Abstract
Main conclusion
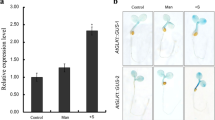
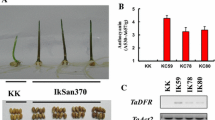
Overexpression of BnaC02.TPS8 increased low N and high sucrose-induced anthocyanin accumulation.
Abstract
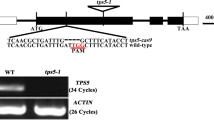
Anthocyanin plays a crucial role in safeguarding photosynthetic tissues against high light, UV radiation, and oxidative stress. Their accumulation is triggered by low nitrogen (N) stress and elevated sucrose levels in Arabidopsis. Trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) serves as a pivotal signaling molecule, sensing sucrose availability, and carbon (C) metabolism. However, the mechanisms governing the regulation of T6P synthase (TPS) genes responsible for anthocyanin accumulation under conditions of low N and high sucrose remain elusive. In a previous study, we demonstrated the positive impact of a cytoplasm-localized class II TPS protein ‘BnaC02.TPS8’ on photosynthesis and seed yield improvement in Brassica napus. The present research delves into the biological role of BnaC02.TPS8 in response to low N and high sucrose. Ectopic overexpression of BnaC02.TPS8 in Arabidopsis seedlings resulted in elevated shoot T6P levels under N-sufficient conditions, as well as an increased carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio, sucrose accumulation, and starch storage under low N conditions. Overexpression of BnaC02.TPS8 in Arabidopsis heightened sensitivity to low N stress and high sucrose levels, accompanied by increased anthocyanin accumulation and upregulation of genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis and regulation. Metabolic profiling revealed increased levels of intermediate products of carbon metabolism, as well as anthocyanin and flavonoid derivatives in BnaC02.TPS8-overexpressing Arabidopsis plants under low N conditions. Furthermore, yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analyses demonstrated that BnaC02.TPS8 interacts with both BnaC08.TPS9 and BnaA01.TPS10. These findings contribute to our understanding of how TPS8-mediated anthocyanin accumulation is modulated under low N and high sucrose conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw RNA-seq data are deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under accession number GSE77396 at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). All other data generated in this study are included in this manuscript and its supplementary information.
Abbreviations
- BiFC:
-
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation
- C:
-
Carbon
- C/N:
-
Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio
- DFR:
-
Dihydroflavonol reductase
- F3'H:
-
Flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- T6P:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate
- TPS8:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase8
- Y2H:
-
Yeast two-hybrid
References
Agati G, Tattini M (2010) Multiple functional roles of flavonoids in photoprotection. New Phytol 186(4):786–793. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03269.x
Albert NW, Davies KM, Lewis DH et al (2014) A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. Plant Cell 26(3):962–980. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.122069
Aoyama S, Lu Y, Yamaguchi J, Sato T (2014) Regulation of senescence under elevated atmospheric CO2 via ubiquitin modification. Plant Signal Behav 9(5):e28839. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.28839
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P, Pachter L (2016) Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat Biotechnol 34(5):525–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3519
Broun P (2005) Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis: a complex network of conserved regulators involved in multiple aspects of differentiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8(3):272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2005.03.006
Cabib E, Leloir LF (1958) The biosynthesis of trehalose phosphate. J Bio Chem 231:259–275
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Coruzzi GM, Zhou L (2001) Carbon and nitrogen sensing and signaling in plants: emerging ‘matrix effects.’ Curr Opin Plant Biol 4(3):247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00168-0
Delatte TL, Selman MH, Schluepmann H, Somsen GW, Smeekens SC, de Jong GJ (2009) Determination of trehalose-6-phosphate in Arabidopsis seedlings by successive extractions followed by anion exchange chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 389(1):12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2009.03.003
Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Feil R, Lunn JE, Van Dijck P (2015) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is not the only active TPS in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 466(2):283–290. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20141322
Dixon RA, Liu C, Jun JH (2013) Metabolic engineering of anthocyanins and condensed tannins in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(2):329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2012.07.004
Falcone Ferreyra ML, Rius SP, Casati P (2012) Flavonoids: biosynthesis, biological functions, and biotechnological applications. Front Plant Sci 3:222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00222
Fichtner F, Olas JJ, Feil R et al (2020) Functional features of TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE SYNTHASE1, an essential enzyme in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32(6):1949–1972. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00837
Figueroa CM, Lunn JE (2016) A tale of two sugars: trehalose 6-phosphate and sucrose. Plant Physiol 172(1):7–27. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00417
Figueroa CM, Feil R, Ishihara H et al (2016) Trehalose 6-phosphate coordinates organic and amino acid metabolism with carbon availability. Plant J 85(3):410–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13114
Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM (2008) Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 53(5):814–827. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03373.x
Gould KS, McKelvie J, Markham R (2002) Do anthocyanins function as antioxidants in leaves? Imaging of H2O2 in red and green leaves after mechanical injury. Plant Cell Environ 25:1261–1269. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2002.00905.x
Hsieh MH, Lam HM, van de Loo FJ, Coruzzi G (1998) A PII-like protein in Arabidopsis: putative role in nitrogen sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(23):13965–13970. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.23.13965
Ilhan S, Ozdemir F, Bor M (2015) Contribution of trehalose biosynthetic pathway to drought stress tolerance of Capparis ovata Desf. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 17(2):402–407. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12227
Lea US, Slimestad R, Smedvig P, Lillo C (2007) Nitrogen deficiency enhances expression of specific MYB and bHLH transcription factors and accumulation of end products in the flavonoid pathway. Planta 225(5):1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0414-x
Leyman B, Van Dijck P, Thevelein JM (2001) An unexpected plethora of trehalose biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Trends Plant Sci 6(11):510–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(01)02125-2
Li Y, Van den Ende W, Rolland F (2014) Sucrose induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis is mediated by DELLA. Mol Plant 7(3):570–572. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst161
Li Q, Yin M, Li Y et al (2015) Expression of Brassica napus TTG2, a regulator of trichome development, increases plant sensitivity to salt stress by suppressing the expression of auxin biosynthesis genes. J Exp Bot 66(19):5821–5836. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv287
Li Z, Wei X, Tong X et al (2022) The OsNAC23-Tre6P-SnRK1a feed-forward loop regulates sugar homeostasis and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 15(4):706–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2022.01.016
Lichtenthaler K, Lang M, Sowinska M, Heisel F, Miehe JA (1996) Detection of vegetation stress via a new high-resolution fluorescence imaging system. J Plant Physiol 148:599–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(96)80081-2
Lillo C, Lea US, Ruoff P (2008) Nutrient depletion as a key factor for manipulating gene expression and product formation in different branches of the flavonoid pathway. Plant Cell Environ 31(5):587–601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01748.x
Lin Y, Zhang J, Gao W et al (2017) Exogenous trehalose improves growth under limiting nitrogen through upregulation of nitrogen metabolism. BMC Plant Biol 17(1):247. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1207-z
Lotkowska ME, Tohge T, Fernie AR, Xue GP, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B (2015) The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB112 promotes anthocyanin formation during salinity and under high light stress. Plant Physiol 169(3):1862–1880. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00605
Lunn JE, Feil R, Hendriks JH et al (2006) Sugar-induced increases in trehalose 6-phosphate are correlated with redox activation of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase and higher rates of starch synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 397(1):139–148. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20060083
Martin T, Oswald O, Graham IA (2002) Arabidopsis seedling growth, storage lipid mobilization, and photosynthetic gene expression are regulated by carbon:nitrogen availability. Plant Physiol 128(2):472–481. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010475
Naing AH, Kim CK (2021) Abiotic stress-induced anthocyanins in plants: their role in tolerance to abiotic stresses. Physiol Plant 172(3):1711–1723. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13373
Nakabayashi R, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Urano K et al (2014) Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J 77(3):367–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12388
Nunes C, O’Hara LE, Primavesi LF et al (2013) The trehalose 6-phosphate/SnRK1 signaling pathway primes growth recovery following relief of sink limitation. Plant Physiol 162(3):1720–1732. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.220657
Panek AC, de Araujo PS, Moura Neto V, Panek AD (1987) Regulation of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase complex in Saccharomyces. I. Interconversion of forms by phosphorylation. Curr Genet 11(6–7):459–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384607
Paul MJ, Primavesi LF, Jhurreea D, Zhang Y (2008) Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:417–441. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092945
Peng M, Hudson D, Schofield A, et al (2008) Adaptation of Arabidopsis to nitrogen limitation involves induction of anthocyanin synthesis which is controlled by the NLA gene. J Exp Bot 59(11):2933–2944. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern148
Ramon M, De Smet I, Vandesteene L et al (2009) Extensive expression regulation and lack of heterologous enzymatic activity of the Class II trehalose metabolism proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 32(8):1015–1032. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01985.x
Ramsay NA, Glover BJ (2005) MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity. Trends Plant Sci 10(2):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.011
Rathke GW, Christen O, Diepenbrock W (2005) Effects of nitrogen source and rate on productivity and quality of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) grown in different crop rotations. Field Crop Res 94:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2004.11.010
