Abstract
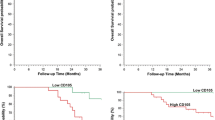
Some markers of angiogenic endothelial cells are emerging as targets of cancer therapy. The present study compares the expression of CD105 with that of other endothelial markers in all tissue layers during the development of colon cancer. We immunohistochemically analyzed the expression of the colon adenoma–carcinoma sequence by endothelial cells using a panel of eight endothelial markers. We examined sections from endoscopic mucosal resection and surgical resection of tubular adenoma (n=31), carcinoma in adenoma (n=11), and adenocarcinoma (n=34). Cylindrical cores were punched out from donor paraffin blocks of normal mucosa adjacent to tumors, from tumor lesions of mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, subserosa, and serosa, and from lymph node metastases. CD31 (PECAM-1) was universally expressed in the blood vessels of adenoma–carcinoma lesions as well as in normal mucosal vessels (80–95%), with no significant differences. In contrast, cancer-associated blood vessels (up to 80%) and cancer cells themselves expressed high levels of CD105. In normal mucosa, CD105 was weakly expressed in endothelial cells of capillaries (≦21%), and significant differences in its expression in endothelial cells between the normal mucosa and adenoma, carcinoma in adenoma, and adenocarcinoma were found. Flt-1, Flk-1, transforming growth factor-β1, transforming growth factor-β receptor II, and CD44 were strongly expressed in the cancer cells but were not expressed in the blood vessels. Vascular endothelial growth factor was expressed at <30% in the blood vessels of adenoma, carcinoma in adenoma, and carcinoma. Moreover, this study provided evidence that CD105 was expressed exclusively in endothelial blood vessels by double immunostaining of CD105 and D2-40. The present study shows that de novo blood vessels of colon cancer specifically express CD105. These findings provide the basis for novel antiangiogenic cancer therapies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi K, Ikeda Y, Sumiyoshi Y, Kimura Y, Kinoshita J, Miyazaki M, Abe T (2002) Estimation of angiogenesis with anti-CD105 immunostaining in the process of colorectal cancer development. Surgery 131:S109–S113
Becker CM, Farnebo FA, Iordanescu I, Behonick DJ, Shih MC, Dunning P, Christofferson R, Mulligan RC, Taylor GA, Kuo CJ, Zetter BR (2002) Gene therapy of prostate cancer with the soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flk1. Cancer Biol Ther 1:548–553
Burrows FJ, Derbyshire EJ, Tazzari PL, Amlot P, Gazdar AF, King SW, Letarte M, Vitetta ES, Thorpe PE (1995) Up-regulation of endoglin on vascular endothelial cells in human solid tumors: implications for diagnosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res 1:1623–1634
Cheryl AB, Jennifer JS, Miao J, Jill MJ, Jordan LM, Mary EM (2000) Endoglin expression as a measure of microvessel density in cervical cancer. Obstet Gynecol 96:224–228
Dales JP, Garcia S, Carpentier S, Andrac L, Ramuz O, Lavaut MN, Allasia C, Bonnier P, Charpin C (2004) Long-term prognostic significance of neoangiogenesis in breast carcinomas: comparison of Tie-2/Tek, CD105, and CD31 immunocytochemical expression. Hum Pathol 35:176–183
Faviana P, Boldrini L, Spisni R, Fontanini G et al (2002) Neoangiogenesis in colon cancer: correlation between vascular density, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and p53 protein expression. Oncol Rep 9:617–620
Feng D, Nagy JA, Pyne K, Dvorak HF, Dvorak AM (2004) Ultra-structural localization of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1, CD31) in vascular endothelium. J Histochem Cytochem 52:87–101
Fonsatti E, Sigalotti L, Arslan P, Altomonte M, Maio M (2003) Emerging role of endoglin (CD105) as a marker of angiogenesis with clinical potential in human malignancies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 3:427–432
Fonsatti E, Altomonte M, Arslan P, Maio M (2003) Endoglin (CD105): a target for anti-angiogenetic cancer therapy. Curr Drug Targets 4:291–296
