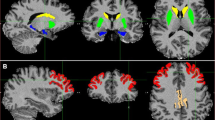
Abstract
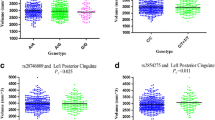
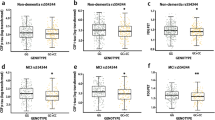
The tau hypothesis has been raised with regard to the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is associated with a high risk for developing AD. However, no study has directly examined the brain topological alterations based on combined effects of tau protein pathway genes in MCI population. Forty-three patients with MCI and 30 healthy controls underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in Chinese Han, and a tau protein pathway-based imaging approaches (7 candidate genes: 17 SNPs) were used to investigate changes in the topological organisation of brain activation associated with MCI. Impaired regional activation is related to tau protein pathway genes (5/7 candidate genes) in patients with MCI and likely in topologically convergent and divergent functional alterations patterns associated with genes, and combined effects of tau protein pathway genes disrupt the topological architecture of cortico-cerebellar loops. The associations between the loops and behaviours further suggest that tau protein pathway genes do play a significant role in non-episodic memory impairment. Tau pathway-based imaging approaches might strengthen the credibility in imaging genetic associations and generate pathway frameworks that might provide powerful new insights into the neural mechanisms that underlie MCI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen G, McColl R, Barnard H, Ringe WK, Fleckenstein J, Cullum CM (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebellar-prefrontal and cerebellarparietal functional connectivity. Neuroimage 28:39–48
Attems J, Thomas A, Jellinger K (2012) Correlations between cortical and subcortical tau pathology. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38:582–590
Bai F, Shi Y, Yuan Y, Yue C, Zhuang L, Xu X, Liu X, Zhang Z (2012) Association of a GSK-3β polymorphism with brain resting-state function in amnestic-type mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 32:387–396
Bero AW, Yan P, Roh JH, Cirrito JR, Stewart FR, Raichle ME, Lee JM, Holtzman DM (2011) Neuronal activity regulates the regional vulnerability to amyloid-β deposition. Nat Neurosci 14:750–756
Bing X, Ming-Guo Q, Ye Z, Jing-Na Z, Min L, Han C, Yu Z, Jia-Jia Z, Jian W, Wei C, Han-Jian D, Shao-Xiang Z (2012) Alterations in the cortical thickness and the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. Brain Res 1490:225–232
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2012) Where, when, and in what form does sporadic Alzheimer’s disease begin? Curr Opin Neurol 25:708–714
Chen S, Townsend K, Goldberg TE, Davies P, Conejero-Goldberg C (2010) MAPT isoforms: differential transcriptional profiles related to 3R and 4R splice variants. J Alzheimers Dis 22:1313–1329
Clément F, Belleville S (2010) Compensation and disease severity on the memory-related activations in mild cognitive impairment. Biol Psychiatry 68:894–902
Delacourte A, David JP, Sergeant N, Buée L, Wattez A, Vermersch P, Ghozali F, Fallet-Bianco C, Pasquier F, Lebert F, Petit H, Di Menza C (1999) The biochemical pathway of neurofibrillary degeneration in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 52:1158–1165
Diniz Behn C, Booth V (2012) A fast-slow analysis of the dynamics of REM sleep. SIAM J Appl Dyn System 11(1):212–242
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Cummings JL, Dekosky ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Delacourte A, Frisoni G, Fox NC, Galasko D, Gauthier S, Hampel H, Jicha GA, Meguro K, O’Brien J, Pasquier F, Robert P, Rossor M, Salloway S, Sarazin M, de Souza LC, Stern Y, Visser PJ, Scheltens P (2010) Revising the definition of Alzheimer’s disease: a new lexicon. Lancet Neurol 9:1118–1127
Dugger BN, Tu M, Murray ME, Dickson DW (2011) Disease specificity and pathologic progression of tau pathology in brainstem nuclei of Alzheimer’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 491:122–126
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9673–9678
Frank G, Hennig-Fast K, Klünemann HH, Schmitz G, Greenlee MW (2011) Differential impact of ApoE ε4 on cortical activation during famous face recognition in cognitively intact individuals and patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 25:250–261
Georgiou-Karistianis N, Akhlaghi H, Corben LA, Delatycki MB, Storey E, Bradshaw JL, Egan GF (2012) Decreased functional brain activation in Friedreich ataxia using the Simon effect task. Brain Cogn 79:200–208
Gomez-Beldarrain M, Garcia-Monco JC (1998) The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 121:2202–2205
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4913–4917
