Abstract
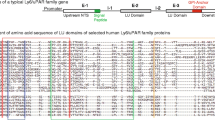
We describe here the first full-length sequence of a member of a novel gene family encoding a protein in the mouse that we call Lupin. Lupin is homologous to a human protein previously called p36, which was purified from α-interferon-treated cells that formed lupus inclusions. Lupus inclusions are dense intracellular deposits found in endothelial cells and lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosis and AIDS. Proteins closely related to Lupin exist in evolutionarily divergent species including Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila and zebrafish. At least one other lupin-related gene is expressed in the mouse and in man. Lupin is expressed in mouse embryos and adults, notably in liver, spleen, central nervous system, multiple epithelia and all types of muscle. In skeletal muscle, expression analysis suggests that Lupin associates with the contractile apparatus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 April 2000 / Accepted: 14 June 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Chen, F., Gitler, A. et al. Cloning and expression analysis of murine lupin, a member of a novel gene family that is conserved through evolution and associated with Lupus inclusions. Dev Gene Evol 210, 512–517 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270000093
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270000093