Fonsatti E, Altomonte M, Nicotra MR, Natali PG, Maio M (2003) Endoglin (CD105): a powerful therapeutic target on tumor-associated angiogenetic blood vessels. Oncogene 22:6557–6563
Greenaway J, Connor K, Pederson HG, Coomber BL, LaMarre J, Petrik J (2004) VEGF and its receptor, Flk-1/KDR, are cytoprotective in the extravascular compartment of the ovarian follicle. Endocrinology 145:2896–2905
Jourdan F, Sebbagh N, Comperat E, Flejou JF (2003) Tissue microarray technology: validation in colorectal carcinoma and analysis of p53, hMLH1, and hMSH2 immunohistochemical expression. Virchows Arch 443:115–121
Kahn HJ, Marks A (2002) A new monoclonal antibody, D2-40, for detection of lymphatic invasion in primary tumors. Lab Invest 82:1255–1257
Kawaguchi T, Yamamoto S, Kudoh S, Goto K, Wakasa K, Sakurai M (1997) Tumor angiogenesis as a major prognostic factor in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res 17:3743–3746
Kumar P, Wang JM, Bernabeu C (1996) CD105 and angiogenesis. J. Pathol 178:363–366
Li C, Gardy R, Seon BK, Duff SE, Abdalla S, Ranehan A, O'Dwyer ST, Haboubi N, Kumar S (2003) Both high intratumoral microvessel density determined using CD105 antibody and elevated plasma levels of CD105 in colorectal cancer patients correlate with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer 88:1424–1431
Li C, Guo B, Bernabeu C, Kumar C (2001) Angiogenesis in breast cancer: the role of transforming growth factor and CD105. Microsc Res Tech 4:437–449
Nasi A, Boulware D, Kaiser HE, Coppola D (2004) Flat and polyploid adenocarcinomas of the colorectum: a comparative histomorphologic analysis of 47 cases. Hum Pathol 35:604–611
Nicholl ID, Dunlop MG (1999) Molecular markers of prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1267–1269
Okada K, Satoh T, Fujimoto K, Tokunaga O (2004) Interaction between morphology and angiogenesis in human early colorectal cancers. Pathol Int 54:490–497
Price EA, Coombe DR, Murray JC (1998) Endothelial CD44H mediates adhesion of a melanoma cell line to quiescent human endothelial cells in vitro. Int J Cancer 65:513–518
Duff SE, Li C, Garland JM, Kumar S (2003) CD105 is important for angiogenesis: evidence and potential applications. FASEB J 17:984–992
Siemann DW, Chaplin DJ, Horsman MR (2004) Vascular-targeting therapies for treatment of malignant disease. Cancer 100:2491–2499 [review]
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM (1995) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res 55:3964–3968
Volgestein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR (1988) Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med 319:525–532
Von Marschall Z, Cramer T, Hocker M, Burde R, Rosewicz S (2000) De novo expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pancreatic cancer: evidence for an autocrine mitogenic loop. Gastroenterology 119:1358–1372
Wang JM, Kumar S, Pye D, van Agthoven AJ, Krupinski J, Hunter RD (1993) A monoclonal antibody detects heterogeneity in vascular endothelium of tumours and normal tissues. Int J Cancer 54:363–370
Wilkstrom P, Lissbrant IF, Stattin P, Egevad L, Bergh A (2002) Endoglin (CD105) is expressed on immature blood vessels and is a marker for survival in prostate cancer. Prostate 51:268–275
Yasutomi M (ed) (1999) Japanese classification of colorectal carcinoma. Kanehara, Tokyo
Yu JX, Zhang XT, Liao YQ, Zhang QY, Chen H, Lin M, Kumar S (2003) Relationship between expression of CD105 and growth factors in malignant tumors of gastrointestinal tract and its significance. World J Gastroenterol 9:2866–2869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minhajat, R., Mori, D., Yamasaki, F. et al. Endoglin (CD105) expression in angiogenesis of colon cancer: analysis using tissue microarrays and comparison with other endothelial markers. Virchows Arch 448, 127–134 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0062-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0062-8