Abstract
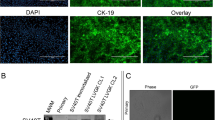
Mutation of the K-ras gene is thought to be an early and important event in pancreatic carcinogenesis. In order to study the role of this molecular alteration in the transition from the normal to the neoplastic pancreatic cell, bovine pancreatic duct cells were first immortalized by SV40 large T antigen (Ag) complementary (c)DNA transfection and then transfected with a mutated K-ras gene. As did primary duct cells, the immortalized duct cells (more than 100 passages) expressed cytokeratins, carbonic anhydrase type-II, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), and multidrug resistance (mdr). They grew as a single layer after transplantation under plastic domes and formed three-dimensional structures resembling ducts when grown on Matrigel. Cell growth was stimulated by insulin, epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor (TGF)-α, but cells did not respond to gastrin and CCK-8. They did not form colonies in soft agar nor did they form tumors in nude mice. Immortalized cells transfected with mutated K-ras acquired the ability to form tumors after orthotopic injection into the nude mouse pancreas. It is concluded that SV 40 immortalized bovine pancreatic duct cells retain the features of normal duct cells and gain tumorigenicity by transfection with mutated K-ras. This suggests an important role for K-ras in this pancreatic carcinoma model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham JA, Mergia A, Whang JL, Tumolo A, Friedman J, Hjerrild KA, et al (1986) Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science 233:545–548
Case RM, Argent BE (1993) Pancreatic duct cell secretion: control and mechanisms of transport. In: Go VLW, DiMagno EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, Scheele GA (eds) The pancreas: biology, pathobiology, and disease, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 301–350
Casey G, Smith R, McGillivray D, Peters G, Dickson C (1986) Characterization and chromosome assignment of the human homolog of int-2, a potential proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol 6:502–500
Cavender JF, Conn A, Epler M, Lacko H, Tevethia MJ (1995) Simian virus 40 large T antigen contains two independent activities that cooperate with a ras oncogene to transform rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol 69:923–934
Chen SL, Tsao YP, Chen YL, Huang SJ, Chang JL, Wu SF (1998) The induction of apoptosis by SV40 T antigen correlates with c-jun overexpression. Virology 244:521–529
Chey WY (1993) Hormonal control of pancreatic exocrine secretion. In: Go VLW, DiMagno EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, Scheele GA (eds) The exocrine pancreas. Biology, pathobiology, and disease, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 403–424
Farré A, Ishikuza J, Gómez G, Evers BM, Sadyari R, Koo JK, et al (1994) Bombesin inhibits growth of pancreatic ductal carcinoma (H2T) in nude mice. Pancreas 9:652–656
Frazier ML, Lilly BJ, Wu EF, Ota T, Hewett-Emmett D (1990) Carbonic anhydrase II gene expression in cell lines from human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 5:507–514
Furukawa T, Duguid WP, Rosenberg L, Viallet J, Galloway DA, Tsao MS (1996) Long-term culture and immortalization of epithelial cells from normal adult human pancreatic ducts transfected by the E6E7 gene of human papilloma virus 16. Am J Pathol 148:1763–1770
Fusenig NE, Breitkreutz D, Dzarlieva RT, Boukamp P, Bohnert A, Tilgen W (1983) Growth and differentiation characteristics of transformed keratinocytes from mouse and human skin in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 81:168s–175s
Gilles C, Piette J, Peter W, Fusenig NE, Foidart JM (1994) Differentiation ability and oncogenic potential of HPV-33 — and HPV-33 + ras-transfected keratinocytes. Int J Cancer 58:847–854
Goldammer T, Brunner RM, Schwerin M (1997) Comparative analysis of Y chromosome structure in Bos taurus and B. indicus by FISH using region-specific, microdissected, and locus-specific DNA probes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 77:238–412
Guthridge CJ, Conn A, Epler M, Lacko H (1994) Phospholipases A2 in ras-transformed and immortalized human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Lett 86:11–21
Hahn WC, Counter CM, Lundberg AS, Beijersbergen RL, Brooks MW, Weinberg RA (1999) Creation of human tumor cells with defined genetic elements. Nature 400:464–468
Halevy O, Michalovitz D, Oren M (1990) Different tumorderived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological activities. Science 250:113–116
Heimendahl GV, Gebhardt E, Dingermann TH (1988) Protooncogene activation in surgical specimens of rectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 8:805–812
Heinze H, Arnold HH, Fischer D, Kruppa J (1988) The primary structure of the human ribosomal protein S6 derived from a cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem 263:4139–4144
Heller T, Trautmann B, Zöller-Utz I, König HJ, Ell C, Liebe S, et al (1995) Restriktionsenzym-Mismatch-Polymerase-Kettenreaktion zum Nachweis von ki-ras-Onkogen-Mutationen beim Pankreaskarzinom. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 120:826–830
Jesnowski R, Liebe S, Löhr M (1998) Increasing the transfection efficacy and subsequent long-term culture of resting human pancreatic duct epithelial cells. Pancreas 17:262–265
Joneson T, Bar-Sagi D (1999) Suppression of ras-induced apoptosis by the rac GTPase. Mol Cell Biol 19:5892–5901
Kartner N, Evernden-Porelle D, Bradley G, Ling V (1985) Detection of P-glycoprotein in multidrug-resistant cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Nature 316:820–823
Kartner N, Hanrahan JW, Jensen TJ, Naismith AL, Sun SZ, Ackerley CA, et al (1991) Expression of the cystic fibrosis gene in non-epithelial invertebrate cells produces a regulated anion conductance. Cell 64:681–691
