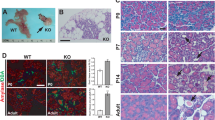
Abstract
Human ciliopathies are genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes responsible for the formation and function of primary cilia. Some are associated with hyperphagia and obesity (e.g., Bardet–Biedl Syndrome, Alström Syndrome), but the mechanisms underlying these problems are not fully understood. The human gene ANKRD26 is located on 10p12, a locus that is associated with some forms of hereditary obesity. Previously, we reported that disruption of this gene causes hyperphagia, obesity and gigantism in mice. In the present study, we looked for the mechanisms that induce hyperphagia in the Ankrd26−/− mice and found defects in primary cilia in regions of the central nervous system that control appetite and energy homeostasis.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC3:
-
Adenylyl cyclase 3
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
- ADX:
-
Adrenalectomy
- α-MSH:
-
α-Melanocyte stimulating hormone
- AgRP:
-
Agouti-related protein
- Ankrd26:
-
Ankyrin repeat domain 26
- ARC:
-
Arcuate nucleus
- BBS:
-
Bardet–Biedl syndrome
- BW:
-
Body weight
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CORT:
-
Corticosterone
- CRH:
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
- DM:
-
Dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- HPA:
-
Hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- MC4R:
-
Melanocortin 4 receptor
- Mchr1:
-
Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1
- NPY:
-
Neuropeptide Y
- NTS:
-
Nucleus of the solitary tract
- POMC:
-
Proopiomelanocortin
- PVN:
-
Paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
- Sstr3:
-
Somatostatin receptor 3
- TRH:
-
Thyrotropin releasing hormone
- VM:
-
Ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus
- VP:
-
Arginine vasopressin
References
Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Blacque OE, Hill J, Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Kim JC, Ross AJ, Eichers ER, Teslovich TM, Mah AK, Johnsen RC, Cavender JC, Lewis RA, Leroux MR, Beales PL, Katsanis N (2003) Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature 425(6958):628–633. doi:10.1038/nature02030
Ao Y, Go VL, Toy N, Li T, Wang Y, Song MK, Reeve JR Jr, Liu Y, Yang H (2006) Brainstem thyrotropin-releasing hormone regulates food intake through vagal-dependent cholinergic stimulation of ghrelin secretion. Endocrinology 147(12):6004–6010. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0820
Arens J, Moar KM, Eiden S, Weide K, Schmidt I, Mercer JG, Simon E, Korf HW (2003) Age-dependent hypothalamic expression of neuropeptides in wild-type and melanocortin-4 receptor-deficient mice. Physiol Genomics 16(1):38–46. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00123.2003
Bates SH, Stearns WH, Dundon TA, Schubert M, Tso AW, Wang Y, Banks AS, Lavery HJ, Haq AK, Maratos-Flier E, Neel BG, Schwartz MW, Myers MG Jr (2003) STAT3 signalling is required for leptin regulation of energy balance but not reproduction. Nature 421(6925):856–859. doi:10.1038/nature01388
Beckers S, Zegers D, Van Gaal LF, Van Hul W (2009) The role of the leptin-melanocortin signalling pathway in the control of food intake. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 19(4):267–287
Beckers S, Zegers D, de Freitas F, Peeters AV, Verhulst SL, Massa G, Van Gaal LF, Timmermans JP, Desager KN, Van Hul W (2010) Identification and functional characterization of novel mutations in the melanocortin-4 receptor. Obes Facts 3(5):304–311. doi:10.1159/000321565
Benzinou M, Walley A, Lobbens S, Charles MA, Jouret B, Fumeron F, Balkau B, Meyre D, Froguel P (2006) Bardet-Biedl syndrome gene variants are associated with both childhood and adult common obesity in French Caucasians. Diabetes 55(10):2876–2882. doi:10.2337/db06-0337
Bera TK, Liu XF, Yamada M, Gavrilova O, Mezey E, Tessarollo L, Anver M, Hahn Y, Lee B, Pastan I (2008) A model for obesity and gigantism due to disruption of the Ankrd26 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(1):270–275. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710978105
Berbari NF, Johnson AD, Lewis JS, Askwith CC, Mykytyn K (2008a) Identification of ciliary localization sequences within the third intracellular loop of G protein-coupled receptors. Mol Biol Cell 19(4):1540–1547. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-09-0942
