Abstract
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are responsible for the transcriptional control of genes through chromatin remodeling and control tumor suppressor genes. In several tumors, their expression has been linked to clinicopathological factors and patient survival. This study investigates HDACs 1, 2, 3, and 7 expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and their correlation with clinical data and patient survival. Tissue microarrays of 170 surgically resected primary HCCs and adjacent uninvolved tissue were evaluated immunohistochemically for the expression of HDACs 1, 2, 3, 7, and Ki-67 and were analyzed with respect to clinicopathological data and patient survival. HDACs 1, 2, 3, and Ki-67 were expressed significantly higher in cancer cells compared to normal tissue (HDAC1: p = 0.034, HDACs 2 and 3 and Ki-67: p < 0.001), while HDAC7 expression did not differ between HCC and non-cancerous liver tissue. In tumor tissue HDACs 1–3 expression levels showed high concordance with each other, Ki-67 and tumor grade (p < 0.001). High HDAC2 expression was associated with poor survival in low-grade and early-stage tumors (p < 0.05). The expression of the HDACs 1, 2, and 3 (but not HDAC7) isoenzymes correlates with clinicopathological factors, and HDAC2 expression has an impact on patient survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Cleries R, Diaz M (2005) Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 9(2):191–211
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 362(9399):1907–1917
Okamoto K, Neureiter D, Ocker M (2009) Biomarkers for novel targeted therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma. Histol Histopathol 24(4):493–502
Greten TF, Korangy F, Manns MP, Malek NP (2009) Molecular therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Canc 100(1):19–23
Finn RS (2010) Development of molecularly targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: where do we go now? Clin Canc Res 16(2):390–397
Ocker M, Schneider-Stock R (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: signalling towards p21cip1/waf1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(7–8):1367–1374
Ocker M (2010) Deacetylase inhibitors-focus on non-histone targets and effects. World J Biol Chem 1(5):55–61
Di Fazio P, Schneider-Stock R, Neureiter D, Okamoto K, Wissniowski T, Gahr S, Quint K, Meissnitzer M, Alinger B, Montalbano R, Sass G, Hohenstein B, Hahn EG, Ocker M (2010) The pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma models by alternative pathways of apoptosis. Cell Oncol 32(4):285–300
Gahr S, Peter G, Wissniowski TT, Hahn EG, Herold C, Ocker M (2008) The histone-deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 and the CDK-inhibitor CYC-202 promote anti-tumor effects in hepatoma cell lines. Oncol Rep 20(5):1249–1256
Ocker M, Alajati A, Ganslmayer M, Zopf S, Luders M, Neureiter D, Hahn EG, Schuppan D, Herold C (2005) The histone-deacetylase inhibitor SAHA potentiates proapoptotic effects of 5-fluorouracil and irinotecan in hepatoma cells. J Canc Res Clin Oncol 131(6):385–394
Weichert W (2009) HDAC expression and clinical prognosis in human malignancies. Canc Lett 280(2):168–176
Fritzsche FR, Weichert W, Roske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T, Stephan C, Jung K, Scholman K, Denkert C, Dietel M, Kristiansen G (2008) Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in renal cell cancer. BMC Canc 8:381
Ouaissi M, Sielezneff I, Silvestre R, Sastre B, Bernard JP, Lafontaine JS, Payan MJ, Dahan L, Pirro N, Seitz JF, Mas E, Lombardo D, Ouaissi A (2008) High histone deacetylase 7 (HDAC7) expression is significantly associated with adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. Ann Surg Oncol 15(8):2318–2328
Weichert W, Roske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T, Ebert MP, Pross M, Dietel M, Denkert C, Rocken C (2008) Association of patterns of class I histone deacetylase expression with patient prognosis in gastric cancer: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 9(2):139–148
Weichert W, Roske A, Niesporek S, Noske A, Buckendahl AC, Dietel M, Gekeler V, Boehm M, Beckers T, Denkert C (2008) Class I histone deacetylase expression has independent prognostic impact in human colorectal cancer: specific role of class I histone deacetylases in vitro and in vivo. Clin Canc Res 14(6):1669–1677
Rikimaru T, Taketomi A, Yamashita Y, Shirabe K, Hamatsu T, Shimada M, Maehara Y (2007) Clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 72(1–2):69–74
