Abstract
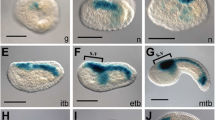
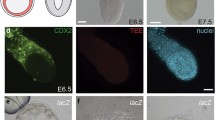
We identified 5′ upstream enhancers of two Ci-ZicL genes and characterized one of them in detail. Although the genes are tandemly repeated in the genome, the transcription of each seemed to be individually regulated. The 259-bp 5′ flanking sequence contained essential elements for driving a correct spatiotemporal expression. This enhancer can be divided into two distinct modules. The A module was located between nucleotide positions −259 and −205 upstream of the putative transcription start site, and was necessary for activation in A6.2 and A6.4 blastomeres at the 32-cell stage. The BM module lay between nucleotide positions −205 and −89 and was responsible for activation in B6.2 and B6.4 blastomeres at the 32-cell stage and in A-line presumptive notochord, nerve cord, and muscle lineage cells at later stages. Two putative Fox-binding sites, one located within and the other downstream of the BM module, were necessary for the latter activity. Mutation at a potential Ets-binding site, located downstream of the BM module, caused ectopic activation of the reporter gene in a-line presumptive ectoderm cells. This suggests that repression in the a-line blastomeres is necessary for correct transcriptional control of the Ci-ZicL gene.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertrand V, Hudson C, Caillol D, Popovici C, Lemaire P (2003) Neural tissue in ascidian embryos is induced by FGF9/16/20, acting via a combination of maternal GATA and Ets transcription factors. Cell 115:615–627
Conklin EG (1905) The organization and cell lineage of the ascidian egg. J Acad Nat Sci Phila 13:1–119
Corbo JC, Erives A, Di Gregorio A, Chang A, Levine M (1997a) Dorsoventral patterning of the vertebrate neural tube is conserved in a protochordate. Development 124:2335–2344
Corbo JC, Levine M, Zeller RW (1997b) Characterization of a notochord-specific enhancer from the Brachyury promoter region of the ascidian, Ciona intestinalis. Development 124:589–602
Dehal P, Satou Y, Campbell RK, Chapman J, Degnan B, De Tomaso A, Davidson B, Di Gregorio A, Gelpke M, Goodstein DM, Harafuji N, Hastings KEM, Ho I, Hotta K, Huang W, Kawashima T, Lemaire P, Martinez D, Meinertzhagen IA, Necula S, Nonaka M, Putnam N, Rash S, Saiga H, Satake M, Terry A, Yamada L, Wang H-G, Awazu S, Azumi K, Boore J, Branno M, Chin-bow S, De Santis R, Doyle S, Francino P, Keys DN, Haga S, Hayashi H, Hino K, Imai KS, Inaba K, Kano S, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi M, Lee B-I, Makabe KW, Manohar C, Matassi G, Medina M, Mochizuki Y, Mount S, Morishita T, Miura S, Nakayama A, Nishizaka S, Nomoto H, Ohta F, Oishi K, Rigoutsos I, Sano M, Sasaki A, Sasakura Y, Shoguchi E, Shin-i T, Spagnuolo A, Stainier D, Suzuki MM, Tassy O, Takatori N, Tokuoka M, Yagi K, Yoshizaki F, Wada S, Zhang C, Hyatt PD, Larimer F, Detter C, Doggett N, Glavina T, Hawkins T, Richardson P, Lucas S, Kohara Y, Levine M, Satoh N, Rokhsar DS (2002) The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science 298:2157–2167
Di Gregorio A, Corbo JC, Levine M (2001) The regulation of forkhead/HNF-3β expression in the Ciona embryo. Dev Biol 229:31–41
Di Gregorio A, Levine M (1998) Ascidian embryogenesis and the origins of the chordate body plan. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8:457–463
Di Gregorio A, Levine M (1999) Regulation of Ci-tropomyosin-like, a Brachyury target gene in the ascidian, Ciona intestinalis. Development 126:5599–5609
Fujiwara S, Maeda Y, Shin-i T, Kohara Y, Takatori N, Satou Y, Satoh N (2002) Gene expression profiles in Ciona intestinalis cleavage-stage embryos. Mech Dev 112:115–127
Hotta K, Takahashi H, Asakura T, Saitoh B, Takatori N, Satou Y, Satoh N (2000) Characterization of Brachyury-downstream notochord genes in the Ciona intestinalis embryo. Dev Biol 224:69–80
Hudson C, Darras S, Caillol D, Yasuo H, Lemaire P (2003) A conserved role for the MEK signalling pathway in neural tissue specification and posteriorization in the invertebrate chordate, the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Development 130:147–159
Imai KS, Satoh N, Satou Y (2002a) Early embryonic expression of FGF4/6/9 gene and its role in the induction of mesenchyme and notochord in Ciona savignyi embryos. Development 129:1729–1738
Imai KS, Satoh N, Satou Y (2002b) An essential role of a FoxD gene in notochord induction in Ciona embryos. Development 129:3441–3453
Imai KS, Satou Y, Satoh N (2002c) Multiple functions of a Zic-like gene in the differentiation of notochord, central nervous system and muscle in Ciona savignyi embryos. Development 129:2723–2732
Kim GJ, Nishida H (2001) Role of the FGF and MEK signaling pathway in the ascidian embryo. Dev Growth Differ 43:521–533
