Abstract.
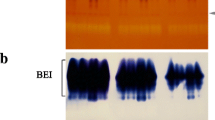
Isoforms of starch synthase (EC 2.4.1.21) in pea (Pisum sativum L.) leaves have been identified and compared with those in developing pea embryos. Purification and immunoprecipitation experiments show that most of the soluble starch synthase activity of the leaf is contributed by a novel isoform (SSIII) that is antigenically related to the major soluble isoform of the potato tuber. The major soluble isoform of the embryo (SSII) is also present in the leaf, but contributes only 15% of the soluble activity. Study of the leaf starch of lam mutant peas, which lack the abundant granule-bound isoform responsible for amylose synthesis in the embryo (GBSSI), indicates that GBSSI is not responsible for the synthesis of amylose-like material in the leaf. Leaves appear to contain a novel granule-bound isoform, antigenically related to GBSSI. The implications of the results for understanding of the role of isoforms of starch synthase are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 March 1997 / Accepted: 13 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomlinson, K., Craig, J. & Smith, A. Major differences in isoform composition of starch synthase between leaves and embryos of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Planta 204, 86–92 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050233
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050233