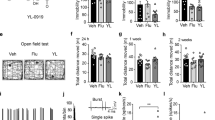
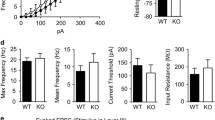
Abstract
This study investigates the mechanism of action of spadin, a putative fast-acting peptidic antidepressant (AD) and a functional blocker of the K+ TREK-1 channel, in relation with the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)–dorsal raphé (DRN) serotonergic (5-HT) neurons connectivity. Spadin increased 5-HT neuron firing rate by 113 %, an augmentation abolished after electrolytic lesion of the mPFC. Among the few receptor subtypes known to modulate TREK-1, the stimulation of 5-HT4 receptors and the blockade of mGluR2/3 ones both activated 5-HT impulse flow, effects also suppressed by mPFC lesion. The combination of spadin with the 5-HT4 agonist RS 67333 paradoxically reduced 5-HT firing, an effect reversed by acutely administering the 5-HT1A agonist flesinoxan. It also had a robust synergetic effect on the expression of Zif268 within the DRN. Together, these results strongly suggest that 5-HT neurons underwent a state of depolarization block, and that the mechanisms underlying the influences exerted by spadin and RS 67333 are additive and independent from each other. In contrast, the mGluR2/3 antagonist LY 341495 occluded the effect of spadin, showing that it likely depends on mPFC TREK-1 channels coupled to mGluR2/3 receptors. These in vivo electrophysiological data were confirmed by in vitro Ca2+ cell imaging performed in cultured cortical neurons. Altogether, our results indicate that spadin, as a natural compound, constitutes a very good candidate to explore the “glutamatergic path” of fast-acting AD research. In addition, they provide the first evidence of 5-HT depolarization block, showing that the combination of 5-HT activators for strategies of AD augmentation should be performed with extreme caution.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adell A, Castro E, Celada P, Bortolozzi A, Pazos A et al (2005) Strategies for producing faster acting antidepressants. Drug Discov Today 10:578–585
Ansanay H, Dumuis A, Sebben M, Bockaert J, Fagni L (1995) cAMP-dependent, long-lasting inhibition of a K+ current in mammalian neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6635–6639
Barreto-Chang OL, Dolmetsch RE (2009) Calcium imaging of cortical neurons using Fura-2 AM. J Vis Exp 23:1067
Berton O, Nestler EJ (2006) New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:137–151
Bespalov AY, van Gaalen MM, Sukhotina IA, Wicke K, Mezler M et al (2008) Behavioral characterization of the mGlu group II/III receptor antagonist, LY-341495, in animal models of anxiety and depression. Eur J Pharmacol 592:96–102
Blier P, de Montigny C (1994) Current advances and trends in the treatment of depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:220–226
Blier P, El Mansari M (2013) Serotonin and beyond: therapeutics for major depression. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 368:20120536
Cain SM, Meadows HJ, Dunlop J, Bushell TJ (2008) mGlu4 potentiation of K(2P)2.1 is dependant on C-terminal dephosphorylation. Mol Cell Neurosci 37:32–39
Celada P, Puig MV, Casanovas JM, Guillazo G, Artigas F (2001) Control of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons by the medial prefrontal cortex: involvement of serotonin-1A, GABA(A), and glutamate receptors. J Neurosci 21:9917–9929
Chaki S, Yoshikawa R, Hirota S, Shimazaki T, Maeda M et al (2004) MGS0039: a potent and selective group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist with antidepressant-like activity. Neuropharmacology 46:457–467
Chapin EM, Haj-Dahmane S, Torres G, Andrade R (2002) The 5-HT(4) receptor-induced depolarization in rat hippocampal neurons is mediated by cAMP but is independent of I(h). Neurosci Lett 324:1–4
Chemin J, Girard C, Duprat F, Lesage F, Romey G et al (2003) Mechanisms underlying excitatory effects of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors via inhibition of 2P domain K+ channels. EMBO J 22:5403–5411
Chiodo LA, Bunney BS (1983) Typical and atypical neuroleptics: differential effects of chronic administration on the activity of A9 and A10 midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 3:1607–1619
Chiodo LA, Bunney BS (1985) Possible mechanisms by which repeated clozapine administration differentially affects the activity of two subpopulations of midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 5:2539–2544
Dicou E, Vincent JP, Mazella J (2004) Neurotensin receptor-3/sortilin mediates neurotensin-induced cytokine/chemokine expression in a murine microglial cell line. J Neurosci Res 78:92–99
Duman RS (2007) A silver bullet for the treatment of depression? Neuron 55:679–681
Dwyer JM, Lepack AE, Duman RS (2012) mTOR activation is required for the antidepressant effects of mGluR2/3 blockade. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:429–434
Etiévant A, Oosterhof C, Bétry C, Abrial E, Lambas-Senas L et al (2010) Effects of medial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation on dorsal raphe 5-HT neuronal activity and hippocampal metaplasticity. Society for Neurosciences 572:17
