Abstract
Main conclusion
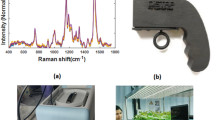
Hand-held Raman spectroscopy can be used for highly accurate differentiation between drought, heat and light-triggered stresses in hemp. The differentiation is based on the changes in the biochemistry of plants caused by such stresses.
Abstract
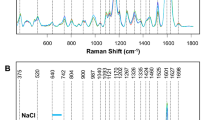
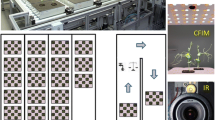
Hemp farming is a rapidly growing industry. This dioecious plant is primarily cultivated for its fibers, seeds, and cannabinoid-rich oils. The yield of these materials can be drastically lowered by many abiotic stresses, such as drought, heat and light. It becomes critically important to develop robust and reliable approaches that can be used to diagnose such abiotic stresses in hemp. In this study, we investigate the accuracy of Raman spectroscopy, an emerging tool within crop monitoring, in the confirmatory identification of drought, heat, and light-induced stresses in three varieties of hemp. Our results showed that mono, double and triple stresses uniquely alter plant biochemistry that results in small spectroscopic changes detected in the Raman spectra acquired from the hemp leaves. These changes could be used for the 80–100% accurate identification of individual abiotic stresses and their combinations in plants. These results demonstrate that a hand-held Raman spectrometer can be used for highly accurate, non-invasive, non-destructive, and label-free diagnostics of hemp stresses directly in the greenhouse or in the field.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- THC:
-
Tetrahydrocannabinol
- CBD:
-
Cannabidiol
- RS:
-
Raman spectroscopy
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial least squares discriminant analysis
- LV:
-
Latent variable
- CW:
-
Cherry Wine
- JM:
-
Jin Ma
- OB:
-
Otto/Boux
References
Adar F (2017) Carotenoids—Their resonance raman spectra and how they can be helpful in characterizing a number of biological systems. Spectroscopy 32(6):12–20
Adesina I, Bhowmik A, Sharma H, Shahbazi A (2020) A review on the current state of knowledge of growing conditions, agronomic soil health practices and utilities of hemp in the United States. Agriculture 10(4):129
Altangerel N, Huang P-C, Kolomiets MV, Scully MO, Hemmer PR (2021) Raman spectroscopy as a robust new tool for rapid and accurate evaluation of drought tolerance levels in both genetically diverse and near-isogenic maize lines. Front Plant Sci 12:621711
Climate and Average Weather Year Round in Winters Texas, United States (2023) Available: https://weatherspark.com/y/6225/Average-Weather-in-Winters-Texas-United-States-Year-Round#:~:text=In%20Winters%2C%20the%20summers%20are,or%20above%20102%C2%B0F
Devitt G, Howard K, Mudher A, Mahajan S (2018) Raman spectroscopy: an emerging tool in neurodegenerative disease research and diagnosis. ACS Chem Neurosci 9(3):404–420. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00413
Dey S (2022) Hemp was supposed to save Texas farmers during a drought. It hasn’t yet. Available: https://www.texastribune.org/2022/09/07/texas-hemp-drought-agriculture/
Dou T, Sanchez L, Irigoyen S, Goff N, Niraula P, Mandadi K, Kurouski D (2021) Biochemical origin of raman-based diagnostics of huanglongbing in grapefruit trees. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.680991
Edwards HGM, Farwell DW, Webster D (1997) FT Raman microscopy of untreated natural plant fibres. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 53(13):2383–2392. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-1425(97)00178-9
Goble P (2023) Colorado climate. Available: https://coloradoencyclopedia.org/article/colorado-climate. Accessed 23 Feb 2023
Heider CG, Itenberg SA, Rao J, Ma H, Wu X (2022) Mechanisms of cannabidiol (CBD) in cancer treatment: a review. Biology 11(6):817
Higgins S, Serada V, Herron B, Gadhave KR, Kurouski D (2022) Confirmatory detection and identification of biotic and abiotic stresses in wheat using Raman spectroscopy. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1035522
Industrial hemp faces challenges in Texas (2021) Available: https://agrilifetoday.tamu.edu/2021/07/07/industrial-hemp-faces-challenges-in-texas/. Accessed 7 July 2021
Miller S (2020) The Texas department of agriculture proposed hemp plan for Texas. Available: https://www.texasagriculture.gov/Regulatory-Programs/Hemp-Background
O’Brien K (2022) Cannabidiol (CBD) in cancer management. Cancers 14(4):885
Park S-H, Pauli CS, Gostin EL, Staples SK, Seifried D, Kinney C, Heuvel BDV (2022) Effects of short-term environmental stresses on the onset of cannabinoid production in young immature flowers of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). J Cannabis Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00111-y
Rehman M, Fahad S, Du G, Cheng X, Yang Y, Tang K, Liu L, Liu F-H, Deng G (2021) Evaluation of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as an industrial crop: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(38):52832–52843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16264-5
Sanchez L, Ermolenkov A, Biswas S, Septiningsih EM, Kurouski D (2020) Raman spectroscopy enables non-invasive and confirmatory diagnostics of salinity stresses, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium deficiencies in rice. Front Plant Sci 11:573321
Schulz H, Baranska M, Baranski R (2005) Potential of NIR-FT-Raman spectroscopy in natural carotenoid analysis. Biopolymers 77(4):212–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.20215
Small E (2015) Evolution and classification of Cannabis sativa (Marijuana, hemp) in relation to human utilization. Bot Rev 81(3):189–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-015-9157-3
Small E, Marcus D (2002) Hemp: a new crop with new uses for North America. Trends New Crops New Uses 24(5):284–326
Synytsya A, Čopı́ková J, Matějka P, Machovič V (2003) Fourier transform Raman and infrared spectroscopy of pectins. Carbohyd Polym 54:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00158-9
Yu MML, Schulze HG, Jetter R, Blades MW, Turner RFB (2007) Raman microspectroscopic analysis of triterpenoids found in plant cuticles. Appl Spectrosc 61(1):32–37. https://doi.org/10.1366/000370207779701352
Zhelyazkova M, Kirilov B, Momekov G (2020) The pharmacological basis for application of cannabidiol in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacia 67(4):239–252
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mariposa for provided financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and KM performed the experiment, collected and analyzed spectra. MS performed PLS-DA; RJ and DK conceptualized the idea, supervised the project, wrote the manuscript and administrated the work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Steczkowski, M., McClellan, K., Jessup, R. et al. Raman-based diagnostics of drought, heat and light-induced stresses in three different varieties of hemp. Planta 259, 21 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04299-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04299-6