Berbari NF, Lewis JS, Bishop GA, Askwith CC, Mykytyn K (2008b) Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins are required for the localization of G protein-coupled receptors to primary cilia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(11):4242–4246. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711027105
Blacque OE, Leroux MR (2006) Bardet-Biedl syndrome: an emerging pathomechanism of intracellular transport. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(18):2145–2161. doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6180-x
Chua SC Jr, Chung WK, Wu-Peng XS, Zhang Y, Liu SM, Tartaglia L, Leibel RL (1996) Phenotypes of mouse diabetes and rat fatty due to mutations in the OB (leptin) receptor. Science 271(5251):994–996
Collin GB, Marshall JD, Ikeda A, So WV, Russell-Eggitt I, Maffei P, Beck S, Boerkoel CF, Sicolo N, Martin M, Nishina PM, Naggert JK (2002) Mutations in ALMS1 cause obesity, type 2 diabetes and neurosensory degeneration in Alstrom syndrome. Nat Genet 31(1):74–78. doi:10.1038/ng867
de Backer MW, la Fleur SE, Brans MA, van Rozen AJ, Luijendijk MC, Merkestein M, Garner KM, van der Zwaal EM, Adan RA (2011) Melanocortin receptor-mediated effects on obesity are distributed over specific hypothalamic regions. Int J Obes (Lond) 35(5):629–641. doi:10.1038/ijo.2010.169
Dimitrov EL, DeJoseph MR, Brownfield MS, Urban JH (2007) Involvement of neuropeptide Y Y1 receptors in the regulation of neuroendocrine corticotropin-releasing hormone neuronal activity. Endocrinology 148(8):3666–3673. doi:10.1210/en.2006-1730
Dong C, Li WD, Geller F, Lei L, Li D, Gorlova OY, Hebebrand J, Amos CI, Nicholls RD, Price RA (2005) Possible genomic imprinting of three human obesity-related genetic loci. Am J Hum Genet 76(3):427–437. doi:10.1086/428438
Friedman JM (2000) Obesity in the new millennium. Nature 404(6778):632–634. doi:10.1038/35007504
Friedman JM, Halaas JL (1998) Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395(6704):763–770. doi:10.1038/27376
Goldstone AP, Beales PL (2008) Genetic obesity syndromes. Front Horm Res 36:37–60. doi:10.1159/0000115336
Grace C, Beales P, Summerbell C, Jebb SA, Wright A, Parker D, Kopelman P (2003) Energy metabolism in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27(11):1319–1324. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802420
Grill HJ, Hayes MR (2009) The nucleus tractus solitarius: a portal for visceral afferent signal processing, energy status assessment and integration of their combined effects on food intake. Int J Obes (Lond) 33(Suppl 1):S11–S15. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.10
Guo DF, Rahmouni K (2011) Molecular basis of the obesity associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Trends Endocrinol Metab: TEM 22(7):286–293. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2011.02.009
Harris M, Aschkenasi C, Elias CF, Chandrankunnel A, Nillni EA, Bjoorbaek C, Elmquist JK, Flier JS, Hollenberg AN (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene by leptin and melanocortin signaling. J Clin Invest 107(1):111–120. doi:10.1172/jci10741
Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, Dunmore JH, Fang Q, Berkemeier LR, Gu W, Kesterson RA, Boston BA, Cone RD, Smith FJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Lee F (1997) Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 88(1):131–141
Itoi K, Jiang YQ, Iwasaki Y, Watson SJ (2004) Regulatory mechanisms of corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin gene expression in the hypothalamus. J Neuroendocrinol 16(4):348–355. doi:10.1111/j.0953-8194.2004.01172.x
Kim JC, Badano JL, Sibold S, Esmail MA, Hill J, Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Venner K, Ansley SJ, Ross AJ, Leroux MR, Katsanis N, Beales PL (2004) The Bardet-Biedl protein BBS4 targets cargo to the pericentriolar region and is required for microtubule anchoring and cell cycle progression. Nat Genet 36(5):462–470. doi:10.1038/ng1352
Kiss JZ, Mezey E, Skirboll L (1984) Corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus become vasopressin positive after adrenalectomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(6):1854–1858
Leibowitz SF, Hammer NJ, Chang K (1981) Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus lesions produce overeating and obesity in the rat. Physiol Behav 27(6):1031–1040
Lloyd DJ, Bohan S, Gekakis N (2006) Obesity, hyperphagia and increased metabolic efficiency in Pc1 mutant mice. Hum Mol Genet 15(11):1884–1893. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl111
