Abstract.
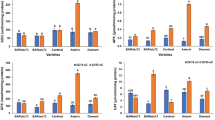
Changes in the steady-state mRNA levels of the gene encoding cytochrome c were analyzed after feeding carbohydrates to detached leaves of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Glucose, fructose and sucrose promoted an increase in mRNA levels, which was not observed with mannitol and other metabolites such as glycerol or acetate. The increase in mRNA levels was proportionally higher in dark-treated leaves. The effect of sugars could be mimicked by compounds that are phosphorylated by hexokinase but not further metabolized, such as mannose or 2-deoxyglucose. This may indicate that hexokinase is involved in the induction of the cytochrome c gene by carbohydrates. The presence of potassium phosphate had no significant effect on the induction by sugars. Our results indicate that the modulation of the expression of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial components should be added to the list of known effects of carbohydrates on respiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 February 1998 / Accepted: 22 April 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felitti, S., Gonzalez, D. Carbohydrates modulate the expression of the sunflower cytochrome c gene at the mRNA level. Planta 206, 410–415 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050416
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050416