Etiévant A, Lambás-Señas L, Abrial E, Bétry C, Haddjeri H et al (2011) Connection re-established: neurotransmission between the medial prefrontal cortex and serotonergic neurons offers perspectives for fast antidepressant action. Neuropsychiatry 1:165–177
Furukawa TA, Cipriani A, Barbui C, Geddes JR (2007) Long-term treatment of depression with antidepressants: a systematic narrative review. Can J Psychiatry 52:545–552
Gale JD, Grossman CJ, Darton J, Bunce KT, Whitehead JWF et al (1994) GR125487: a selective and high affinity 5-HT4 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 113:120P
Gil V, Gallego D, Moha Ou, Maati H, Peyronnet R, Martínez-Cutillas M et al (2012) Relative contribution of SKCa and TREK1 channels in purinergic and nitrergic neuromuscular transmission in the rat colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303:412–423
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1986) Induction of depolarization block in midbrain dopamine neurons by repeated administration of haloperidol: analysis using in vivo intracellular recording. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:1092–1100
Grace AA, Bunney BS, Moore H, Todd CL (1997) Dopamine-cell depolarization block as a model for the therapeutic actions of antipsychotic drugs. TINS 20:31–37
Haddjeri N, Ortemann C, de Montigny C, Blier P (1999) Effect of sustained administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist flesinoxan on rat 5-HT neurotransmission. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9:427–440
Hadrava V, Blier P, Dennis T, Ortemann C, de Montigny C (1995) Characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A properties of flesinoxan: in vivo electrophysiology and hypothermia study. Neuropharmacology 34:1311–1326
Hajós M, Richards CD, Székely AD, Sharp T (1998) An electrophysiological and neuroanatomical study of the medial prefrontal cortical projection to the midbrain raphe nuclei in the rat. Neuroscience 87:95–108
Hamani C, Diwan M, Macedo CE, Brandão ML, Shumake J et al (2010) Antidepressant-like effects of medial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation in rats. Biol Psychiatry 67:117–124
Hervieu GJ, Cluderay JE, Gray CW, Green PJ, Ranson JL et al (2001) Distribution and expression of TREK-1, a two-pore-domain potassium channel, in the adult rat CNS. Neuroscience 103:899–919
Heurteaux C, Lucas G, Guy N, El Yacoubi M, Thümmler S et al (2006) Deletion of the background potassium channel TREK-1 results in a depression-resistant phenotype. Nat Neurosci 9:1134–1141
Heurteaux C, Gandin C, Borsotto M, Widmann C, Brau F et al (2010) Neuroprotective and neuroproliferative activities of NeuroAid (MLC601, MLC901), a Chinese medicine, in vitro and in vivo. Neuropharmacology 58:987–1001
Hovelsø N, Sotty F, Montezinho LP, Pinheiro PS, Herrik KF et al (2012) Therapeutic potential of metabotropic glutamate receptor modulators. Curr Neuropharmacol 10:12–48
Johnson BG, Wright RA, Arnold MB, Wheeler WJ, Ornstein PL et al (1999) [3H]-LY341495 as a novel antagonist radioligand for group II metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors: characterization of binding to membranes of mGlu receptor subtype expressing cells. Neuropharmacolog 38:1519–1529
Juckel G, Mendlin A, Jacobs BL (1999) Electrical stimulation of rat medial prefrontal cortex enhances forebrain serotonin output: implications for electroconvulsive therapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:391–398
Kawashima N, Karasawa J, Shimazaki T, Chaki S, Okuyama S et al (2005) Neuropharmacological profiles of antagonists of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neurosci Lett 378:131–134
Kern N, Sheldrick AJ, Schmidt FM, Minkwitz J (2012) Neurobiology of Depression and novel antidepressant drug targets. Curr Pharm Des 18:5791–5801
Knapska E, Kaczmarek L (2004) A gene for neuronal plasticity in the mammalian brain: zif268/Egr-1/NGFI-A/Krox-24/TIS8/ZENK? Prog Neurobiol 74:183–211
Koike H, Iijima M, Chaki S (2011) Involvement of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in the antidepressant-like effect of group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 61:1419–1423
Lesage F (2003) Pharmacology of neuronal background potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 44:1–7
Lesage F, Lazdunski M (2000) Molecular and functional properties of two-pore-domain potassium channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:793–801
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM et al (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329:959–964
Lucas G, Debonnel G (2002) 5-HT4 receptors exert a frequency-related facilitatory control on dorsal raphe nucleus 5-HT neuronal activity. Eur J Neurosci 16:817–822
Lucas G, Compan V, Charnay Y, Neve RL, Nestler EJ et al (2005) Frontocortical 5-HT4 receptors exert positive feedback on serotonergic activity: viral transfections, subacute and chronic treatments with 5-HT4 agonists. Biol Psychiatry 15:918–925
Lucas G, Rymar VV, Du J, Mnie-Filali O, Bisgaard C et al (2007) Serotonin4 (5-HT4) receptor agonists are putative antidepressants with a rapid onset of action. Neuron 55:712–725