Rubin G, Tohge T, Matsuda F, Saito K, Scheible WR (2009) Members of the LBD family of transcription factors repress anthocyanin synthesis and affect additional nitrogen responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21(11):3567–3584. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.067041
Saigo T, Wang T, Watanabe M, Tohge T (2020) Diversity of anthocyanin and proanthocyanin biosynthesis in land plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 55:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2020.04.001
Scheible WR, Morcuende R, Czechowski T et al (2004) Genome-wide reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism, protein synthesis, cellular growth processes, and the regulatory infrastructure of Arabidopsis in response to nitrogen. Plant Physiol 136(1):2483–2499. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.047019
Schluepmann H, van Dijken A, Aghdasi M, Wobbes B, Paul M, Smeekens S (2004) Trehalose mediated growth inhibition of Arabidopsis seedlings is due to trehalose-6-phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiol 135(2):879–890. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.039503
Shirley BW, Kubasek WL, Storz G et al (1995) Analysis of Arabidopsis mutants deficient in flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J 8(5):659–671. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.08050659.x
Soubeyrand E, Colombié S, Beauvoit B et al (2018) Constraint-based modeling highlights cell energy, redox status and α-ketoglutarate availability as metabolic drivers for anthocyanin accumulation in grape cells under nitrogen limitation. Front Plant Sci 9:421. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00421
Trevisol ET, Panek AD, De Mesquita JF (1840) Eleutherio EC (2014) Regulation of the yeast trehalose-synthase complex by cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 6:1646–1650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.12.010
Vandercammen A, François J, Hers HG (1989) Characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 182(3):613–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14870.x
Vidal EA, Moyano TC, Riveras E, Contreras-López O, Gutiérrez RA (2013) Systems approaches map regulatory networks downstream of the auxin receptor AFB3 in the nitrate response of Arabidopsis thaliana roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(31):12840–12845. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1310937110
Vinnichek L, Pogorelova E, Dergunov A (2019) Oilseed market: global trends. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 274:012030. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/274/1/012030
Vishal B, Krishnamurthy P, Ramamoorthy R, Kumar PP (2019) OsTPS8 controls yield-related traits and confers salt stress tolerance in rice by enhancing suberin deposition. New Phytol 221(3):1369–1386. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15464
Wingler A, Delatte TL, O’Hara LE et al (2012) Trehalose 6-phosphate is required for the onset of leaf senescence associated with high carbon availability. Plant Physiol 158(3):1241–1251. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.191908
Winkel-Shirley B (2001) Flavonoid biosynthesis: a colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol 126(2):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.126.2.485
Xu W, Dubos C, Lepiniec L (2015) Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci 20(3):176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.12.001
Yadav UP, Ivakov A, Feil R et al (2014) The sucrose-trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) nexus: specificity and mechanisms of sucrose signalling by Tre6P. J Exp Bot 65(4):1051–1068. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert457
Yuan P, Zhou GL, Yu MZ et al (2024) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 8 increases photosynthesis and seed yield in Brassica napus. Plant J. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.16617
Zang B, Li H, Li W, Deng XW, Wang X (2011) Analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family suggests the formation of TPS complexes in rice. Plant Mol Biol 76(6):507–522
Zhang Y, Primavesi LF, Jhurreea D et al (2009) Inhibition of SNF1-related protein kinase1 activity and regulation of metabolic pathways by trehalose-6-phosphate. Plant Physiol 149:1860–1871. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.133934
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Liu J et al (2017) GA-DELLA pathway is involved in regulation of nitrogen deficiency-induced anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Cell Rep 36(4):557–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2102-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32301885 and 32172662). Pan Yuan gratefully acknowledges financial support from the China Scholarship Council to Reading University for joint doctoral student education. The authors thank Prof. Junpei Takano (Osaka Metropolitan University) for providing us the vectors for the BiFC system. The authors owe thank Qi Li, Limei Zhang, Shu Zhu, Huan He at the public laboratory platform of the College of Resources and Environment, Huazhong Agricultural University, for their help with experimental test. The authors thank Wuhan Greensword Creation Technology Co. Ltd. for their technical support for T6P concentration analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PY and LS conceived and designed the study. PY, MZY, and HJL performed experiments and analyzed the data. PY, JPH, HC, GDD, SLW, FSX, CW, DFH, and LS wrote the manuscript. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, P., Yu, M., Liu, H. et al. Overexpression of oilseed rape trehalose-6-phosphate synthesis gene BnaC02.TPS8 confers sensitivity to low nitrogen and high sucrose-induced anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Planta 259, 122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04404-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04404-3