Lu XY, Barsh GS, Akil H, Watson SJ (2003) Interaction between alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone in the regulation of feeding and hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal responses. J Neurosci 23(21):7863–7872
Mercer RE, Chee MJ, Colmers WF (2011) The role of NPY in hypothalamic mediated food intake. Front Neuroendocrinol. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2011.06.001
Nakayama S, Nishiyama M, Iwasaki Y, Shinahara M, Okada Y, Tsuda M, Okazaki M, Tsugita M, Taguchi T, Makino S, Stenzel-Poore MP, Hashimoto K, Terada Y (2011) Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) transgenic mice display hyperphagia with increased Agouti-related protein mRNA in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Endocr J 58(4):279–286
Nordman S, Abulaiti A, Hilding A, Langberg EC, Humphreys K, Ostenson CG, Efendic S, Gu HF (2008) Genetic variation of the adenylyl cyclase 3 (AC3) locus and its influence on type 2 diabetes and obesity susceptibility in Swedish men. Int J Obes (Lond) 32(3):407–412. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0803742
Palkovits M (1973) Isolated removal of hypothalamic or other brain nuclei of the rat. Brain Res 59:449–450
Palkovits M (1983) Punch sampling biopsy technique. Methods Enzymol 103:368–376
Palkovits M (2008) Stress-induced activation of neurons in the ventromedial arcuate nucleus: a blood-brain-CSF interface of the hypothalamus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1148:57–63. doi:10.1196/annals.1410.062
Pandit R, de Jong JW, Vanderschuren LJ, Adan RA (2011) Neurobiology of overeating and obesity: the role of melanocortins and beyond. Eur J Pharmacol 660(1):28–42. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.01.034
Raciti GA, Bera TK, Gavrilova O, Pastan I (2011) Partial inactivation of Ankrd26 causes diabetes with enhanced insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue in mice. Diabetologia. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2263-9
Rahmouni K, Fath MA, Seo S, Thedens DR, Berry CJ, Weiss R, Nishimura DY, Sheffield VC (2008) Leptin resistance contributes to obesity and hypertension in mouse models of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. J Clin Invest 118(4):1458–1467. doi:10.1172/jci32357
Ramachandrappa S, Farooqi IS (2011) Genetic approaches to understanding human obesity. J Clin Invest 121(6):2080–2086. doi:10.1172/jci46044
Sabatier N, Caquineau C, Dayanithi G, Bull P, Douglas AJ, Guan XM, Jiang M, Van der Ploeg L, Leng G (2003) Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone stimulates oxytocin release from the dendrites of hypothalamic neurons while inhibiting oxytocin release from their terminals in the neurohypophysis. J Neurosci 23(32):10351–10358
Saito Y, Cheng M, Leslie FM, Civelli O (2001) Expression of the melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) receptor mRNA in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 435(1):26–40
Savontaus E, Conwell IM, Wardlaw SL (2002) Effects of adrenalectomy on AGRP, POMC, NPY and CART gene expression in the basal hypothalamus of fed and fasted rats. Brain Res 958(1):130–138
Sawchenko PE, Swanson LW, Vale WW (1984) Co-expression of corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin immunoreactivity in parvocellular neurosecretory neurons of the adrenalectomized rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(6):1883–1887
Sebag JA, Hinkle PM (2006) Regulation of endogenous melanocortin-4 receptor expression and signaling by glucocorticoids. Endocrinology 147(12):5948–5955. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0984
Sen Gupta P, Prodromou NV, Chapple JP (2009) Can faulty antennae increase adiposity? The link between cilia proteins and obesity. J Endocrinol 203(3):327–336. doi:10.1677/joe-09-0116
Seo S, Guo DF, Bugge K, Morgan DA, Rahmouni K, Sheffield VC (2009) Requirement of Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins for leptin receptor signaling. Hum Mol Genet 18(7):1323–1331. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp031
Seo S, Zhang Q, Bugge K, Breslow DK, Searby CC, Nachury MV, Sheffield VC (2011) A novel protein LZTFL1 regulates ciliary trafficking of the BBSome and smoothened. PLoS Genet 7(11):e1002358. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002358
Singla V, Reiter JF (2006) The primary cilium as the cell’s antenna: signaling at a sensory organelle. Science 313(5787):629–633. doi:10.1126/science.1124534
Stofkova A, Skurlova M, Kiss A, Zelezna B, Zorad S, Jurcovicova J (2009) Activation of hypothalamic NPY, AgRP, MC4R, AND IL-6 mRNA levels in young Lewis rats with early-life diet-induced obesity. Endocr Regul 43(3):99–106
