Abstract
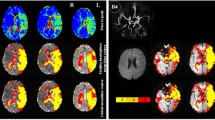
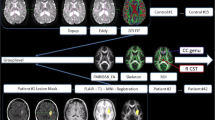
Commonly, in lesion-behaviour studies structural changes in brain matter are depicted and analysed. However, in addition to these structural changes, brain areas might be structurally intact but non-functional due to malperfusion. These changes may be detected using perfusion-weighted MRI (PWI). Perfusion parameters most commonly used [e.g. time-to-peak (TTP)] are semi-quantitative and perfusion is evaluated in relation to a non-affected reference area. Traditionally, the mean of a larger region in the non-affected hemisphere or the cerebellum has been used [“mean contra-region of interest (ROI) comparison”]. Our results suggest that this method is prone to biases (in particular in periventricular regions) because perfusion differs between different parts of the brain, for example, between grey and white matter. We reduced such potential biases with voxelwise inter-hemispheric comparisons. Each voxel is compared with its homologous voxel and thus white matter with white matter and grey matter with grey matter. This automated method seems to correspond with results deriving from manual delineation of perfusion deficits. The TTP delay maps with a threshold of 3 s seem to be best comparable to manual delineation. Our method avoids the observer-dependent choice of a reference region and involves the spatial normalisation of perfusion maps. It is well suited for whole-brain analysis of abnormal perfusion in neuroscience studies as well as in clinical contexts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubert-Broche B, Grova C, Jannin P, Buvat I, Benali H, Gibaud B (2003) Detection of inter-hemispheric asymmetries of brain perfusion in SPECT. Phys Med Biol 48(11):1505–1517
Beaulieu C, de Crespigny A, Tong DC, Moseley ME, Albers GW, Marks MP (1999) Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study of perfusion and diffusion in stroke: evolution of lesion volume and correlation with clinical outcome. Ann Neurol 46:568–578
Brett M, Leff AP, Rorden C, Ashburner J (2001) Spatial normalization of brain images with focal lesions using cost function masking. Neuroimage 14(2):486–500
Butcher K, Parsons M, Allport L, Lee SB, Barber PA, Tress B, Donnan GA, Davis SM (2008) Rapid assessment of perfusion-diffusion mismatch. Stroke 39(1):75–81
Coutts SB, Simon JE, Tomanek AI, Barber PA, Chan J, Hudon ME, Mitchell JR, Frayne R, Eliasziw M, Buchan AM, Demchuk AM (2003) Reliability of assessing percentage of diffusion-perfusion mismatch. Stroke 34(7):1681–1683
Demeurisse G, Hublet C, Paternot J, Colson C, Serniclaes W (1997) Pathogenesis of subcortical visuo-spatial neglect. A HMPAO SPECT study. Neuropsychologia 35(5):731–735
Dwyer MG, Bergsland N, Saluste E, Sharma J, Jaisani Z, Durfee J, Abdelrahman N, Minagar A, Hoque R, Munschauer FE 3rd, Zivadinov R (2008) Application of hidden Markov random field approach for quantification of perfusion/diffusion mismatch in acute ischemic stroke. Neurol Res 30(8):827–834
Helenius J, Perkio J, Soinne L, Ostergaard L, Carano RA, Salonen O, Savolainen S, Kaste M, Aronen HJ, Tatlisumak T (2003) Cerebral hemodynamics in a healthy population measured by dynamic susceptibility contrast MR imaging. Acta Radiol 44(5):538–546
Hillis AE, Wityk RJ, Tuffiash E, Beauchamp NJ, Jacobs MA, Barker PB, Selnes OA (2001) Hypoperfusion of Wernicke’s area predicts severity of semantic deficit in acute stroke. Ann Neurol 50:561–566
Hillis AE, Wityk RJ, Barker PB, Beauchamp NJ, Gailloud P, Murphy K, Cooper O, Metter EJ (2002) Subcortical aphasia and neglect in acute stroke: the role of cortical hyperfusion. Brain 125:1094–1104