Lesko LJ, Atkinson AJ Jr (2001) Use of biomarkers and surrogate endpoints in drug development and regulatory decision making: criteria, validation, strategies. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:347–366
Bakhtiar R (2008) Biomarkers in drug discovery and development. J Pharmacol Toxicol Meth 57(2):85–91
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J, Kramer BS, Lencioni R, Zhu AX, Sherman M, Schwartz M, Lotze M, Talwalkar J, Gores GJ (2008) Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Canc Inst 100(10):698–711
Amann T, Maegdefrau U, Hartmann A, Agaimy A, Marienhagen J, Weiss TS, Stoeltzing O, Warnecke C, Scholmerich J, Oefner PJ, Kreutz M, Bosserhoff AK, Hellerbrand C (2009) GLUT1 expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol 174(4):1544–1552
Hellerbrand C, Amann T, Schlegel J, Wild P, Bataille F, Spruss T, Hartmann A, Bosserhoff AK (2008) The novel gene MIA2 acts as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 57(2):243–251
Tannapfel A, Denk H, Dienes HP, Langner C, Schirmacher P, Trauner M, Flott-Rahmel B (2010) Histopathological diagnose of non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. Z Gastroenterol 48(4):486–498
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2009) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Wiley-Blackwell
Weichert W, Denkert C, Noske A, Darb-Esfahani S, Dietel M, Kalloger SE, Huntsman DG, Kobel M (2008) Expression of class I histone deacetylases indicates poor prognosis in endometrioid subtypes of ovarian and endometrial carcinomas. Neoplasia 10(9):1021–1027
Miyake K, Yoshizumi T, Imura S, Sugimoto K, Batmunkh E, Kanemura H, Morine Y, Shimada M (2008) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, histone deacetylase 1, and metastasis-associated protein 1 in pancreatic carcinoma: correlation with poor prognosis with possible regulation. Pancreas 36(3):e1–e9
Lehmann A, Denkert C, Budczies J, Buckendahl AC, Darb-Esfahani S, Noske A, Muller BM, Bahra M, Neuhaus P, Dietel M, Kristiansen G, Weichert W (2009) High class I HDAC activity and expression are associated with RelA/p65 activation in pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. BMC Canc 9:395
Krusche CA, Wulfing P, Kersting C, Vloet A, Bocker W, Kiesel L, Beier HM, Alfer J (2005) Histone deacetylase-1 and −3 protein expression in human breast cancer: a tissue microarray analysis. Breast Canc Res Treat 90(1):15–23
Glaser KB, Li J, Staver MJ, Wei RQ, Albert DH, Davidsen SK (2003) Role of class I and class II histone deacetylases in carcinoma cells using siRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310(2):529–536
Fakhry H, Miyamoto T, Kashima H, Suzuki A, Ke H, Konishi I, Shiozawa T (2010) Immunohistochemical detection of histone deacetylases in endometrial carcinoma: involvement of histone deacetylase 2 in the proliferation of endometrial carcinoma cells. Hum Pathol 41(6):848–858
Langer R, Mutze K, Becker K, Feith M, Ott K, Hofler H, Keller G (2010) Expression of class I histone deacetylases (HDAC1 and HDAC2) in oesophageal adenocarcinomas: an immunohistochemical study. J Clin Pathol 63:994–998
Hrzenjak A, Moinfar F, Kremser ML, Strohmeier B, Staber PB, Zatloukal K, Denk H (2006) Valproate inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 affects differentiation and decreases proliferation of endometrial stromal sarcoma cells. Mol Canc Ther 5(9):2203–2210
Huang BH, Laban M, Leung CH, Lee L, Lee CK, Salto-Tellez M, Raju GC, Hooi SC (2005) Inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 increases apoptosis and p21Cip1/WAF1 expression, independent of histone deacetylase 1. Cell Death Differ 12(4):395–404
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Peter Rexin and Susanne Lingelbach for their help in this study. This study is supported by a Research Grant of the University Medical Center Giessen and Marburg (UKGM).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online resource 1
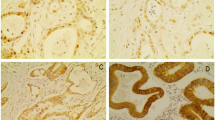
HDAC expression stained on traditional slides. HDACs 1–3 are shown to be homogenously expressed in cancer cells throughout the tumor section. (PPT 429 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quint, K., Agaimy, A., Di Fazio, P. et al. Clinical significance of histone deacetylases 1, 2, 3, and 7: HDAC2 is an independent predictor of survival in HCC. Virchows Arch 459, 129–139 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1103-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1103-0