction: ongoing research in Asia. World Psychiatry 9(2):97
Young K (1998) Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. CyberPsychol Behav 1(3):237–244
Young K (2010) Internet addiction over the decade: a personal look back. World Psychiatry 9(2):91
Yuan K, Qin W, Liu Y, Tian J (2011a) Internet addiction: neuroimaging findings. Commun Integr Biol 4(6):637–639
Yuan K, Qin W, Wang G, Zeng F, Zhao L, Yang X, Liu P, Liu J, Sun J, von Deneen KM (2011b) Microstructure Abnormalities in Adolescents with Internet Addiction Disorder. PLoS One 6(6):e20708
Yuan K, Cheng P, Dong T, Bi Y, Xing L, Yu D, Zhao L, Dong M, von Deneen KM, Liu Y (2013a) Cortical thickness abnormalities in late adolescence with online gaming addiction. PLoS One 8(1):e53055
Yuan K, Jin C, Cheng P, Yang X, Dong T, Bi Y, Xing L, von Deneen KM, Yu D, Liu J (2013b) Amplitude of low frequency fluctuation abnormalities in adolescents with online gaming addiction. PLoS One 8(11):e78708
Zang Z-X, Yan C-G, Dong Z-Y, Huang J, Zang Y-F (2012) Granger causality analysis implementation on MATLAB: a graphic user interface toolkit for fMRI data processing. J Neurosci Methods 203(2):418–426
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Haifeng Luo, Changjian Hu, and Jun Liang for valuable technical assistance in conducting this research. This paper is supported by the Project for the National Key Basic Research and Development Program (973) under Grant Nos. 2014CB543203, 2011CB707700, 2012CB518501, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81227901, 81271644, 81271546, 81101036, 81101108, 31200837, 81030027, 81301281, 81401488, 81401478, 81471737, 81471811, 81471738, 61401346, the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China under Grant No. 2014JQ4118, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia under Grant No. 2012MS0908. General Financial Grant the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2014M552416.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Yuan, W. Qin and D. Yu contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Yu, D. et al. Core brain networks interactions and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder individuals in late adolescence/early adulthood. Brain Struct Funct 221, 1427–1442 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0982-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0982-7