Hillis AE, Newhart M, Heidler J, Barker PB, Herskovits EH, Degaonkar M (2005) Anatomy of spatial attention: insights from perfusion imaging and hemispatial neglect in acute stroke. J Neurosci 25(12):3161–3167
Infeld B, Davis SM, Lichtenstein M, Mitchell PJ, Hopper JL (1995) Crossed cerebellar diaschisis and brain recovery after stroke. Stroke 26(1):90–95
Karnath HO, Zopf R, Johannsen L, Fruhmann Berger M, Nägele T, Klose U (2005) Normalized perfusion MRI to identify common areas of dysfunction: patients with basal ganglia neglect. Brain 128:2462–2469
Klose U, Nägele T, Friese S, Bitzer M (1999) Charakteristische Größen bei der MR-Untersuchung der zerebralen Durchblutung mit hoher räumlicher und zeitlicher Auflösung. Fortschr Röntgenstr 170:474–481
Neumann-Haefelin T, Wittsack HJ, Wenserski F, Siebler M, Seitz RJ, Modder U, Freund HJ (1999) Diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI. The DWI/PWI mismatch region in acute stroke. Stroke 30(8):1591–1597
Rorden C, Karnath HO (2004) Using human brain lesions to infer function: a relic from a past era in the fMRI age? Nat Rev Neurosci 5(10):813–819
Rorden C, Karnath HO, Bonilha L (2007) Improving lesion-symptom mapping. J Cogn Neurosci 19(7):1081–1088
Rorden C, Bonilha L, Fridriksson J, Bender B, Karnath HO (2011) Age-adapted templates for spatial normalization of CT and MRI scans (submitted)
Schlaug G, Benfield A, Baird AE, Siewert B, Lövblad K-O, Parker RA, Edelman RR, Warach S (1999) The ischemic penumbra. Operationally defined by diffusion and perfusion MRI. Neurology 53:1528–1537
Singer OC, de Rochemont R, Foerch C, Stengel A, Lanfermann H, Sitzer M, Neumann-Haefelin T (2003) Relation between relative cerebral blood flow, relative cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time in patients with acute ischemic stroke determined by perfusion-weighted MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:605–611
Ticini LF, Klose U, Nagele T, Karnath HO (2009) Perfusion imaging in Pusher syndrome to investigate the neural substrates involved in controlling upright body position. PLoS One 4(5):e5737
Ticini LF, de Haan B, Klose U, Nagele T, Karnath HO (2010) The role of temporo-parietal cortex in subcortical visual extinction. J Cogn Neurosci 22(9):2141–2150
Weiller C, Ringelstein EB, Reiche W, Thron A, Buell U (1990) The large striatocapsular infarct. A clinical and pathophysiological entity. Arch Neurol 47(10):1085–1091
Weiller C, Willmes K, Reiche W, Thron A, Isensee C, Buell U, Ringelstein EB (1993) The case of aphasia or neglect after striatocapsular infarction. Brain 116(Pt 6):1509–1525
Yamada K, Wu O, Gonzalez RG, Bakker D, Ostergard L, Copen WA, Weisskoff RM, Rosen BR, Yagi K, Nishimura T, Sorensen AG (2002) Magnetic resonance perfusion-weighted imaging of acute cerebral infarction. Effect of the calculation methods and underlying vasculopathy. Stroke 33:87–94
Zopf R, Fruhmann Berger M, Klose U, Karnath HO (2009) Perfusion imaging of the right perisylvian neural network in acute spatial neglect. Front Hum Neurosci 3:15
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KA 1258/10-1). We thank Leif Johannsen, Monika Fruhmann Berger and the team of the Division of Neuropsychology for their help in data acquisition and clinical assessments as well as for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zopf, R., Klose, U. & Karnath, HO. Evaluation of methods for detecting perfusion abnormalities after stroke in dysfunctional brain regions. Brain Struct Funct 217, 667–675 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-011-0363-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-011-0363-4