Guadagna S, Esiri MM, Williams RJ, Francis PT (2012) Tau phosphorylation in human brain: relationship to behavioral disturbance in dementia. Neurobiol Aging 33:2798–2806
Habas C, Kamdar N, Nguyen D, Prater K, Beckmann CF, Menon V, Greicius MD (2009) Distinct cerebellar contributions to intrinsic connectivity networks. J Neurosci 29:8586–8594
He Y, Zang Y, Jiang T, Liang M, Gong G (2004) Detecting functional connectivity of the cerebellum using low frequency fluctuations (LFFs). Lect Notes Comput Sci 3217:907–915
Hita-Yañez E, Atienza M, Gil-Neciga E, Cantero JL (2012) Disturbed sleep patterns in elders with mild cognitive impairment: the role of memory decline and ApoE ε4 genotype. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:290–297
Hooper C, Killick R, Lovestone S (2008) The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 104:1433–1439
Inkster B, Nichols TE, Saemann PG, Auer DP, Holsboer F, Muglia P, Matthews PM (2009) Association of GSK3beta polymorphisms with brain structural changes in major depressive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:721–728
Inkster B, Nichols TE, Saemann PG, Auer DP, Holsboer F, Muglia P, Matthews PM (2010) Pathway-based approaches to imaging genetics association studies: wnt signaling, GSK3beta substrates and major depression. Neuroimage 53:908–917
Jaeger S, Pietrzik CU (2008) Functional role of lipoprotein receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 5:15–25
Koch W, Teipel S, Mueller S, Benninghoff J, Wagner M, Bokde AL, Hampel H, Coates U, Reiser M, Meindl T (2012) Diagnostic power of default mode network resting state fMRI in the detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33:466–478
Kwok JB, Hallupp M, Loy CT, Chan DK, Woo J, Mellick GD, Buchanan DD, Silburn PA, Halliday GM, Schofield PR (2005) GSK3B polymorphisms alter transcription and splicing in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 58:829–839
Lancaster TM, Baird A, Wolf C, Jackson MC, Johnston SJ, Donev R, Thome J, Linden DE (2011) Neural hyperactivation in carriers of the Alzheimer’s risk variant on the clusterin gene. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:880–884
Leinonen V, Koivisto AM, Savolainen S, Rummukainen J, Tamminen JN, Tillgren T, Vainikka S, Pyykkö OT, Mölsä J, Fraunberg M, Pirttilä T, Jääskeläinen JE, Soininen H, Rinne J, Alafuzoff I (2010) Amyloid and tau proteins in cortical brain biopsy and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 68:446–453
Liu X, Yue C, Xu Z, Shu H, Pu M, Yu H, Shi Y, Zhuang L, Xu X, Zhang Z (2012) Association study of candidate gene polymorphisms with amnestic mild cognitive impairment in a Chinese population. PLoS One 7:e41198
Long D, Wang J, Xuan M, Gu Q, Xu X, Kong D, Zhang M (2012) Automatic classification of early Parkinson’s disease with multi-modal MR imaging. PLoS One 7:e47714
Maccioni RB, Farías G, Morales I, Navarrete L (2010) The revitalized tau hypothesis on Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Med Res 41:226–231
Marcus JN, Schachter J (2011) Targeting post-translational modifications on tau as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurogenet 25:127–133
Martinez A, Gil C, Perez DI (2011) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors in the next horizon for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:280502
Mortimer JA (1997) Brain reserve and the clinical expression of Alzheimer’s disease. Geriatrics 52(Suppl 2):S50–S53
Oakes TR, Fox AS, Johnstone T, Chung MK, Kalin N, Davidson RJ (2007) Integrating VBM into the General Linear Model with voxelwise anatomical covariates. Neuroimage 34:500–508
Pei JJ, Braak H, Gong CX, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Winblad B, Cowburn RF (2002) Up-regulation of cell division cycle (cdc) 2 kinase in neurons with early stage Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 104:369–376
Petersen RC, Negash S (2008) Mild cognitive impairment: an overview. CNS Spectr 13:45–53
Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E (1999) Mild cognitive impairment, clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol 56:303–308
Ryoo SR, Jeong HK, Radnaabazar C, Yoo JJ, Cho HJ, Lee HW, Kim IS, Cheon YH, Ahn YS, Chung SH, Song WJ (2007) DYRK1A-mediated hyperphosphorylation of Tau. A functional link between Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 282:34850–34857
Schuff N, Woerner N, Boreta L, Kornfield T, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Thompson PM, Jack CR Jr, Weiner MW, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2009) MRI of hippocampal volume loss in early Alzheimer’s disease in relation to ApoE genotype and biomarkers. Brain 132:1067–1077