Lemaire P, Bertrand V, Hudson C (2002) Early steps in the formation of neural tissue in ascidian embryos. Dev Biol 252:151–169
Miya T, Nishida H (2003) An Ets transcription factor, HrEts, is target of FGF signaling and involved in induction of notochord, mesenchyme, and brain in ascidian embryos. Dev Biol 261:25–38
Nakatani Y, Nishida H (1994) Induction of notochord during ascidian embryogenesis. Dev Biol 166:289–299
Nakatani Y, Yasuo H, Satoh N, Nishida H (1996) Basic fibroblast growth factor induces notochord formation and the expression of As-T, a brachyury homolog, during ascidian embryogenesis. Development 122:2023–2031
Nishida H (1987) Cell lineage analysis in ascidian embryos by intracellular injection of a tracer enzyme. III. Up to the tissue-restricted stage. Dev Biol 121:526–541
Nishida H (2005) Specification of embryonic axis and mosaic development in ascidians. Dev Dyn 233:1177–1193
Nishikata T, Yamada L, Mochizuki Y, Satou Y, Shin-i T, Kohara Y, Satoh N (2001) Profiles of maternally expressed genes in fertilized eggs of Ciona intestinalis. Dev Biol 238:315–331
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Satoh N (2003) The ascidian tadpole larva: comparative molecular development and genomics. Nat Rev Genet 4:285–295
Satou Y, Satoh N (1999) Developmental gene activities in ascidian embryos. Curr Opin Genet Dev 9:542–547
Satou Y, Kusakabe T, Araki I, Satoh N (1995) Timing of initiation of muscle-specific gene expression in the ascidian embryo precedes that of developmental fate restriction in lineage cells. Dev Growth Differ 37:319–327
Satou Y, Takatori N, Fujiwara S, Nishikata T, Saiga H, Kusakabe T, Shin-i T, KoharaY, Satoh N (2002) Ciona intestinalis cDNA projects: expressed sequence tag analyses and gene expression profiles during embryogenesis. Gene 287:83–96
Silverman ES, Baron RM, Palmer LJ, Le L, Hallock A, Subramaniam V, Riese RJ, McKenna MD, Gu X, Libermann TA, Tugores A, Haley KJ, Shore S, Drazen JM, Weiss ST (2002) Constitutive and cytokine-induced expression of the ETS transcription factor ESE-3 in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27:697–704
Takahashi H, Hotta K, Erives A, Di Gregorio A, Zeller RW, Levine M, Satoh N (1999) Brachyury downstream notochord differentiation in the ascidian embryo. Genes Dev 13:1519–1523
Tugores A, Le J, Sorokina I, Snijders AJ, Duyao M, Reddy PS, Carlée L, Ronshaugen M, Mushegian A, Watanaskul T, Chu S, Buckler A, Emtage S, McCormick MK (2001) The epithelium-specific ETS protein EHF/ESE-3 is a context-dependent transcriptional repressor downstream of MAPK signaling cascades. J Biol Chem 276:20397–20406
Wada S, Saiga H (2002) HrzicN, a new Zic family gene of ascidians, plays essential roles in the neural tube and notochord development. Development 129:5597–5608
Yagi K, Satou Y, Mazet F, Shimeld SM, Degnan B, Rokhsar D, Levine M, Kohara Y, Satoh N (2003) A genomewide survey of developmentally relevant genes in Ciona intestinalis. III. Genes for Fox, ETS, nuclear receptors and NFκB. Dev Genes Evol 213:235–244
Yagi K, Satou Y, Satoh N (2004) A zinc finger transcription factor, ZicL, is a direct activator of Brachyury in the notochord specification of Ciona intestinalis. Development 131:1279–1288
Yagi K, Takatori N, Satou Y, Satoh N (2005) Ci-Tbx6b and Ci-Tbx6c are key mediators of the maternal effect gene Ci-macho1 in muscle cell differentiation in Ciona intestinalis embryos. Dev Biol 282:535–549
Yamada L, Kobayashi K, Degnan B, Satoh N, Satou Y (2003) A genomewide survey of developmentally relevant genes in Ciona intestinalis. IV. Genes for HMG transcriptional regulators, bZip and GATA/Gli/Zic/Snail. Dev Genes Evol 213:245–253
Yang S-H, Bumpass DC, Perkins ND, Sharrocks AD (2002) The ETS domain transcription factor Elk-1 contains a novel class of repression domain. Mol Cell Biol 22:5036–5046
Yasuo H, Satoh N (1993) Function of vertebrate T gene. Nature 364:582–583
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Z. Imoto at Usa Marine Biological Institute of Kochi University for collecting animals, and the staff of Usa Marine Biological Institute for their hospitality. We are grateful to T. Nishikata at Konan University, N. Satoh and Y. Satou at Kyoto University, and H. Takahashi at the National Institute for Basic Biology for providing the animals. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas ‘Genome Science’ from MEXT Japan and Asahi Glass Foundation to S.F.A.S. was supported by the Japan Science Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by N. Satoh
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anno, C., Satou, A. & Fujiwara, S. Transcriptional regulation of ZicL in the Ciona intestinalis embryo. Dev Genes Evol 216, 597–605 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-006-0080-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-006-0080-9