Abstract
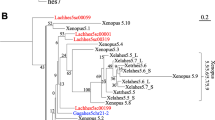
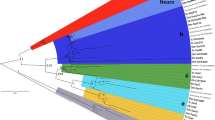
The T-box (Tbx) genes encode a family of transcription factors required for development of vertebrate embryos. In an attempt to discover human orthologues of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) tbx6 and tbx16/spadetail genes, we found that the most similar human (Homo sapiens) gene is the orthologue of mouse (Mus musculus) Mga (MAX gene associated). We have identified the zebrafish orthologue of Mga using analyses of sequence similarity and the orthologies of syntenic genes. Zebrafish mga maps close to dtk (developmental receptor tyrosine kinase), the orthologue of human TYRO3 (TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase). Like its human and mouse orthologues, zebrafish mga lacks the three conserved introns within the T-box coding sequences that are characteristic of the vertebrate T-box gene family. This suggests that these genes are derived from an ancient reverse transcription event. The human genome does not appear to possess orthologues of zebrafish tbx6 or tbx16/spadetail.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Harrison PM, Gerstein M (2002) Studying genomes through the aeons: protein families, pseudogenes and proteome evolution. J Mol Biol 318:1155–1174
Hurlin PJ, Steingrimsson E, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Eisenman RN (1999) Mga, a dual-specificity transcription factor that interacts with Max and contains a T-domain DNA-binding motif. EMBO J 18:7019–7028
Ruvinsky I, Silver LM, Gibson-Brown JJ (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of T-Box genes demonstrates the importance of amphioxus for understanding evolution of the vertebrate genome. Genetics 156:1249–1257
Ruvinsky I, Silver LM, Ho RK (1998) Characterization of the zebrafish tbx16 gene and evolution of the vertebrate T-box family. Dev Genes Evol 208:94–99
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thornton JW, DeSalle R (2000) Gene family evolution and homology: genomics meets phylogenetics. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 1:41–73
Wattler S, Russ A, Evans M, Nehls M (1998) A combined analysis of genomic and primary protein structure defines the phylogenetic relationship of new members of the T-box family. Genomics 48:24–33
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Rory Hope and Steve Donnellan for critical comments on the manuscript. M.L. is supported by funding from the Australian Research Council through the Centre for the Molecular Genetics of Development and by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by J. Campos-Ortego
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lardelli, M. The evolutionary relationships of zebrafish genes tbx6, tbx16/spadetail and mga . Dev Genes Evol 213, 519–522 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-003-0348-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-003-0348-2