Lucas G, Rymar VV, Sadikot AF, Debonnel G (2008) Further evidence for an antidepressant potential of the selective sigma1 agonist SA 4503: electrophysiological, morphological and behavioural studies. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:485–495
Lucas G, Du J, Romeas T, Mnie-Filali O, Haddjeri N et al (2010) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors potentiate the rapid antidepressant-like effects of serotonin4 receptor agonists in the rat. PLoS One 5:e9253
Martin S, Vincent JP, Mazella J (2003) Involvement of the neurotensin receptor-3 in the neurotensin-induced migration of human microglia. J Neurosci 23:1198–1205
Matrisciano F, Scaccianoce S, Del Bianco P, Panaccione I, Canudas AM et al (2005) Metabotropic glutamate receptors and neuroadaptation to antidepressants: imipramine-induced down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors in mice treated with metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor ligands. J Neurochem 93:1345–1352
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D et al (2005) Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron 45:651–660
Mazella J, Pétrault O, Lucas G, Deval E, Béraud-Dufour S et al (2010) Spadin, a sortilin-derived peptide, targeting rodent TREK-1 channels: a new concept in the antidepressant drug design. PLoS Biol 8:e1000355
Moha ou Maati H, Peyronnet R, Devader C, Veyssiere J, Labbal F et al (2011) A human TREK-1/HEK cell line: a highly efficient screening tool for drug development in neurological diseases. PLoS One 6:e25602
Moha ou Maati H, Veyssiere J, Labbal F, Coppola T, Gandin C et al (2012) Spadin as a new antidepressant: absence of TREK-1-related side effects. Neuropharmacology 62:278–288
Munck Petersen C, Nielsen MS, Jacobsen C, Tauris J, Jacobsen L et al (1999) Propeptide cleavage conditions sortilin/neurotensin receptor-3 for ligand binding. EMBO J 18:595–604
Neafsey EJ, Terreberry RR, Hurley KM, Ruit KG, Frystak RJ (1993) Anterior cingulated cortex in rodents: connections, visceral control functions, and implications for emotion. In: Vogt BA, Gabriel M (eds) Neurobiology of the cingulated cortex and limbic thalamus: a comprehensive handbook. Birkhauser, Boston, pp 216–223
Pascual-Brazo J, Castro E, Díaz A, Valdizán EM, Pilar-Cuéllar F et al (2012) Modulation of neuroplasticity pathways and antidepressant-like behavioural responses following the short-term (3 and 7 days) administration of the 5-HT4 receptor agonist RS67333. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:631–643
Patel AJ, Honoré E, Maingret F, Lesage F, Fink M et al (1998) A mammalian two pore domain mechano-gated S-like K+ channel. EMBO J 17:4283–4290
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Petralia RS, Wang YX, Niedzielski AS, Wenthold RJ (1996) The metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR2 and mGluR3, show unique postsynaptic, presynaptic and glial localizations. Neuroscience 71:949–976
Peyron C, Petit JM, Rampon C, Jouvet M, Luppi PH (1998) Forebrain afferents to the rat dorsal raphe nucleus demonstrated by retrograde and anterograde tracing methods. Neuroscience 82:443–468
Rush AJ, Warden D, Wisniewski SR, Fava M, Trivedi MH et al (2009) STAR*D: revising conventional wisdom. CNS Drugs 23:627–647
Sarret P, Krzywkowski P, Segal L, Nielsen MS, Petersen CM et al (2003) Distribution of NTS3 receptor/sortilin mRNA and protein in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 461:483–505
Takagishi M, Chiba T (1991) Efferent projections of the infralimbic (area 25) region of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tracer PHA-L study. Brain Res 566:26–39
Thase ME (2012) Using adjunctive treatments when first-line antidepressants fail. J Clin Psychiatry 73:e01
Vogt KE, Gerharz S, Graham J, Canepari M (2011) High-resolution simultaneous voltage and Ca2+ imaging. J Physiol 589:489–494
Warden MR, Selimbeyoglu A, Mirzabekov JJ, Lo M, Thompson KR et al (2012) A prefrontal cortex–brainstem neuronal projection that controls response to behavioural challenge. Nature 492:428–432
Westergaard UB, Sorensen ES, Hermey G, Nielsen MS, Nykjaer A et al (2004) Functional organization of the sortilin Vps10p domain. J Biol Chem 279:50221–50229
White FJ, Wang RY (1983) Differential effects of classical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on A9 and A10 dopamine neurons. Science 221:1054–1057
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by grants from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-2009-MNPS-026.01 and ANR EMMA 11-050), as well as by financial supports from the INSERM, the CNRS, the Université de Nice-Sophia Antipolis, and the LabEx Ionic Channels Science and Therapeutics (ICST, ANR-11 LABX 0015).
Conflict of interest
Doctors Heurteaux and Borsotto have patented the use of spadin as a putative antidepressant. The other authors reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Moha ou Maati and C. Bourcier-Lucas contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moha ou Maati, H., Bourcier-Lucas, C., Veyssiere, J. et al. The peptidic antidepressant spadin interacts with prefrontal 5-HT4 and mGluR2 receptors in the control of serotonergic function. Brain Struct Funct 221, 21–37 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0890-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0890-x