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriphage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee GH, Ogawa K, Drinkwater NR (1995) Conditional transformation of mouse liver epithelial cells. An in vitro model for analysis of genetic events in hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 147:1811–1822
Lloyd AC, Obermüller F, Staddon S, Barth CF, McMahon M, Land H (1997) Cooperating oncogenes converge to regulate cyclin/cdk complexes (abstract). Genes Dev 11:663–677
Löhr M, Trautmann B, Göttler M, Peters S, Zauner I, Maillet B, et al (1994) Human ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas express extracellular matrix proteins. Br J Cancer 69:144–151
Löhr M, Trautmann B, Peters S, Zauner I, Meier A, Klöppel G, et al (1996) Expression and function of receptors for extracellular matrix proteins in human ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. Pancreas 12:248–259
Marino LR, Cotton CU (1996) Immortalization of bovine pancreatic duct epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 270:G676-G683
Marino CR, Matovcik LM, Gorelick FS, Cohn JA (1991) Localization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in pancreas. J Clin Invest 88:712–716
Olson MF, Paterson HF, Marshall CJ (1998) Signals from ras and rho GTPases interact to regulate expression of p21Waf1/Cip1 (abstract). Nature 394:295–299
Peng X, Lang CM, Kreider JW (1996) Immortalization of inbred rabbit keratinocytes from a Shope papilloma and tumorigenic transformation of the cells by EJ-ras. Cancer Lett 108:101–109
Ray FA, Peabody DS, Cooper JL, Cram LS, Kraemer PM (1990) SV40 T antigen alone drives karyotype instability that precedes neoplastic transformation of human diploid fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 42:13–31
Reddel RR, De Silva R, Duncan EL, Rogan EM, Whitaker NJ, Zahra DG, et al (1995) SV40-induced immortalization and ras-transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Int J Cancer 61:199–205
Reyes G, Villanueva A, Garciá C, Sancho FJ, Piulats J, Lluís F, et al (1996) Orthotopic xenografts of human pancreatic carcinomas acquire genetic aberrations during dissemination in nude mice. Cancer Res 56:5713–5719
Rhim JS, Webber MM, Bello D, Lee MS, Arnstein P, Chen LS, et al (1994) Stepwise immortalization and transformation of adult human prostate epithelial cells by a combination of HPV-18 and v-Ki-ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11874–11878
Sack GH (1981) Human cell transformation by simian virus 40. In Vitro 17:1–19
Sandberg M, Vuorio E (1987) Localization of types I, II, and III collagen mRNAs in developing human skeletal tissue by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol 104:1077–1084
Schwarzbauer JE, Tamkun JW, Lemischka IR, Hynes RO (1983) Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell 35:421–428
Seifert D, Keeton M, Eguchi Y, Sawdey M, Loskutoff DJ (1991) Detection of vitronectin mRNA in tissues and cells of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9402–9406
Sirica AE, Longnecker DS (1997) Biliary and pancreatic ductal epithelia. Pathobiology and pathophysiology. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Southern PJ, Berg P (1982) Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet 1:327–341
Sridhar KS, Ohnuma T, Plasse TF, Holland JF (1988) Simultaneous soft agar cloning of ascites and solid tumor specimens from patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer 62:1577–1581
Tada M, Ohashi M, Shiratori Y, Okudaira T, Komatsu Y, Kawabe T, et al (1996) Analysis of k-ras gene mutation in hyperplastic duct cells of the pancreas without pancreatic disease. Gastroenterology 110:227–231
Terhune PG, Phifer DM, Tosteson TD, Longnecker DS (1998) K-ras mutation in focal proliferative lesions of human pancreas. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7:515–521
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesmann MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC (1987) Cellular localization of the multidrugresistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:7735–7738
Trautmann B, Schlitt HJ, Hahn EG, Lohr M (1993) Isolation, culture, and characterization of human pancreatic duct cells. Pancreas 8:248–254
Truckenmiller ME, Tornatore C, Wright RD, Dillon-Carter O, Meiners S, Geler HM, et al (1998) A truncated SV40 large T antigen lacking the p53 binding domain overcomes p53-induced growth arrest and immortalizes primary mesencephalic cells (abstract). Cell Tissue Res 291:175–189
Ulrich E, Boehmelt G, Bird A, Beug H (1992) Immortalization of conditionally transformed chicken cells: loss of normal p53 expression is an early step that is independent of cell transformation. Genes Dev 6:876–887
Webber MM, Bello D, Quader S (1997) Immortalized and tumorigenic adult human prostatic epithelial cell lines: characteristics and applications. Part 3: oncogenes, suppressor genes, and applications. Prostate 30:136–142
Wigler M, Pellicer A, Silverstein S, Axel R, Urlaub G, Chasin L (1979) DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1373–1376
Woods D, Parry D, Cherwinski H, Bosch E, Lees E, McMahon M (1997) Raf-induced proliferation or cell cycle arrest is determined by the level of raf activity with arrest mediated by p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 17:5589–5611
Wrann M, Bodmer S, Martin Rd, Siepl C, Hofer-Warbinek R, Frei K, et al (1987) T cell suppressor factor from human glioblastoma cells is a 12.5 kd protein closely related to transforming growth factor-β. EMBO J 6:1633–1636
Zhang M, Schleicher RL, Fink AS, Gunter-Smith P, Savard C, Nguyen T, et al (2000) Growth and function of isolated canine pancreatic ductal cells. Pancreas 20:67–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1221-3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Löhr, M., Müller, P., Zauner, I. et al. Immortalized bovine pancreatic duct cells become tumorigenic after transfection with mutant k-ras. Virchows Arch 438, 581–590 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280100397
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280100397