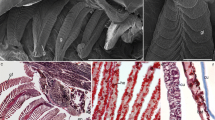
Abstract
In mammals, glutathione S-transferase (GST) in the olfactory epithelium is involved in assistance of the olfactory reception by the xenobiotic metabolism. We previously reported the protein and gene expressions of salmon olfactory GST class pi (soGST) in the olfactory receptor cells (ORCs) of the salmonid fish. However, the chronological appearances of soGST in ORCs during ontogeny and cell proliferation are still unknown in this species. In this study, we performed immunohistochemistry of soGST using an antibody specific to soGST in the olfactory system (olfactory placode, olfactory pit, olfactory epithelium, olfactory nerve and olfactory bulb) of lacustrine sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) embryos and 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) experimental fish. The projection of olfactory nerve bundles from the olfactory pit to the presumptive olfactory bulb was identified at embryonic day 28 after fertilization. The olfactory cilia were first detected on the apical surface of ORCs at day 43. soGST-immunoreactivity was first detected within the olfactory pit cells at day 55. At 58 day, the number of soGST-immunoreactive cells increased markedly in the olfactory epithelia, and soGST-immunoreactive fibers were observed in the olfactory nerves and olfactory bulbs. By in vivo uptake of BrdU in 1-year-old fish, we observed for the first time at day 7 after labeling that the olfactory epithelia showed ORCs in which both soGST-immunoreactivity and BrdU coexisted. These results indicate that soGST is synthesized in the mature ORCs of lacustrine sockeye salmon after cell formation and differentiation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banger KK, Foster JR, Lock EA, Reed CJ (1994) Immunohistochemical localization of six glutathione S-transferases within the nasal cavity of the rat. Arch Toxicol 69:91–98
Banger KK, Lock EA, Reed CJ (1993) The characterization of glutathione S-transferases from rat olfactory epithelium. Biochem J 290:199–204
Ben-Arie N, Khen M, Lancet D (1993) Glutathione S-transferase in rat olfactory epithelium: purification, molecular properties and odorant biotransformation. Biochem J 292:379–384
Dittman AH, Quinn TP (1996) Homing in pacific salmon: mechanisms and ecological basis. J Exp Biol 199:83–91
Farbman AI, Margolis FL (1980) Olfactory marker protein during ontogeny: immunohistochemical localization. Dev Biol 74:205–215
Graziadei PPC, Metcalf JF (1971) Autoradiographic and ultrastructural observations on the frog’s olfactory mucosa. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 116:305–318
Graziadei PPC, Monti-Graziadei GA (1979) Neurogenesis and neuron regeneration in the olfactory system of mammals. I. Morphological aspects of differentiation and structural organization of the olfactory sensory neurons. J Neurocytol 8:1–18
Jakoby WB (1978) The glutathione S-transferase: a group of multifunctional detoxification proteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 46:383–414
Krishna NS, Getchell TV, Getchell ML (1994) Differential expression of alpha, mu, and pi classes of glutathione S-transferases in chemosensory mucosae of rats during development. Cell Tissue Res 275:435–450
Kudo H, Doi Y, Nishino T, Nara S, Hamasaki K, Fujimoto S (2000) Dietary zinc deficiency decreases glutathione S-transferase expression in the rat olfactory epithelium. J Nutr 130:38–44
Kudo H, Ueda H, Mochida K, Adachi S, Hara A, Nagasawa H, Doi Y, Fujimoto S, Yamauchi K (1999) Salmonid olfactory system-specific protein (N24) exhibits glutathione S-transferase class pi-like structure. J Neurochem 72:1344–1352
Kudo H, Ueda H, Yamauchi K (1996) Immunocytochemical investigation of a salmonid olfactory system-specific protein in the olfactory system of kokanee salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Zool Sci 13:647–653
Mannervik B, Danielson UH (1988) Glutathione transferases, structure and catalytic activity. Crit Rev Biochem 23:283–337
Meyer DJ, Coles B, Pemble SE, Gilmore KS, Fraser GM, Ketterer B (1991) Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man. Biochem J 274:409–414
Monti-Graziadei GA, Stanley RS, Graziadei PPC (1980) The olfactory marker protein in the olfactory system of the mouse during development. Neuroscience 5:1239–1252
Nakamura H (1991) Immunohistochemical observations of dividing cells in olfactory epithelium using anti-BrdU antibody. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 248:298–301
Riddle DR, Oakley B (1992) Immunocytochemical identification of primary olfactory afferents in rainbow trout. J Comp Neurol 324:575–589
Salinas AE, Wong MG (1999) Glutathione S-transferases: a review. Curr Med Chem 6:279–309
Shimizu M, Kudo H, Ueda H, Hara A, Shimazaki K, Yamauchi K (1993) Identification and immunological properties of an olfactory system-specific protein in kokanee salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Zool Sci 10:287–294
Stabell OB (1992) Olfactory control of homing behaviour in salmonids: In: Hara TJ (ed) Fish Chemoreception. Chapman, London, pp 249–270
Starcevic SL, Muruganandam A, Mutus B, Zielinski BS (1993) Glutathione in the olfactory mucosa of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Chem Senses 18:57–65
Starcevic SL, Zielinski BS (1995) Immunohistochemical localization of glutathione S-transferase pi in rainbow trout olfactory receptor neurons. Neurosci Lett 183:175–178
Suzuki Y, Takeda M (1993) Basal cells in the mouse olfactory epithelium during development: immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic studies. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 73:107–113
Wang MM, Tsai RY, Schrader KA, Reed RR (1993) Genes encoding components of the olfactory signal transduction cascade contain a DNA binding site that may direct neuronal expression. Mol Cell Biol 13:5805–5813
Zielinski B, Hara TJ (1988) Morphological and physiological development of olfactory receptor cells in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) embryos. J Comp Neurol 271:300–311
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Jill B.K. Leonard, Northern Michigan University for critical reading of the manuscript and Mr. Hiroyuki Haruna, Toya Lake Station for Environmental Biology, for his technical assistance in this study. This study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aids from the Fisheries Agency of Japan and from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanagi, S., Kudo, H., Doi, Y. et al. Immunohistochemical demonstration of salmon olfactory glutathione S-transferase class pi (N24) in the olfactory system of lacustrine sockeye salmon during ontogenesis and cell proliferation. Anat Embryol 208, 231–238 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-004-0392-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-004-0392-3