Tung YC, Piper SJ, Yeung D, O’Rahilly S, Coll AP (2006) A comparative study of the central effects of specific proopiomelancortin (POMC)-derived melanocortin peptides on food intake and body weight in pomc null mice. Endocrinology 147(12):5940–5947. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0866
Valassi E, Scacchi M, Cavagnini F (2008) Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 18(2):158–168. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2007.06.004
Wang Z, Li V, Chan GC, Phan T, Nudelman AS, Xia Z, Storm DR (2009) Adult type 3 adenylyl cyclase-deficient mice are obese. PLoS ONE 4(9):e6979. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006979
Wardlaw SL (2011) Hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin processing and the regulation of energy balance. Eur J Pharmacol 660(1):213–219. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.10.107
Wardle J, Carnell S, Haworth CM, Plomin R (2008) Evidence for a strong genetic influence on childhood adiposity despite the force of the obesogenic environment. Am J Clin Nutr 87(2):398–404
Yang J, Li T (2005) The ciliary rootlet interacts with kinesin light chains and may provide a scaffold for kinesin-1 vesicular cargos. Exp Cell Res 309(2):379–389. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.05.026
Yang J, Liu X, Yue G, Adamian M, Bulgakov O, Li T (2002) Rootletin, a novel coiled-coil protein, is a structural component of the ciliary rootlet. J Cell Biol 159(3):431–440. doi:10.1083/jcb.200207153
Yang L, Scott KA, Hyun J, Tamashiro KL, Tray N, Moran TH, Bi S (2009) Role of dorsomedial hypothalamic neuropeptide Y in modulating food intake and energy balance. J Neurosci 29(1):179–190. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.4379-08.2009
Yaswen L, Diehl N, Brennan MB, Hochgeschwender U (1999) Obesity in the mouse model of pro-opiomelanocortin deficiency responds to peripheral melanocortin. Nat Med 5(9):1066–1070. doi:10.1038/12506
Young WS 3rd, Mezey E (2004) Hybridization histochemistry of neural transcripts. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 1:Unit 1 3. doi:10.1002/0471142301.ns0103s25
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge the invaluable help of Miklos Palkovits, Harold Gainer and Michael Brownstein for their continuous support and advice as well as help with editing the manuscript. We also thank Prof. Ronald DeKloet (Leiden University) for his expert advice regarding studies on adrenal function. This research was supported by the Division of Intramural Research program of NCI and NIDCR in the Intramural Research Program, NIH, DHHS. We dedicate this work to the memory of Wylie Vale, who discovered CRF and who was an outstanding scientist; a wonderful human being and a good friend.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
E. Mezey and I. Pastan contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
429_2014_741_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Combination of immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization to show specificity of the antibodies used. Leptin receptor (LeptinR) and melanocortin receptor 4 (MC4R) mRNA were detected using specific probes and the RNAScope technique (Advanced Cell Diagnostics) according to the company’s protocol. Following detection of the specific mRNAs (red color), immunostaining was performed as described in the methods, using the TSA amplification technique and a Tyramide-680 Plus substrate (yellow color). The significant overlap between the labelings indicates that the immunostaining is indeed specific for the two receptors. (JPEG 663 kb)
429_2014_741_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Expression of rootletin in WT and Ankrd − / − mice. IHC for rootletin in the CA3 region of the hippocampus in WT (A and B) and in Ankrd26−/− (C and D) mice. Note that the stronger cytoplasmic signal is accompanied by apparent ciliary rootlets (indicated by arrows) in Ankrd26−/− mice. Nuclei are visualized with Dapi (blue). Scale bar: 15 μm. Images are representative of four independent observations (n = 3 in each group, four different litters). (TIFF 9527 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acs, P., Bauer, P.O., Mayer, B. et al. A novel form of ciliopathy underlies hyperphagia and obesity in Ankrd26 knockout mice. Brain Struct Funct 220, 1511–1528 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0741-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0741-9