Sepulveda-Falla D, Matschke J, Bernreuther C, Hagel C, Puig B, Villegas A, Garcia G, Zea J, Gomez-Mancilla B, Ferrer I, Lopera F, Glatzel M (2011) Deposition of hyperphosphorylated tau in cerebellum of PS1 E280A Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol 21:452–463
Sheline YI, Morris JC, Snyder AZ, Price JL, Yan Z, D’Angelo G, Liu C, Dixit S, Benzinger T, Fagan A, Goate A, Mintun MA (2010) APOE4 allele disrupts resting state fMRI connectivity in the absence of amyloid plaques or decreased CSF Aβ42. J Neurosci 30:17035–17040
Shelton SB, Johnson GV (2004) Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 in neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 88:1313–1326
Small SA, Duff K (2008) Linking Abeta and tau in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: a dual pathway hypothesis. Neuron 60:534–542
Sperling R (2011) The potential of functional MRI as a biomarker in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:S37–S43
Tolnay M, Probst A (1999) Review: tau protein pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 25:171–187
Trachtenberg AJ, Filippini N, Ebmeier KP, Smith SM, Karpe F, Mackay CE (2012) The effects of APOE on the functional architecture of the resting brain. Neuroimage 59:565–572
Vemuri P, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, Knopman DS, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM, Bernstein MA, Aisen PS, Weiner M, Petersen RC, Jack CR Jr, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2010) Serial MRI and CSF biomarkers in normal aging, MCI, and AD. Neurology 75:143–151
Wang J, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2007) Kinases and phosphatases and tau sites involved in Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration. Eur J Neurosci 25:59–68
Wang Z, Yan C, Zhao C, Qi Z, Zhou W, Lu J, He Y, Li K (2011) Spatial patterns of intrinsic brain activity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a resting-state functional MRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 32:1720–1740
Westlye ET, Lundervold A, Rootwelt H, Lundervold AJ, Westlye LT (2011) Increased hippocampal default mode synchronization during rest in middle-aged and elderly APOE ε4 carriers: relationships with memory performance. J Neurosci 31:7775–7783
Williamson J, Goldman J, Marder KS (2009) Genetic aspects of Alzheimer disease. Neurologist 15:80–86
Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, Nordberg A, Bäckman L, Albert M, Almkvist O, Arai H, Basun H, Blennow K, de Leon M, DeCarli C, Erkinjuntti T, Giacobini E, Graff C, Hardy J, Jack C, Jorm A, Ritchie K, van Duijn C, Visser P, Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment-beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the international working group on mild cognitive impairment. J Intern Med 256:240–246
Yamamoto H, Hiragami Y, Murayama M, Ishizuka K, Kawahara M, Takashima A (2005) Phosphorylation of tau at serine 416 by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in neuronal soma in brain. J Neurochem 94:1438–1447
Yu R, Chien YL, Wang HL, Liu CM, Liu CC, Hwang TJ, Hsieh MH, Hwu HG, Tseng WY (2014) Frequency-specific alternations in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia. Hum Brain Mapp 35:627–637
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29:83–91
Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H, Habas R, Okamura H, Woodgett J, He X (2005) A dual-kinase mechanism for Wnt co-receptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature 438:873–877
Zhang Z, Deng L, Bai F, Shi Y, Yu H, Yuan Y, Wang K, Jiang T, Jia J, Zhang Z (2010) Alteration of resting brain function by genetic variation in angiotensin converting enzyme in amnestic-type mild cognitive impairment of Chinese Han. Behav Brain Res 208:619–625
Acknowledgments
Thanks to all participants. This research was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81201080, 91332104); Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-13-0117); Key Program for Clinical Medicine and Science and Tochnology: Jiangsu Provence Clinical Medical Research Center (No.BL2013025); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK2012337) and Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (20120092120068). None of the authors have a conflict of interest, financial or otherwise, directly or indirectly related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
F. Bai and W. Liao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, F., Liao, W., Yue, C. et al. Genetics pathway-based imaging approaches in Chinese Han population with Alzheimer’s disease risk. Brain Struct Funct 221, 433–446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0916-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0916-4